From DSC:
Perhaps folks might want to experiment with the teaching strategy as mentioned below from Dr. Barbi Honeycutt’s Lecture Breakers Weekly e-newsletter.
From The Scholarly Teacher blog — who just added a new section on the blog which includes teaching tip infographics.
This week, they shared variations of Think, Pair, Share. In this teaching strategy, you give the students a problem or question. Then, you ask them to think about the question, pair up with a partner to discuss it, and then share it with the rest of the class (hence the name “think, pair, share”).
In this adaption, you do the same process, but instead of asking them to share with the class, you ask them to post a tweet using a class hashtag. Then you can read the tweets aloud, integrate them into your lecture, and/or facilitate a class discussion. This teaching strategy works well for blended, in-person, and online course formats, so it’s very adaptable to any topic or lesson.











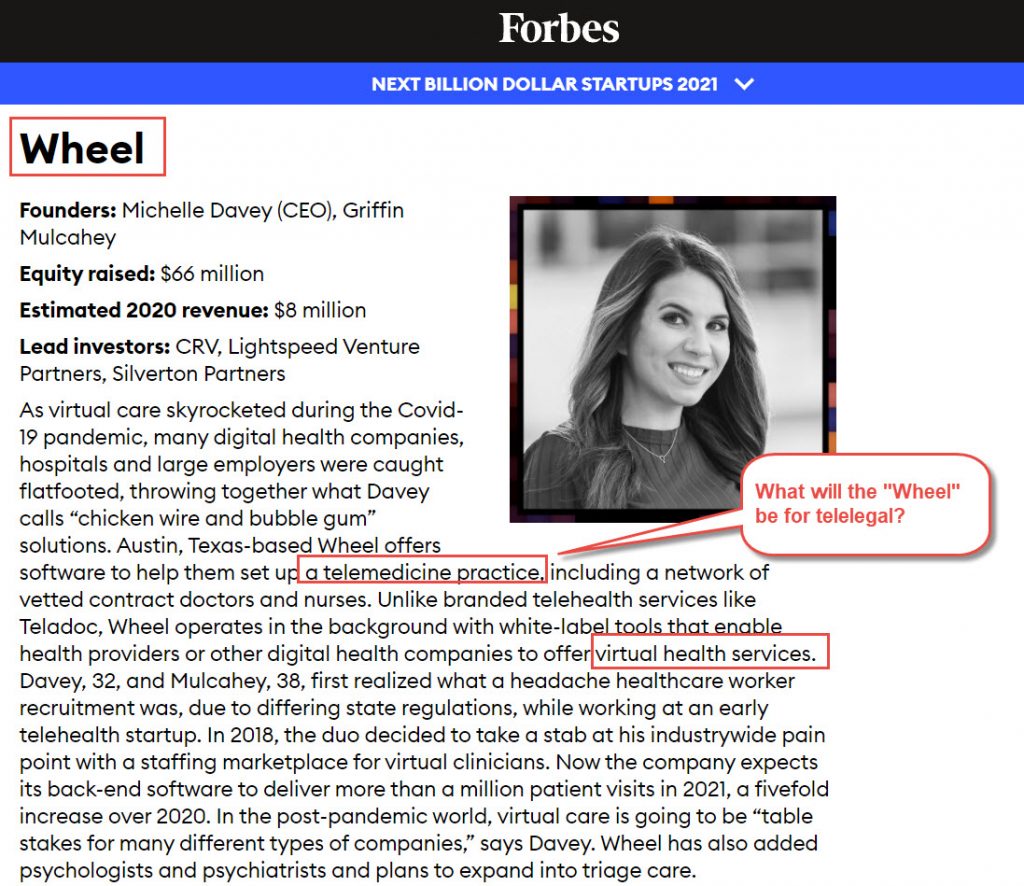
 Source:
Source: