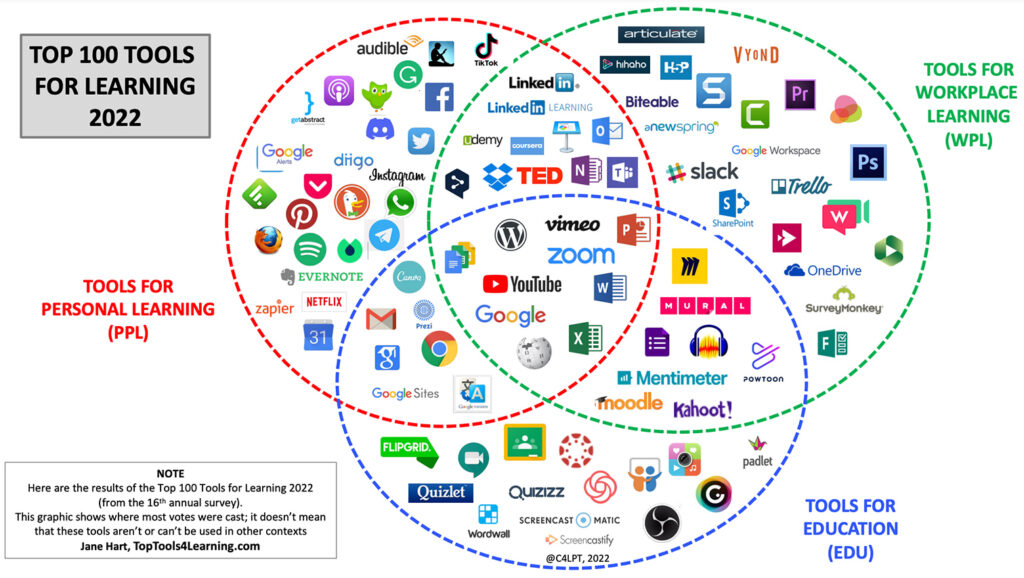
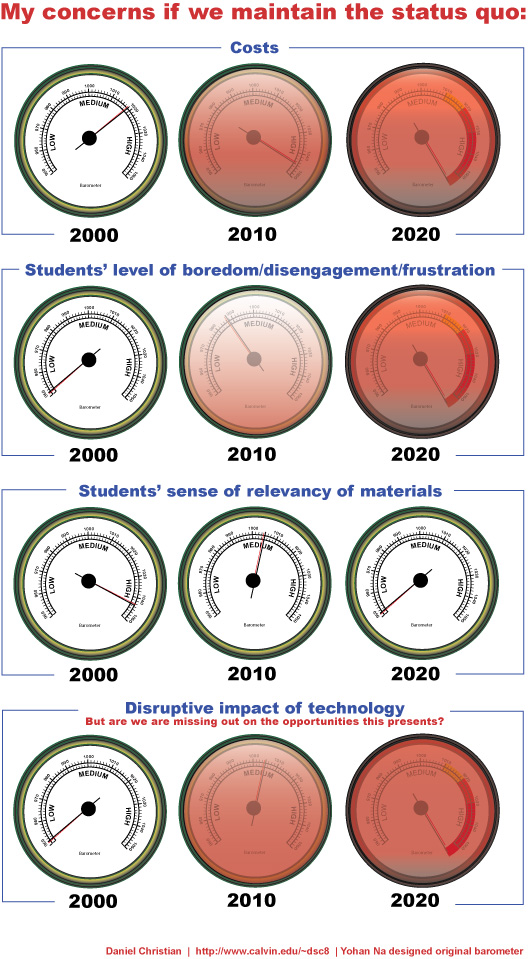
To Improve Outcomes for Students, We Must Improve Support for Faculty — from campustechnology.com by Dr. David Wiley
The doctoral programs that prepare faculty for their positions often fail to train them on effective teaching practices. We owe it to our students to provide faculty with the professional development they need to help learners realize their full potential.
Excerpts:
Why do we allow so much student potential to go unrealized? Why are well-researched, highly effective teaching practices not used more widely?
The doctoral programs that are supposed to prepare them to become faculty in physics, philosophy, and other disciplines don’t require them to take a single course in effective teaching practices.
The entire faculty preparation enterprise seems to be caught in a loop, unintentionally but consistently passing on an unawareness that some teaching practices are significantly more effective than others. How do we break this cycle and help students realize their full potential as learners?
From DSC:
First of all, I greatly appreciate the work of Dr. David Wiley. His career has been dedicated to teaching and learning, open educational resources, and more. I also appreciate and agree with what David is saying here — i.e., that professors need to be taught how to teach as well as what we know about how people learn at this point in time.
For years now, I’ve been (unpleasantly) amazed that we hire and pay our professors primarily for their research capabilities — vs. their teaching competence. At the same time, we continually increase the cost of tuition, books, and other fees. Students have the right to let their feet do the walking. As the alternatives to traditional institutions of higher education increase, I’m quite sure that we’ll see that happen more and more.
While I think that training faculty members about effective teaching practices is highly beneficial, I also think that TEAM-BASED content creation and delivery will deliver the best learning experiences that we can provide. I say this because multiple disciplines and specialists are involved, such as:
- Subject Matter Experts (i.e., faculty members)
- Instructional Designers
- Graphic Designers
- Web Designers
- Learning Scientists; Cognitive Learning Researchers
- Audio/Video Specialists and Learning Space Designers/Architects
- CMS/LMS Administrators
- Programmers
- Multimedia Artists who are skilled in working with digital audio and digital video
- Accessibility Specialists
- Librarians
- Illustrators and Animators
- and more
The point here is that one person can’t do it all — especially now that the expectation is that courses should be offered in a hybrid format or in an online-based format. For a solid example of the power of team-based content creation/delivery, see this posting.
One last thought/question here though. Once a professor is teaching, are they open to working with and learning from the Instructional Designers, Learning Scientists, and/or others from the Teaching & Learning Centers that do exist on their campus? Or do they, like many faculty members, think that such people are irrelevant because they aren’t faculty members themselves? Oftentimes, faculty members look to each other and don’t really care what support is offered (unless they need help with some of the technology.)
Also relevant/see:
- The unasked question about the student loan bailout: What’s colleges’ responsibility? — from hechingerreport.org by Jon Marcus
Schools that benefit from all that debt share almost no accountability for poor returns