DC: Is the future of one of our powerful learning ecosystems more like adding your own desired groups/cohorts, topics, items, etc. to your server? Like a learning-focused type of Discord service? (https://t.co/Vq4dZamBf2)#future #learningecosystems #personalizedlearning pic.twitter.com/wVMWYBN3R1
— Daniel Christian (he/him/his) (@dchristian5) August 17, 2023
AI for Education Webinars — from youtube.com by Tom Barrett and others
Post-AI Assessment Design — from drphilippahardman.substack.com by Dr. Philippa Hardman
A simple, three-step guide on how to design assessments in a post-AI world
Excerpt:
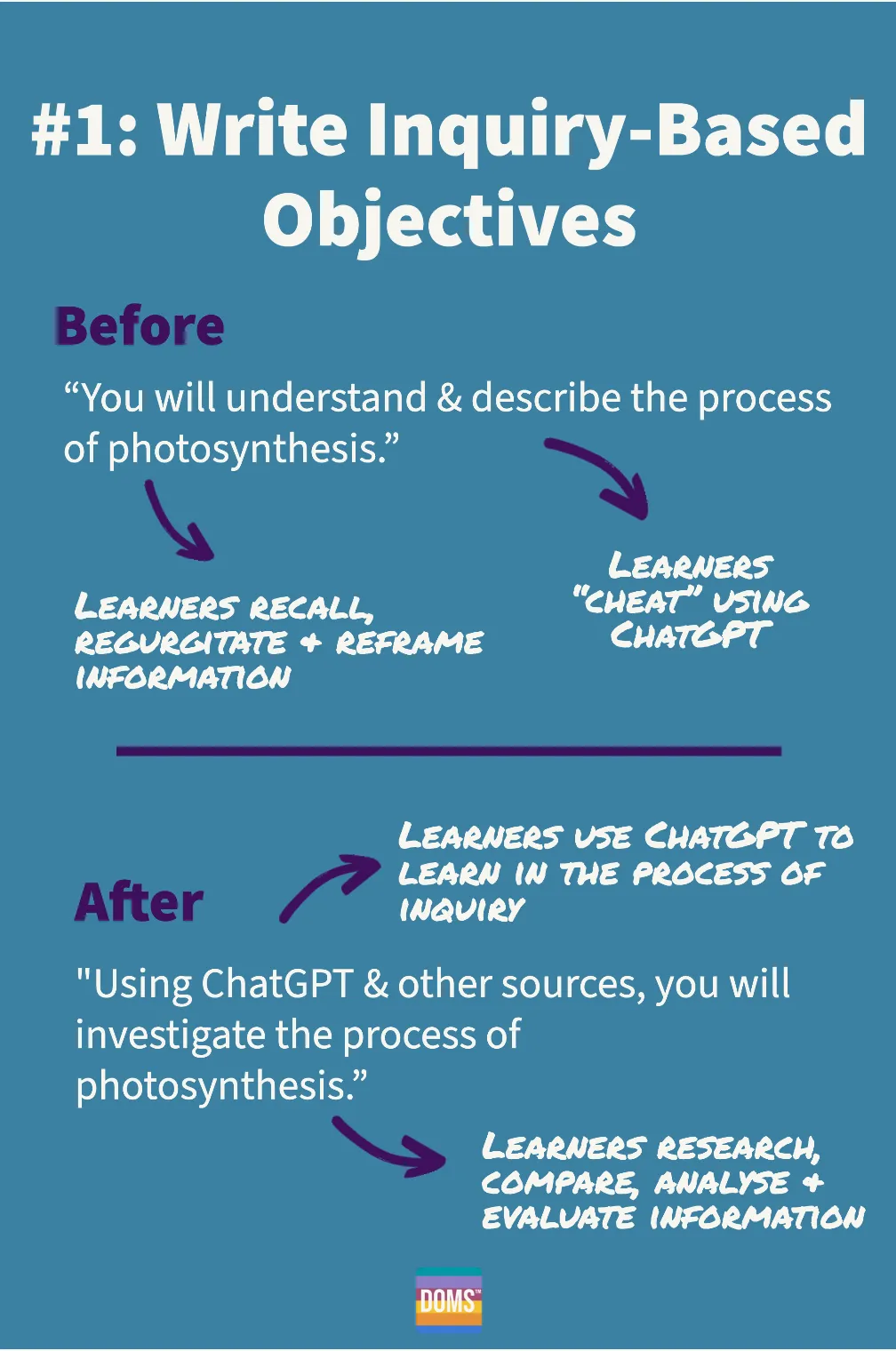
Step 1: Write Inquiry-Based Objectives
Inquiry-based objectives focus not just on the acquisition of knowledge but also on the development of skills and behaviours, like critical thinking, problem-solving, collaboration and research skills.
They do this by requiring learners not just to recall or “describe back” concepts that are delivered via text, lecture or video. Instead, inquiry-based objectives require learners to construct their own understanding through the process of investigation, analysis and questioning.
.
Massive Disruption Now: What AI Means for Students, Educators, Administrators and Accreditation Boards
— from stefanbauschard.substack.com by Stefan Bauschard; via Will Richardson on LinkedIn
The choices many colleges and universities make regarding AI over the next 9 months will determine if they survive. The same may be true for schools.
Excerpts:
Just for a minute, consider how education would change if the following were true –
- AIs “hallucinated” less than humans
- AIs could write in our own voices
- AIs could accurately do math
- AIs understood the unique academic (and eventually developmental) needs of each student and adapt instruction to that student
- AIs could teach anything any student wanted or need to know any time of day or night
- AIs could do this at a fraction of the cost of a human teacher or professor
Fall 2026 is three years away. Do you have a three year plan? Perhaps you should scrap it and write a new one (or at least realize that your current one cannot survive). If you run an academic institution in 2026 the same way you ran it in 2022, you might as well run it like you would have in 1920. If you run an academic institution in 2030 (or any year when AI surpasses human intelligence) the same way you ran it in 2022, you might as well run it like you would have in 1820. AIs will become more intelligent than us, perhaps in 10-20 years (LeCun), though there could be unanticipated breakthroughs that lower the time frame to a few years or less (Benjio); it’s just a question of when, not “if.”
On one creative use of AI — from aiandacademia.substack.com by Bryan Alexander
A new practice with pedagogical possibilities
Excerpt:
Look at those material items again. The voiceover? Written by an AI and turned into audio by software. The images? Created by human prompts in Midjourney. The music is, I think, human created. And the idea came from a discussion between a human and an AI?
…
How might this play out in a college or university class?
Imagine assignments which require students to craft such a video. Start from film, media studies, or computer science classes. Students work through a process:
Generative Textbooks — from opencontent.org by David Wiley
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
I continue to try to imagine ways generative AI can impact teaching and learning, including learning materials like textbooks. Earlier this week I started wondering – what if, in the future, educators didn’t write textbooks at all? What if, instead, we only wrote structured collections of highly crafted prompts? Instead of reading a static textbook in a linear fashion, the learner would use the prompts to interact with a large language model. These prompts could help learners ask for things like:
- overviews and in-depth explanations of specific topics in a specific sequence,
- examples that the learner finds personally relevant and interesting,
- interactive practice – including open-ended exercises – with immediate, corrective feedback,
- the structure of the relationships between ideas and concepts,
- etc.
Also relevant/see:
.
Generating The Future of Education with AI — from aixeducation.com
Designed for K12 and Higher-Ed Educators & Administrators, this conference aims to provide a platform for educators, administrators, AI experts, students, parents, and EdTech leaders to discuss the impact of AI on education, address current challenges and potentials, share their perspectives and experiences, and explore innovative solutions. A special emphasis will be placed on including students’ voices in the conversation, highlighting their unique experiences and insights as the primary beneficiaries of these educational transformations.
How Teachers Are Using ChatGPT in Class — from edweek.org by Larry Ferlazzo
Excerpt:
The use of generative AI in K-12 settings is complex and still in its infancy. We need to consider how these tools can enhance student creativity, improve writing skills, and be transparent with students about how generative AI works so they can better understand its limitations. As with any new tech, our students will be exposed to it, and it is our task as educators to help them navigate this new territory as well-informed, curious explorers.
Japan emphasizes students’ comprehension of AI in new school guidelines — from japantimes.co.jp by Karin Kaneko; via The Rundown
Excerpt:
The education ministry has emphasized the need for students to understand artificial intelligence in new guidelines released Tuesday, setting out how generative AI can be integrated into schools and the precautions needed to address associated risks.
Students should comprehend the characteristics of AI, including its advantages and disadvantages, with the latter including personal information leakages and copyright infringement, before they use it, according to the guidelines. They explicitly state that passing off reports, essays or any other works produced by AI as one’s own is inappropriate.
AI’s Teachable Moment: How ChatGPT Is Transforming the Classroom — from cnet.com by Mark Serrels
Teachers and students are already harnessing the power of AI, with an eye toward the future.
Excerpt:
Thanks to the rapid development of artificial intelligence tools like Dall-E and ChatGPT, my brother-in-law has been wrestling with low-level anxiety: Is it a good idea to steer his son down this path when AI threatens to devalue the work of creatives? Will there be a job for someone with that skill set in 10 years? He’s unsure. But instead of burying his head in the sand, he’s doing what any tech-savvy parent would do: He’s teaching his son how to use AI.
In recent months the family has picked up subscriptions to AI services. Now, in addition to drawing and sculpting and making movies and video games, my nephew is creating the monsters of his dreams with Midjourney, a generative AI tool that uses language prompts to produce images.
The AI Dictionary for Educators — from blog.profjim.com
To bridge this knowledge gap, I decided to make a quick little dictionary of AI terms specifically tailored for educators worldwide. Initially created for my own benefit, I’ve reworked my own AI Dictionary for Educators and expanded it to help my fellow teachers embrace the advancements AI brings to education.
7 Strategies to Prepare Educators to Teach With AI — from edweek.org by Lauraine Langreo; NOTE: Behind paywall
101 creative ideas to use AI in education, A crowdsourced collection — from zenodo.org by Chrissi Nerantzi, Sandra Abegglen, Marianna Karatsiori, & Antonio Martínez-Arboleda (Eds.); with thanks to George Veletsianos for this resource
As an example, here’s one of the ideas from the crowdsourced collection:
On a somewhat related note, also see:
Merlyn Mind launches education-focused LLMs for classroom integration of generative AI — from venturebeat.com by Victor Dey
Excerpt:
Merlyn Mind, an AI-powered digital assistant platform, announced the launch of a suite of large language models (LLMs) specifically tailored for the education sector under an open-source license.
Designing courses in an age of AI — from teachinginhighered.com by Maria Andersen
Maria Andersen shares about designing courses in an age of artificial intelligence (AI) on episode 469 of the Teaching in Higher Ed podcast.
With generative AI, we have an incredible acceleration of change happening.
Maria Andersen
In Finland, the Future of Learning Has Arrived — Just Not Where You Think — from samchaltain.substack.com by Sam Chaltain
It turns out the “Finnish Miracle” is more (and less) miraculous than you think . . .
But whereas Finland’s schools are still characterized by a culture of teaching, Oodi stands as a beacon of learning — self-organizing, emergent, and overflowing with the life force of its inhabitants.
.
From DSC:
As the above got me to thinking about learning spaces, here’s another somewhat relevant item from Steelcase:
Addendum on 6/6/23:
Also relevant to the first item in this posting, see:
Looking for Miracles in the Wrong Places — from nataliewexler.substack.com by Natalie Wexler
An “edutourist” in Finland finds the ideal school, but it isn’t a school at all.
Counterpoint/excerpt:
It sounds appealing, but any country following that route is not only likely to find itself at the bottom of the PISA heap. It’s also likely to do a profound disservice to many of its children, particularly those from less highly educated families, who depend on teachers to impart information they don’t already have and to systematically build their knowledge.
Of course it’s possible for explicit, teacher-directed instruction to be soul-crushing for students. But it certainly doesn’t have to be, and there’s no indication from Mr. X’s account that the students in the schools he visited felt their experience was oppressive. When teachers get good training—of the kind apparently provided in Finland—they know how to engage students in the content they’re teaching and guide them to think about it deeply and analytically.
That’s not oppressive. In fact, it’s the key to enabling students to reach their full potential. In that sense, it’s liberating.
? So much has happened in the world of AI these past 7 days.
It’s going to change many industries you thought you knew.
12 recent AI developments that are not just reshaping the industry, but our everyday lives:
— Barsee ? (@heyBarsee) May 30, 2023
From DSC:
I also wanted to highlight the item below, which Barsee also mentioned above, as it will likely hit the world of education and training as well:
Last night, Jensen Huang of NVIDIA gave his very first live keynote in 4-years.
The most show-stopping moment from the event was when he showed off the real-time AI in video games. A human speaks, the NPC responds, in real time and the dialogue was generated with AI on the fly. pic.twitter.com/TDoUM1zSiy
— Matt Wolfe (@mreflow) May 29, 2023
Also relevant/see:
- Digital Renaissance: NVIDIA Neuralangelo Research Reconstructs 3D Scenes — from blogs.nvidia.com
Last night, Jensen Huang of NVIDIA gave his very first live keynote in 4-years.
The most show-stopping moment from the event was when he showed off the real-time AI in video games. A human speaks, the NPC responds, in real time and the dialogue was generated with AI on the fly. pic.twitter.com/TDoUM1zSiy
— Matt Wolfe (@mreflow) May 29, 2023
From DSC:
And how long before that type of interactivity is embedded into learning-related applications/games?!
Nvidia ($960B) is now worth more than:
– Facebook ($665B)
– Tesla ($618B)
– Netflix ($168B)This is a company that started 30 years ago at Denny’s and was for decades only a video game chip maker.
Here’s why Nvidia is surging: pic.twitter.com/km7pECk4Kw
— Peter Yang (@petergyang) May 27, 2023
AI in Learning: The Impact of ChatGPT on L&D & Workflow Learning — from linkedin.com; this event by Bob Mosher features his conversation with Donald Clark
The future is already here.
The 1% who understand it will run the world.
Here’s a list of 24 top resources to get up to speed (for free):
— Misha (@mishadavinci) May 28, 2023
Bill Gates says AI is poised to destroy search engines and Amazon — from futurism.com by Victor Tangermann
Who will win the AI [competition]? (DSC: I substituted the word competition here, as that’s what it is. It’s not a war, it’s a part of America’s way of doing business.)
“Whoever wins the personal agent, that’s the big thing, because you will never go to a search site again, you will never go to a productivity site, you’ll never go to Amazon again,” Gates said during a Goldman Sachs event on AI in San Francisco this week, as quoted by CNBC.
These AI assistants could “read the stuff you don’t have time to read,” he said, allowing users to get to information without having to use a search engine like Google.
EdX launches ChatGPT-powered plugin, learning assistant — from edscoop.com
The online learning firm edX introduced two new tools powered by ChatGPT, the “first of many innovations” in generative AI for the platform.
The online learning platform edX introduced two new tools on Friday based on OpenAI’s ChatGPT technology: an edX plugin for ChatGPT and a learning assistant embedded in the edX platform, called Xpert.
According to the company, its plugin will enable ChatGPT Plus subscribers to discover educational programs and explore learning content such as videos and quizzes across edX’s library of 4,200 courses.
Bing is now the default search for ChatGPT — from theverge.com by Tom Warren; via superhuman.beehiiv.com
The close partnership between Microsoft and OpenAI leads to plug-in interoperability and search defaults.
Excerpt:
OpenAI will start using Bing as the default search experience for ChatGPT. The new search functionality will be rolling out to ChatGPT Plus users today and will be enabled for all free ChatGPT users soon through a plug-in in ChatGPT.
How ChatGPT Could Help or Hurt Students With Disabilities — from chronicle.com by Beth McMurtrie
Excerpt:
- Students with mobility challenges may find it easier to use generative AI tools — such as ChatGPT or Elicit — to help them conduct research if that means they can avoid a trip to the library.
- Students who have trouble navigating conversations — such as those along the autism spectrum — could use these tools for “social scripting.” In that scenario, they might ask ChatGPT to give them three ways to start a conversation with classmates about a group project.
- Students who have trouble organizing their thoughts might benefit from asking a generative AI tool to suggest an opening paragraph for an essay they’re working on — not to plagiarize, but to help them get over “the terror of the blank page,” says Karen Costa, a faculty-development facilitator who, among other things, focuses on teaching, learning, and living with ADHD. “AI can help build momentum.”
- ChatGPT is good at productive repetition. That is a practice most teachers use anyway to reinforce learning. But AI can take that to the next level by allowing students who have trouble processing information to repeatedly generate examples, definitions, questions, and scenarios of concepts they are learning.
It’s not all on you to figure this out and have all the answers. Partner with your students and explore this together.
A new antibiotic, discovered with artificial intelligence, may defeat a dangerous superbug — from edition.cnn.com by Brenda Goodman
8 YouTube Channels to Learn AI — from techthatmatters.beehiiv.com by Harsh Makadia
- The AI Advantage (link)
- Jason West (link)
- TheAIGRID (link)
- Prompt Engineering (link)
- Matt Wolfe (link)
- Two-Minute Papers (link)
- Brett Malinowski (link)
- 10X Income (link)
Artificial Intelligence and the Future of Teaching and Learning | Insights and Recommendations — with thanks to Robert Gibson on LinkedIn for this resource
Red Sox Turn Fenway Park into “Learning Lab” for Boston 6th Graders — from by Ira Stoll
“The key to unlock opportunity is education and hard work,” students are told at launch event

Students from the 6th grade at Nathan Hale School complete a “bingo challenge” as part of the Red Sox Hall of Fame stop on their guided tour of the Fenway Park Learning Lab.
Excerpt:
The six-stop tour has students learning history, geography, math, and science. Student visitors get baseball caps, t-shirts, and a backpack full of other souvenir items like baseball cards, binoculars, a calculator, and a pen. The most important piece of equipment may be a 40-page, seriously substantive workbook, developed with the Boston Public Schools, that students work their way through along the hourlong guided tour.
From DSC:
Very interesting.
From DSC:
Before we get to Scott Belsky’s article, here’s an interesting/related item from Tobi Lutke:
I just clued in how insane text2vid will get soon. As crazy as this sounds, we will be able to generate movies from just minor prompts and the path there is pretty clear.
— tobi lutke (@tobi) March 29, 2023
Our World Shaken, Not Stirred: Synthetic entertainment, hybrid social experiences, syncing ourselves with apps, and more. — from implications.com by Scott Belsky
Things will get weird. And exciting.
Excerpts:
Recent advances in technology will stir shake the pot of culture and our day-to-day experiences. Examples? A new era of synthetic entertainment will emerge, online social dynamics will become “hybrid experiences” where AI personas are equal players, and we will sync ourselves with applications as opposed to using applications.
A new era of synthetic entertainment will emerge as the world’s video archives – as well as actors’ bodies and voices – will be used to train models. Expect sequels made without actor participation, a new era of ai-outfitted creative economy participants, a deluge of imaginative media that would have been cost prohibitive, and copyright wars and legislation.
Unauthorized sequels, spin-offs, some amazing stuff, and a legal dumpster fire: Now lets shift beyond Hollywood to the fast-growing long tail of prosumer-made entertainment. This is where entirely new genres of entertainment will emerge including the unauthorized sequels and spinoffs that I expect we will start seeing.
Also relevant/see:
Digital storytelling with generative AI: notes on the appearance of #AICinema — from bryanalexander.org by Bryan Alexander
Excerpt:
This is how I viewed a fascinating article about the so-called #AICinema movement. Benj Edwards describes this nascent current and interviews one of its practitioners, Julie Wieland. It’s a great example of people creating small stories using tech – in this case, generative AI, specifically the image creator Midjourney.
Bryan links to:
Artists astound with AI-generated film stills from a parallel universe — from arstechnica.com by Benj Edwards
A Q&A with “synthographer” Julie Wieland on the #aicinema movement.
From DSC:
How will text-to-video impact the Learning and Development world? Teaching and learning? Those people communicating within communities of practice? Those creating presentations and/or offering webinars?
Hmmm…should be interesting!
Infographic: Gamify your eLearning with these 7 techniques — from thelearningrooms.com
Excerpt:
Gamification refers to the application of gaming elements into the instructional design of a course. Here are 7 ways to incorporate gamification into your eLearning.
5 Ideas To Incorporate AI In Your eLearning Course — from elearningindustry.com by Christopher Pappas
Summary:
Artificial Intelligence is now taking the world of learning by storm. Here are 5 ways you can successfully incorporate AI in online learning.
Let’s say you’re training sales reps on handling different customer personalities. You can use this technology to diversify your branching scenarios so that trainees can also speak and not only type. This way, not only will the training become more realistic, but you’ll also be able to assess and work on additional elements, such as tone of voice, volume, speech tempo, etc.
From DSC:
I’m told by a reliable source (i.e., our oldest daughter, who is now a third-grade teacher) that Blooket is an effective, highly-engaging tool! She said students find these online-based games to be fun. She said it’s competitive, so you may want to make a note of that as well.
Competition Can Motivate, Encourage and Inspire Students. But It Can Also Harm Them. — from edsurge.com by Patrick Harris II
Excerpt:
The American Psychological Association (APA) defines competition as “any performance situation structured in such a way that success depends on performing better than others.” Naturally, this could create challenges in a school setting, but in my experience, whether innate or as a product of a structure, competition itself isn’t always problematic. In fact, some studies confirm that competition has benefits, though they vary based on the individual and the competition.
…
Competition can be thrilling and motivating to those who choose to engage. But it’s important to remember that competition is not a golden key to unlock student engagement. Depending on how we use it, competition can also cause harm, such as anxiety, low self-esteem or negative feelings of self-worth.
For every student who was celebrated, there was another student who, by design, was shamed.
Looking back, these competitions weren’t used to teach students sportsmanship or resilience. They were used as gimmicks and antics to “motivate” students. I now recognize that I played a part in reinforcing a system of inequity by awarding those students who were already privileged.
From DSC:
I appreciate Patrick’s balanced article here — mentioning both the potential advantages and disadvantages of using competitive activities in the classroom.
I’m also going to comment on the topic of competition but from a different perspective. One that involves my faith journey and relationships.
I used to play a lot of sports and I played one sport at the university level. I mention this to establish that I’ve had my share of competition. In my experience, competition was anti-relational. That could have been just my perspective, but perhaps others share this perspective as well.
That is, I viewed people as to be competed against…not to be in relationships with. When my identity was tied up with my sport, that was ok. But as my identity changed in my senior year, it was not ok. When I became a Christian (in faith), my identity shifted big time. And the LORD wanted me to be in relationships with other people. Competition didn’t help that part of my journey.
As an aside, competition was also encouraged in terms of grades and performance in school — including at the university level. Several professors put our results up on the walls outside their offices — clearly showing everyone where they stood in the class. And I saw competition in the corporate world all the time as well. So while it’s something we here in the United States practice big time, it does seem to have its plusses and minuses.
A learning ecosystem is composed of people, tools, technologies, content, processes, culture, strategies, and any other resource that helps one learn. Learning ecosystems can be at an individual level as well as at an organizational level.
Some example components:
- Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) such as faculty, staff, teachers, trainers, parents, coaches, directors, and others
- Fellow employees
- L&D/Training professionals
- Managers
- Instructional Designers
- Librarians
- Consultants
- Types of learning
- Active learning
- Adult learning
- PreK-12 education
- Training/corporate learning
- Vocational learning
- Experiential learning
- Competency-based learning
- Self-directed learning (i.e., heutagogy)
- Mobile learning
- Online learning
- Face-to-face-based learning
- Hybrid/blended learning
- Hyflex-based learning
- Game-based learning
- XR-based learning (AR, MR, and VR)
- Informal learning
- Formal learning
- Lifelong learning
- Microlearning
- Personalized/customized learning
- Play-based learning
- Cloud-based learning apps
- Coaching & mentoring
- Peer feedback
- Job aids/performance tools and other on-demand content
- Websites
- Conferences
- Professional development
- Professional organizations
- Social networking
- Social media – Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook/Meta, other
- Communities of practice
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) — including ChatGPT, learning agents, learner profiles,
- LMS/CMS/Learning Experience Platforms
- Tutorials
- Videos — including on YouTube, Vimeo, other
- Job-aids
- E-learning-based resources
- Books, digital textbooks, journals, and manuals
- Enterprise social networks/tools
- RSS feeds and blogging
- Podcasts/vodcasts
- Videoconferencing/audio-conferencing/virtual meetings
- Capturing and sharing content
- Tagging/rating/curating content
- Decision support tools
- Getting feedback
- Webinars
- In-person workshops
- Discussion boards/forums
- Chat/IM
- VOIP
- Online-based resources (periodicals, journals, magazines, newspapers, and others)
- Learning spaces
- Learning hubs
- Learning preferences
- Learning theories
- Microschools
- MOOCs
- Open courseware
- Portals
- Wikis
- Wikipedia
- Slideshare
- TED talks
- …and many more components.
These people, tools, technologies, etc. are constantly morphing — as well as coming and going in and out of our lives.
Top edtech trends in 2023 and the ASU example — from news.asu.edu
Excerpt:
In spite of our tendency to break things down into tidy time frames, like a new year or academic semester, change constantly turns over the status quo. Especially in the world of technology, where disruptive innovation may evolve rapidly from the fringe to the mainstream.
“At ASU’s Enterprise Technology, we work in spaces where technology is not just revolutionizing higher education, but the world at large,” said Lev Gonick, chief information officer at Arizona State University. “We strive to be proactive, not reactive, to new paradigms changing the ways in which we work, learn and thrive.”
As referenced by the above article:
- Technology Trends in Higher Education 2023 — from fierceeducation.com
Thus, the top higher education technology trends to watch out for in 2023 include Artificial Intelligence (AI), Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), Digital Twins, the Metaverse (including digital avatars and NFT art for use in the Metaverse and other Web3-based virtual environments), Internet of Things (IoT), Blockchain, Cloud, Gamification, and Chatbots. These technologies will support the expansion of the Digital Transformation of higher education going forward.
Also relevant/see:
- Virtual Reality: Trends in Higher Ed for 2023 and Beyond — from fierceeducation.com by Susan Fourtané
A bot that watched 70,000 hours of Minecraft could unlock AI’s next big thing — from technologyreview.com by Will Douglas Heaven
Online videos are a vast and untapped source of training data—and OpenAI says it has a new way to use it.
Excerpt:
OpenAI has built the best Minecraft-playing bot yet by making it watch 70,000 hours of video of people playing the popular computer game. It showcases a powerful new technique that could be used to train machines to carry out a wide range of tasks by binging on sites like YouTube, a vast and untapped source of training data.
The Minecraft AI learned to perform complicated sequences of keyboard and mouse clicks to complete tasks in the game, such as chopping down trees and crafting tools. It’s the first bot that can craft so-called diamond tools, a task that typically takes good human players 20 minutes of high-speed clicking—or around 24,000 actions.
The result is a breakthrough for a technique known as imitation learning, in which neural networks are trained to perform tasks by watching humans do them.
…
The team’s approach, called Video Pre-Training (VPT), gets around the bottleneck in imitation learning by training another neural network to label videos automatically.
Speak lands investment from OpenAI to expand its language learning platform — from techcrunch.com by Kyle Wiggers
Excerpts:
“Most language learning software can help with the beginning part of learning basic vocabulary and grammar, but gaining any degree of fluency requires speaking out loud in an interactive environment,” Zwick told TechCrunch in an email interview. “To date, the only way people can get that sort of practice is through human tutors, which can also be expensive, difficult and intimidating.”
Speak’s solution is a collection of interactive speaking experiences that allow learners to practice conversing in English. Through the platform, users can hold open-ended conversations with an “AI tutor” on a range of topics while receiving feedback on their pronunciation, grammar and vocabulary.
It’s one of the top education apps in Korea on the iOS App Store, with over 15 million lessons started annually, 100,000 active subscribers and “double-digit million” annual recurring revenue.
If you last checked in on AI image makers a month ago & thought “that is a fun toy, but is far from useful…” Well, in just the last week or so two of the major AI systems updated.
You can now generate a solid image in one try. For example, “otter on a plane using wifi” 1st try: pic.twitter.com/DhiYeVMEEV
— Ethan Mollick (@emollick) November 26, 2022
Is AI Generated Art Really Coming for Your Job? — from edugeekjournal.com by Matt Crosslin
Excerpt:
So, is this a cool development that will become a fun tool for many of us to play around with in the future? Sure. Will people use this in their work? Possibly. Will it disrupt artists across the board? Unlikely. There might be a few places where really generic artwork is the norm and the people that were paid very little to crank them out will be paid very little to input prompts. Look, PhotoShop and asset libraries made creating company logos very, very easy a long time ago. But people still don’t want to take the 30 minutes it takes to put one together, because thinking through all the options is not their thing. You still have to think through those options to enter an AI prompt. And people just want to leave that part to the artists. The same thing was true about the printing press. Hundreds of years of innovation has taught us that the hard part of the creation of art is the human coming up with the ideas, not the tools that create the art.
A quick comment from DSC:
Possibly, at least in some cases. But I’ve seen enough home-grown, poorly-designed graphics and logos to make me wonder if that will be the case.
How to Teach With Deep Fake Technology — from techlearning.com by Erik Ofgang
Despite the scary headlines, deep fake technology can be a powerful teaching tool
Excerpt:
The very concept of teaching with deep fake technology may be unsettling to some. After all, deep fake technology, which utilizes AI and machine learning and can alter videos and animate photographs in a manner that appears realistic, has frequently been covered in a negative light. The technology can be used to violate privacy and create fake videos of real people.
However, while these potential abuses of the technology are real and concerning that doesn’t mean we should turn a blind eye to the technology’s potential when using it responsibly, says Jaime Donally, a well-known immersive learning expert.
From DSC:
I’m still not sure about this one…but I’ll try to be open to the possibilities here.
Educators Are Taking Action in AI Education to Make Future-Ready Communities — from edsurge.com by Annie Ning
Excerpt:
AI Explorations and Their Practical Use in School Environments is an ISTE initiative funded by General Motors. The program provides professional learning opportunities for educators, with the goal of preparing all students for careers with AI.
Recently, we spoke with three more participants of the AI Explorations program to learn about its ongoing impact in K-12 classrooms. Here, they share how the program is helping their districts implement AI curriculum with an eye toward equity in the classroom.
Stealth Legal AI Startup Harvey Raises $5M in Round Led By OpenAI — from lawnext.com by Bob Ambrogi
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
A hitherto stealth legal AI startup emerged from the shadows today with news via TechCrunch that it has raised $5 million in funding led by the startup fund of OpenAI, the company that developed advanced neural network AI systems such as GPT-3 and DALL-E 2.
The startup, called Harvey, will build on the GPT-3 technology to enable lawyers to create legal documents or perform legal research by providing simple instructions using natural language.
The company was founded by Winston Weinberg, formerly an associate at law firm O’Melveny & Myers, and Gabriel Pereyra, formerly a research scientist at DeepMind and most recently a machine learning engineer at Meta AI.