







Why everybody’s hiring but nobody’s getting hired — from vox.com by Rani Molla and Emily Stewart; with thanks to Ryan Craig for this resource
America’s broken hiring system, explained.
Tim Brackney, president and COO of management consulting firm RGP, refers to the current situation as the “great mismatch.” That mismatch refers to a number of things, including desires, experience, and skills. And part of the reason is that the skills necessary for a given job are changing faster than ever, as companies more frequently adopt new software.
“Twenty years ago, if I had 10 years experience as a warehouse manager, the likelihood that my skills would be pretty relevant and it wouldn’t take me that long to get up to speed was pretty good,” Joseph Fuller, a management professor at Harvard Business School and co-author of a recent paper on the disconnect between employers and employees, said. “The shelf life of people’s skills for a lot of decent-paying jobs has been shortening.”
From DSC:
I also think those hiring don’t think people can reinvent themselves. Folks who hire someone (and/or the applicant tracking systems as play) always seem to look for an exact match. There is little vision and/or belief that someone can grow into a position, or to lead differently, or to go in a different but better direction. They reach for their cookie cutters and shove their imaginations and ability to think bigger aside.
Employers could help people by investing in their employees’ growth and development — even if it means they actively help an employee take a right turn. Such an employee could hopefully find a new fit within that organization — if they do, they would likely turn out to be fiercely loyal.
Even if it means offering an employee 1-2 courses a year that they want to learn about — NO STRINGS ATTACHED — the learning culture would get a huge boost!!! Peoples’ love/enjoyment of learning would grow. Morale would improve. People would feel valued.
Let me offer a personal example:
Legal Tech’s Predictions for Legal Technology Innovation in 2022 — from legalreader.com by Smith Johnes
Excerpts:
From DSC:
What are the ramifications for law schools and legal departments if these legal tech-related predictions come true?
Surviving Among the Giants — from chronicle.com by Scott Carlson
As growth has become higher ed’s mantra, some colleges seek to stay small.
Excerpts:
The pressures on the higher-education business model are changing those attitudes. The Council of Independent Colleges’ fastest-growing initiative is the Online Course Sharing Consortium, which allows small colleges to offer certain courses to students at other institutions. Currently, there are 2,200 enrollments among almost 6,000 courses on the platform.
“The higher-ed business model is broken,” says Jeffrey R. Docking, who has been president of Adrian College for 16 years. “But where it’s most broken — and the first ones that are going to walk the plank — are the small private institutions. The numbers just don’t work.” Combining some backroom functions or arranging consortial purchases is just “dabbling around the edges” — and won’t get close to driving down the cost of tuition by 30 to 40 percent over the next several years, which is what Docking believes is necessary.
From DSC:
Docking’s last (highlighted) sentence above reminds me of what I predicted back in 2008 when I was working for Calvin College. The vision I relayed in 2008 continues to come to fruition — albeit I’ve since changed the name of the vision.

From DSC (cont’d):
I was trying to bring down the cost of higher education — which we did with Calvin Online for 4-5 years…before the administration, faculty members, and even the leadership within our IT and HR Departments let Calvin Online die on the vine. This was a costly mistake for Calvin, as they later became a university — thus requiring that they get into more online-based learning in order to address the adult learner. Had they supported getting the online-based learning plane off the runway, they could have dovetailed nicely into becoming a university. But instead, they dissed the biggest thing to happen within education in the last 500 years (since the invention of the printing press).
Which brings me to one last excerpted quote here:
“For so many years,” Docking says, “all of these really smart people in Silicon Valley, at the University of Phoenix, at for-profits were saying, We’re going to do it better” — and they came around with their “solutions” in the form of MOOCs, or massive open online courses, and other scaling plans. Small colleges didn’t want to hear it, and, Docking says, maybe it was to their peril.
Twitter rolls out tipping with bitcoin, explores verifying NFT profile pics — from mashable.com by Jack Morse
Bitcoin is coming to Twitter.
Excerpt:
Twitter is leaning into the blockchain.
The social media giant announced Thursday that, starting immediately, users around the globe will be able to post their bitcoin wallet directly into their profile — while a more limited subset will be able to more directly integrate a bitcoin payment app. The addition of cryptocurrency payments to Twitter, via Tips (formerly dubbed Tip Jar), coincides with the larger rollout of Tips to all iOS users globally, with Android access promised in the near future.
How tech will change the way we work by 2030 — from techradar.com by Rob Lamb
Everyday jobs will be augmented by technology
Technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML) and Blockchain will have a significant impact on work in the next decade and beyond. But if you believe the sci-fi hype or get bogged down in the technology, it can be difficult to relate them to today’s workplaces and jobs.
Excerpt:
Here are three everyday examples of their potential, expressed in terms of the business challenge they are addressing or how consumers will experience them. I don’t mean to over simplify – these are powerful tools – but I think their potential shines through best when they’re expressed in their simplest terms.
From DSC:
I have an issue with one of their examples that involves positioning AI as the savior of the hiring process:
The problem with this process isn’t just that it’s hugely time-consuming, it’s that all kinds of unconscious biases can creep in, potentially even into the job advert. These issues can be eradicated with the use of AI, which can vet ads for gendered language, sort through applicants and pick out the most suitable ones in a fraction of the time it would take an HR professional or any other human being.
AI can be biased as well — just like humans. Lamb recognizes this as well when he states that “Provided the algorithms are written correctly, AI will be key to organisations addressing issues around diversity and inclusion in the workplace.” But that’s a big IF in my mind. So far, it appears that the track record isn’t great in this area. Also, as Cathy O’Neil asserts: “Algorithms are opinions embedded in code.”
AI may not be as adept as a skilled HR professional in seeing the possibilities for someone. Can person A’s existing skillsets be leveraged in this new/other position?
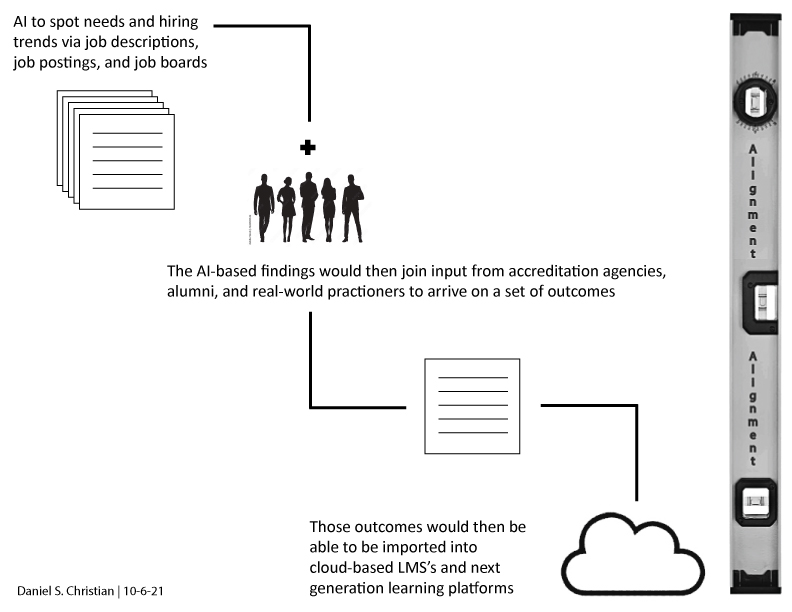
Defining the skills citizens will need in the future world of work — from McKinsey & Company; with thanks to Ryan Craig for this resource
Excerpts:
Our findings help define the particular skills citizens are likely to require in the future world of work and suggest how proficiency in them can influence work-related outcomes, namely employment, income, and job satisfaction. This, in turn, suggests three actions governments may wish to take.
Establish an AI aggregator of training programs to attract adult learners and encourage lifelong learning. AI algorithms could guide users on whether they need to upskill or reskill for a new profession and shortlist relevant training programs.
From DSC:
No one will have all 56 skills that McKinsey recommends here. So (HR) managers, please don’t load up your job postings with every single skill listed here. The search for purple unicorns can get tiring, old, and discouraging for those who are looking for work.
That said, much of what McKinsey’s research/data shows — and what their recommendations are — resonates with me. And that’s why I keep adding to the developments out at:
A powerful, global, next-generation learning platform — meant to help people reinvent themselves quickly, safely, cost-effectively, conveniently, & consistently!!!
What Will Online Learning Look Like in 10 Years? Zoom Has Some Ideas — from edsurge.com by Stephen Noonoo
Excerpt:
This week at Zoom’s annual conference, Zoomtopia, a trio of education-focused Zoom employees (er, Zoomers?) speculated wildly about what hybrid Zoom learning might look like 10 years from now, given the warp speed advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning expected. Below are highlights of their grandiose, if sometimes vague, vision for the future of learning on Zoom.
Zoom very much sees itself as one day innovating on personalized learning in a substantial way, although beyond breakout rooms and instant translation services, they have few concrete ideas in mind. Mostly, the company says it will be working to add more choices to how teachers can present materials and how students can display mastery to teachers in realtime. They’re bullish on Kahoot-like gamification features and new ways of assessing students, too.
Also see:
An Eighth Grader Was Tired of Being Late to Zoom School. So He Made an App for That. — from edsurge.com by Nadia Tamez-Robledo
“I could not find anything else that exists like this to automatically join meetings at the right times,” says Seth, a high school freshman based in Walnut Creek, Calif. “Reminders are just really easy to ignore. I’ll get a notification maybe five minutes before my meeting, and it’ll just sit there and not do anything. [LinkJoin] interrupts whatever you’re doing and says, ‘Join this meeting. In fact it’s already opening, so better get on it.’”
FLEXspace with LSRS v.3 Integration: Your Key to Future Proofing Learning Spaces — from campustechnology.com by Mary Grush
A Q&A roundtable with FLEXspace and LSRS leaders and innovators
Excerpt:
A little more than a year ago, the EDUCAUSE Learning Space Rating System was integrated into FLEXspace. Now, users have a “one-stop shop” to access both the media-rich resources of FLEXspace and the quantitative evaluations of the LSRS.
Here, a round table discussion provides five perspectives on what the integration has meant to users.
In a truly connected campus, time, space and location should be absolutely irrelevant. “We should be able to build a digital twin of space and services and we need to think about things that are physical and digital – ‘phygital’,” he pointed out. https://t.co/cyud0rigZl
— Daniel Christian (he/him/his) (@dchristian5) September 8, 2021
McKinsey for Kids: I, Robot? What technology shifts mean for tomorrow’s jobs — from mckinsey.com
Tomorrow’s jobs will look different from today’s—and not just because you might be working alongside robots. In this edition of McKinsey for Kids, peer into the future of work and what it may hold for you, whether you’re thinking about becoming a doctor, an influencer—or a garbage designer.
DIGITAL SERIES – FUTURE OF WORK: THE NEXT GENERATION
Excerpt:
The working landscape in the United States has rapidly changed in the last 30 years. The one job-for-life model is vanishing and younger workers are trading in stability and security for flexibility and autonomy. GBH and PBS Digital Studios present the Future of Work digital series, a six-part docuseries chronicling six mid-career adults as they navigate the rapidly changing work landscape covering topics such as debt, the gig economy, remote working, career identity, and more.
5 Ways Higher Ed Will Be Upended — from chronicle.com by Arthur Levine and Scott Van Pelt
Colleges will lose power, prices will go down, and credentials will multiply — among other jarring shifts.
Excerpt:
The dominance of degrees and “just in case” education will diminish; nondegree certifications and “just in time” education will increase in status and value.
…
In contrast, “just in time” education teaches students the skills and knowledge they need right now. They may need to learn a foreign language for an coming trip or business deal. They may need to learn an emerging technology. “Just in time” education comes in all shapes and sizes, but diverges from traditional academic time standards, uniform course lengths, and common credit measures. Only a small portion of such programs award degrees; most grant certificates, microcredentials, or badges.
From DSC:
Long-time readers of this blog and my old blog at Calvin (then College) will see no surprises here:

From DSC:
Speaking of learning-related platforms…
#learning #platforms #learningfromthelivingclassroom #onlinelearning #reinvent #education #lifelonglearning #vision #heutagogy #learningexperiencedesign
Art in the Age of the Metaversehttps://t.co/4GZc2rcust#art #creativity #creators #metaverse #future #emergingtechnologies #AI #DigitalArtist
— Daniel Christian (he/him/his) (@dchristian5) August 22, 2021