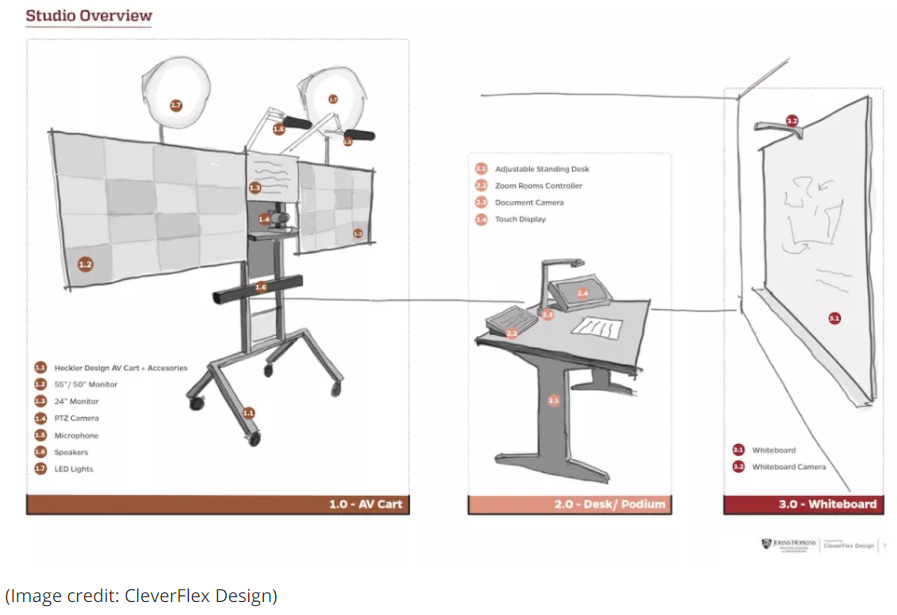
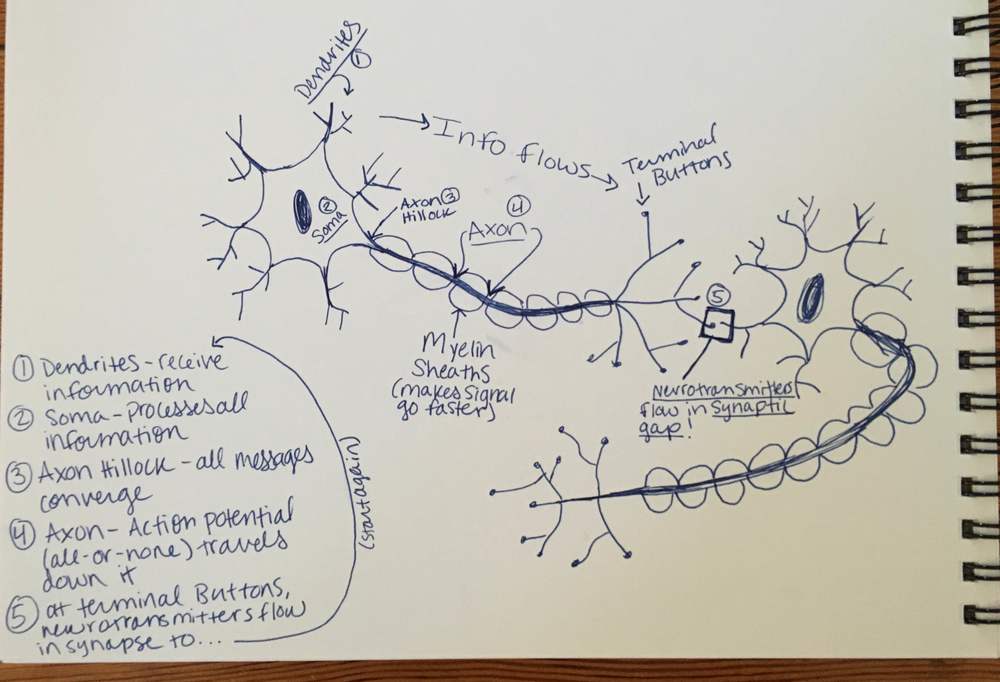
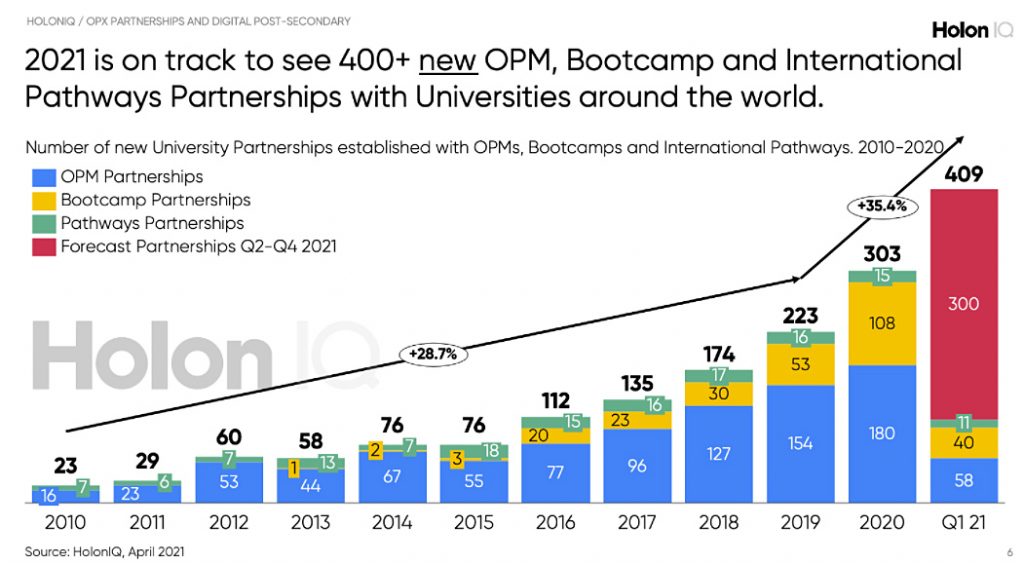
Counting U.S. Postsecondary and Secondary Credentials — from Credential Engine; with thanks to Will Richardson for this resource
February 2021
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
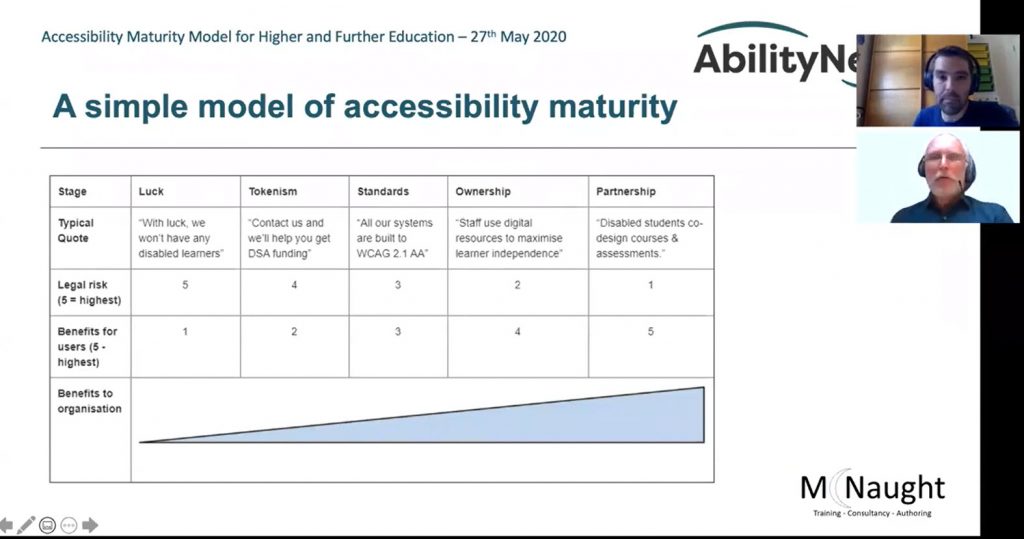
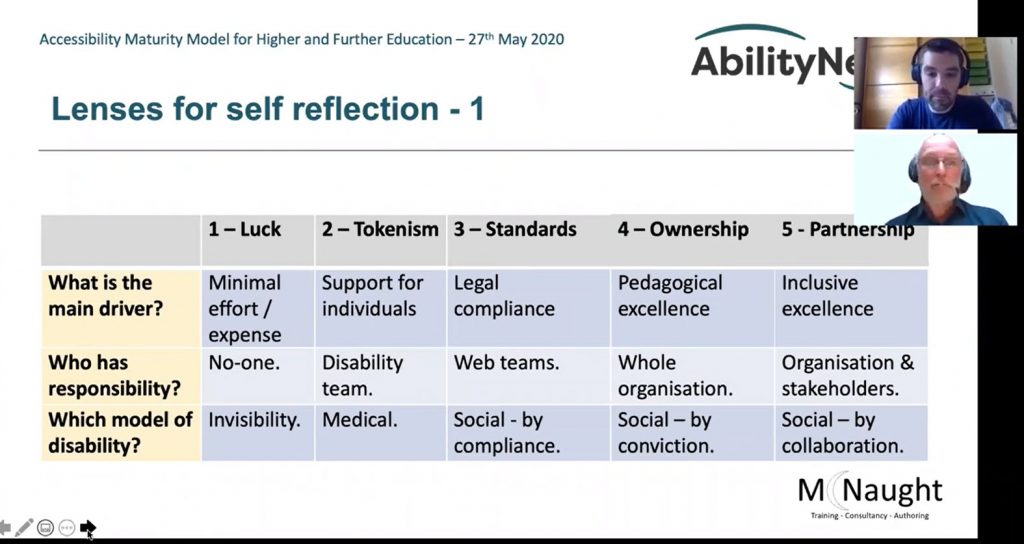
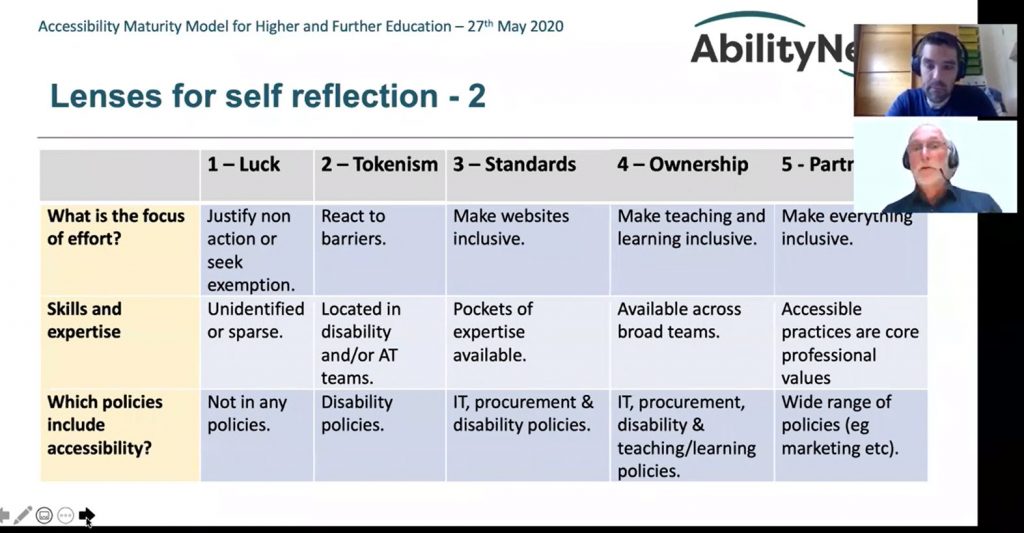
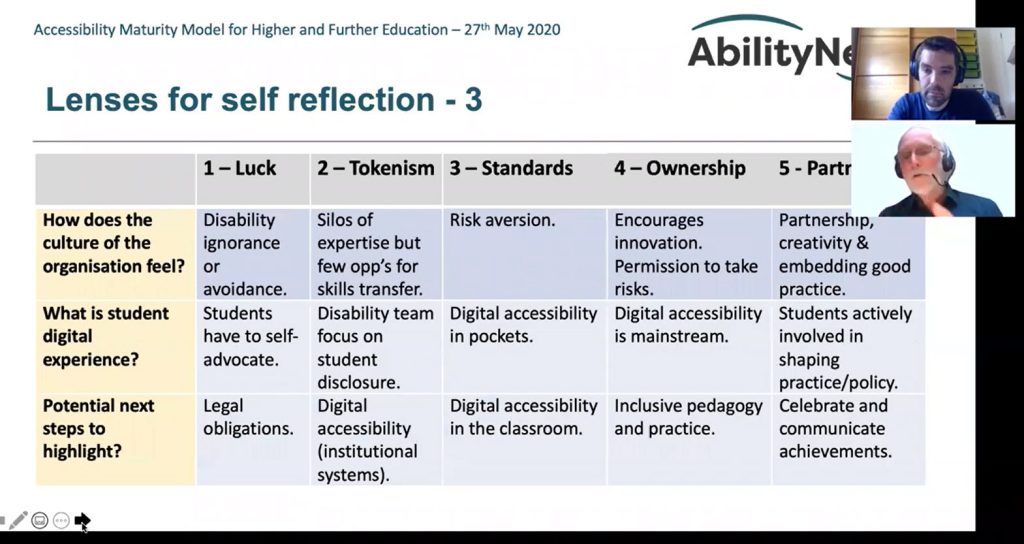
Learners, educators and policymakers understand that high school completion and education beyond high school are critical to thrive in the workforce. However, until recently an inventory of the number or type of secondary and postsecondary credential opportunities in the United States did not exist. This is the third annual report from Credential Engine that attempts to count all these credentials. The report identifies 967,734 unique credentials in the U.S. in 16 detailed credential categories across four types
of credential providers:
- Postsecondary educational institutions—359,713 degrees and certificates
- Massive open online course (MOOC) providers—9,390 course completion certificates, micro-credentials, and online degrees from foreign universities
- Non-academic providers—549,712 badges, course completion certificates, licenses, certifications, and apprenticeships
- Secondary schools—48,919 diplomas from public and private secondary schools
Also see:
NLET Releases “Newest Economy” Paper
In The Newest Economy: Welcome to the Credential Currency Revolution, Gordon Freedman, NLET’s president, examines the discontinuity between high schools, community colleges, career and technical education, and workforce development programs and their alignment and linkages to high demand jobs and careers. The paper suggests moving beyond the current array of offerings and labor market tools to a marketplace solution using modern technology and data analytics to link credentials (badges, certifications, degrees) to hiring outcomes.
The paper is a collaboration among NLET, Credential Engine, Southern Regional Economic Board (SREB) and GoEducate, Inc. who together are building a Credential Alliance to further the work described in the report.