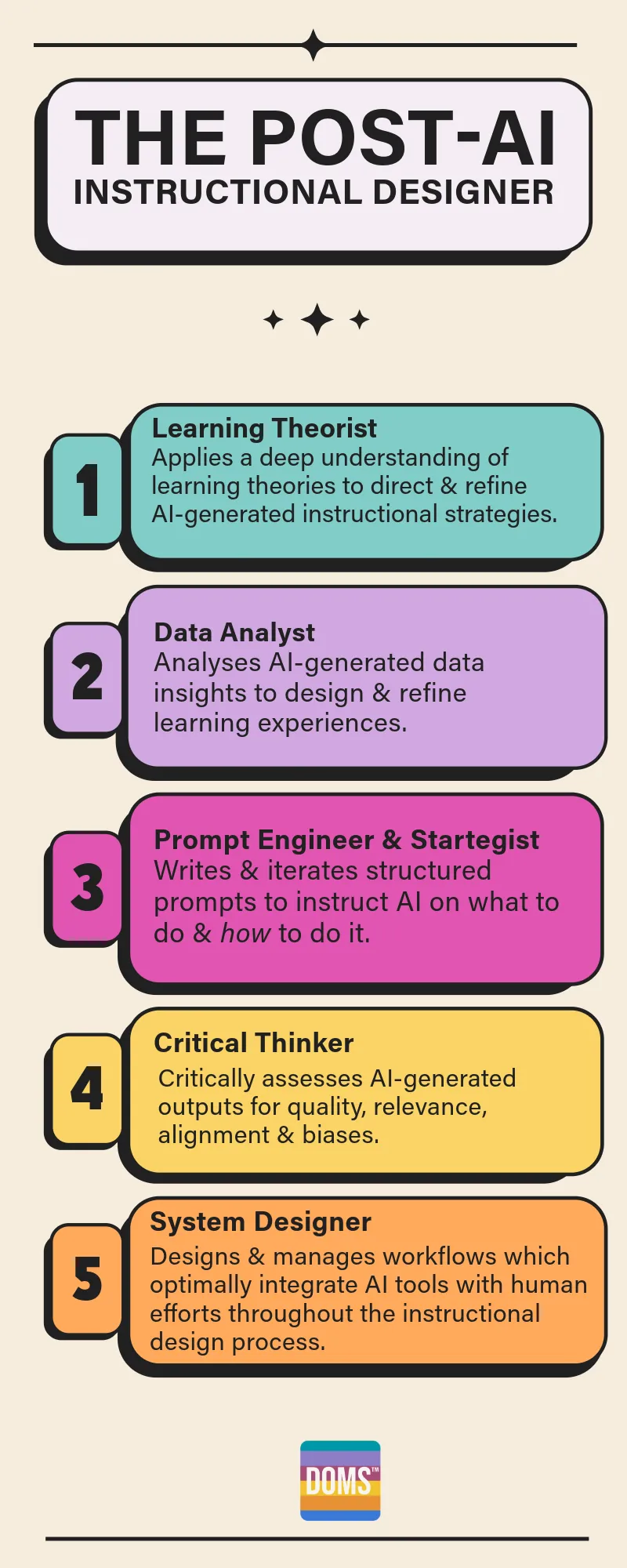
What Students Want When It Comes To AI — from onedtech.philhillaa.com by Glenda Morgan
The Digital Education Council Global AI Student Survey 2024
The Digital Education Council (DEC) this week released the results of a global survey of student opinions on AI. It’s a large survey with nearly 4,000 respondents conducted across 16 countries, but more importantly, it asks some interesting questions. There are many surveys about AI out there right now, but this one stands out. I’m going to go into some depth here, as the entire survey report is worth reading.
.

.

AI is forcing a teaching and learning evolution — from eschoolnews.com by Laura Ascione
AI and technology tools are leading to innovative student learning–along with classroom, school, and district efficiency
Key findings from the 2024 K-12 Educator + AI Survey, which was conducted by Hanover Research, include:
- Teachers are using AI to personalize and improve student learning, not just run classrooms more efficiently, but challenges remain
- While post-pandemic challenges persist, the increased use of technology is viewed positively by most teachers and administrators
- …and more
From DSC:
I wonder…how will the use of AI in education square with the issues of using smartphones/laptops within the classrooms? See:
- Why Schools Are Racing to Ban Student Phones — from nytimes.com by Natasha Singer; via GSV
As the new school year starts, a wave of new laws that aim to curb distracted learning is taking effect in Indiana, Louisiana and other states.
A three-part series from Dr. Phillippa Hardman:
Part 1: Writing Learning Objectives
The Results Part 1: Writing Learning Objectives
In this week’s post I will dive into the results from task 1: writing learning objectives. Stay tuned over the next two weeks to see all of the the results.
Part 2: Selecting Instructional Strategies.
The Results Part 2: Selecting an Instructional Strategy
Welcome back to our three-part series exploring the impact of AI on instructional design.
…
This week, we’re tackling a second task and a crucial aspect of instructional design: selecting instructional strategies. The ability to select appropriate instructional strategies to achieve intended objectives is a mission-critical skill for any instructional designer. So, can AI help us do a good job of it? Let’s find out!
Part 3: How Close is AI to Replacing Instructional Designers?
The Results Part 3: Creating a Course Outline
Today, we’re diving into what many consider to be the role-defining task of the instructional designer: creating a course design outline.
ChatGPT Cheat Sheet for Instructional Designers! — from Alexandra Choy Youatt EdD
Instructional Designers!
Whether you’re new to the field or a seasoned expert, this comprehensive guide will help you leverage AI to create more engaging and effective learning experiences.
What’s Inside?
Roles and Tasks: Tailored prompts for various instructional design roles and tasks.
Formats: Different formats to present your work, from training plans to rubrics.
Learning Models: Guidance on using the ADDIE model and various pedagogical strategies.
Engagement Tips: Techniques for online engagement and collaboration.
Specific Tips: Industry certifications, work-based learning, safety protocols, and more.
Who Can Benefit?
Corporate Trainers
Curriculum Developers
E-Learning Specialists
Instructional Technologists
Learning Experience Designers
And many more!
…
ChatGPT Cheat Sheet | Instructional Designer
5 AI Tools I Use Every Day (as a Busy Student) — from theaigirl.substack.com by Diana Dovgopol
AI tools that I use every day to boost my productivity.
#1 Gamma
#2 Perplexity
#3 Cockatoo
I use this AI tool almost every day as well. Since I’m still a master’s student at university, I have to attend lectures and seminars, which are always in English or German, neither of which is my native language. With the help of Cockatoo, I create scripts of the lectures and/or translations into my language. This means I don’t have to take notes in class and then manually translate them afterward. All I need to do is record the lecture audio on any device or directly in Cockatoo, upload it, and then you’ll have the audio and text ready for you.
…and more
Students Worry Overemphasis on AI Could Devalue Education — from insidehighered.com by Juliette Rowsell
Report stresses that AI is “new standard” and universities need to better communicate policies to learners.
Rising use of AI in higher education could cause students to question the quality and value of education they receive, a report warns.
This year’s Digital Education Council Global AI Student Survey, of more than 3,800 students from 16 countries, found that more than half (55 percent) believed overuse of AI within teaching devalued education, and 52 percent said it negatively impacted their academic performance.
Despite this, significant numbers of students admitted to using such technology. Some 86 percent said they “regularly” used programs such as ChatGPT in their studies, 54 percent said they used it on a weekly basis, and 24 percent said they used it to write a first draft of a submission.
Higher Ed Leadership Is Excited About AI – But Investment Is Lacking — from forbes.com by Vinay Bhaskara
As corporate America races to integrate AI into its core operations, higher education finds itself in a precarious position. I conducted a survey of 63 university leaders revealing that while higher ed leaders recognize AI’s transformative potential, they’re struggling to turn that recognition into action.
This struggle is familiar for higher education — gifted with the mission of educating America’s youth but plagued with a myriad of operational and financial struggles, higher ed institutions often lag behind their corporate peers in technology adoption. In recent years, this gap has become threateningly large. In an era of declining enrollments and shifting demographics, closing this gap could be key to institutional survival and success.
The survey results paint a clear picture of inconsistency: 86% of higher ed leaders see AI as a “massive opportunity,” yet only 21% believe their institutions are prepared for it. This disconnect isn’t just a minor inconsistency – it’s a strategic vulnerability in an era of declining enrollments and shifting demographics.
(Generative) AI Isn’t Going Anywhere but Up — from stefanbauschard.substack.com by Stefan Bauschard
“Hype” claims are nonsense.
There has been a lot of talk recently about an “AI Bubble.” Supposedly, the industry, or at least the generative AI subset of it, will collapse. This is known as the “Generative AI Bubble.” A bubble — a broad one or a generative one — is nonsense. These are the reasons we will continue to see massive growth in AI.
AI Readiness: Prepare Your Workforce to Embrace the Future — from learningguild.com by Danielle Wallace
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing industries, enhancing efficiency, and unlocking new opportunities. To thrive in this landscape, organizations need to be ready to embrace AI not just technologically but also culturally.
Learning leaders play a crucial role in preparing employees to adapt and excel in an AI-driven workplace. Transforming into an AI-empowered organization requires more than just technological adoption; it demands a shift in organizational mindset. This guide delves into how learning leaders can support this transition by fostering the right mindset attributes in employees.
Claude AI for eLearning Developers — from learningguild.com by Bill Brandon
Claude is fast, produces grammatically correct text, and outputs easy-to-read articles, emails, blog posts, summaries, and analyses. Take some time to try it out. If you worry about plagiarism and text scraping, put the results through Grammarly’s plagiarism checker (I did not use Claude for this article, but I did send the text through Grammarly).
Survey: Top Teacher Uses of AI in the Classroom — from thejournal.com by Rhea Kelly
A new report from Cambium Learning Group outlines the top ways educators are using artificial intelligence to manage their classrooms and support student learning. Conducted by Hanover Research, the 2024 K-12 Educator + AI Survey polled 482 teachers and administrators at schools and districts that are actively using AI in the classroom.
More than half of survey respondents (56%) reported that they are leveraging AI to create personalized learning experiences for students. Other uses included providing real-time performance tracking and feedback (cited by 52% of respondents), helping students with critical thinking skills (50%), proofreading writing (47%), and lesson planning (44%).
On the administrator side, top uses of AI included interpreting/analyzing student data (61%), managing student records (56%), and managing professional development (56%).
Addendum on 8/14/24: