HOW DUOLINGO’S AI LEARNS WHAT YOU NEED TO LEARN — from spectrum.ieee.org by Klinton Bicknell, Claire Brust, and Burr Settles
The AI that powers the language-learning app today could disrupt education tomorrow
Excerpt:
It’s lunchtime when your phone pings you with a green owl who cheerily reminds you to “Keep Duo Happy!” It’s a nudge from Duolingo, the popular language-learning app, whose algorithms know you’re most likely to do your 5 minutes of Spanish practice at this time of day. The app chooses its notification words based on what has worked for you in the past and the specifics of your recent achievements, adding a dash of attention-catching novelty. When you open the app, the lesson that’s queued up is calibrated for your skill level, and it includes a review of some words and concepts you flubbed during your last session.
The AI systems we continue to refine are necessary to scale the learning experience beyond the more than 50 million active learners who currently complete about 1 billion exercises per day on the platform.
Although Duolingo is known as a language-learning app, the company’s ambitions go further. We recently launched apps covering childhood literacy and third-grade mathematics, and these expansions are just the beginning. We hope that anyone who wants help with academic learning will one day be able to turn to the friendly green owl in their pocket who hoots at them, “Ready for your daily lesson?”
Also relevant/see:
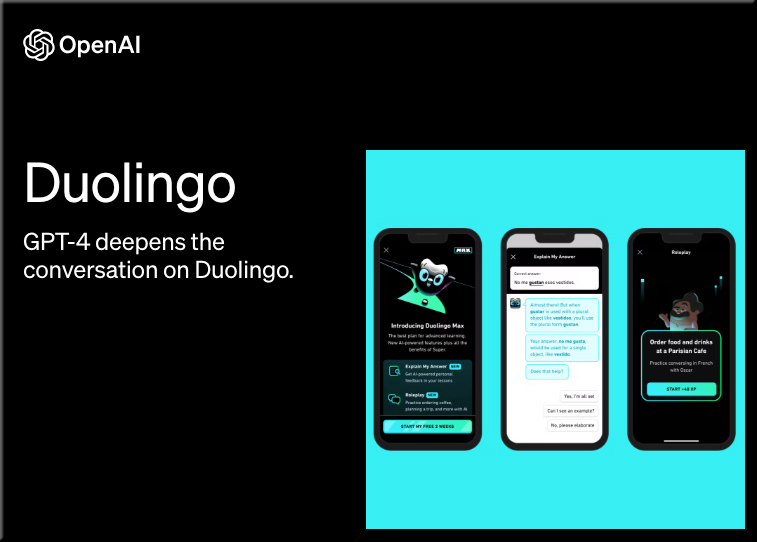
Duolingo turned to OpenAI’s GPT-4 to advance the product with two new features: Role Play, an AI conversation partner, and Explain my Answer, which breaks down the rules when you make a mistake, in a new subscription tier called Duolingo Max.
“We wanted AI-powered features that were deeply integrated into the app and leveraged the gamified aspect of Duolingo that our learners love,” says Bodge.
Also relevant/see:
The following is a quote from Donald Clark’s posting on LinkedIn.com today:
The whole idea of AI as a useful teacher is here. Honestly it’s astounding. They have provided a Socratic approach to an algebra problem that is totally on point. Most people learn in the absence of a teacher or lecturer. They need constant scaffolding, someone to help them move forward, with feedback. This changes our whole relationship with what we need to know, and how we get to know it. Its reasoning ability is also off the scale.
We now have human teachers, human learners but also AI teachers and AI that learns. It used to be a diad, it is now a tetrad – that is the basis of the new pedAIgogy.
Personalised, tutor-led learning, in any subject, anywhere, at any time for anyone. That has suddenly become real.
Also relevant/see:
Introducing Duolingo Max, a learning experience powered by GPT-4 — from blog.duolingo.com
Excerpts:
We believe that AI and education make a great duo, and we’ve leveraged AI to help us deliver highly-personalized language lessons, affordable and accessible English proficiency testing, and more. Our mission to make high-quality education available to everyone in the world is made possible by advanced AI technology.
Explain My Answer offers learners the chance to learn more about their response in a lesson (whether their answer was correct or incorrect!)
…
Roleplay allows learners to practice real-world conversation skills with world characters in the app.

















