The Mass Exodus of Teachers — from educationoneducation.substack.com by Jeannine Proctor
Understanding Why Educators Are Fleeing the Classroom and How to Bring Them Back
Stemming the tide will require nuance, empathy, and listening to what teachers say they need. While pay raises are indispensable, they alone won’t be enough. Districts must take an integrated approach that also addresses unmanageable workloads, lack of resources, and toxic school cultures.
Some best practices include utilizing multi-classroom teaching models, providing duty-free “coverage” periods, and hiring support staff to shoulder non-instructional burdens. Investing in mentoring and leadership opportunities can stem the turnover of principals and administrators too. Public recognition and appreciation can also go a long way.
Most importantly, we must work to restore teacher well-being, purpose, and passion.
From DSC:
The primary things that would help this very troubling situation:
- provide higher salaries
- deal with unreasonable workload expectations
- address a lack of teacher well-being.
California’s dramatic jump in chronically absent students part of a nationwide surge — from edsource.org by Betty Marquez Rosales, Millika Seshadri, and Daniel J. Willis
Dee’s analysis found that since the pandemic the number of students who were chronically absent nearly doubled to about 13.6 million, with 1.8 million of them in California.
Compared with before the pandemic, Dee found that about 6.5 million additional students became chronically absent in 2021-22, including more than 1 million in California.
Daily Briefing: Dual enrollment for every 9th grader? — from chronicle.com by Rick Seltzer
The idea of default is also an important idea. If we do it by invitation, what we have noticed is that those who know about it know to say yes to the invitation. If it is a default schedule, and then you have to opt out, then our ability to address equity and enrollment for our low-income students and students of color, it makes us much more successful.
These would-be teachers graduated into the pandemic. Will they stick with teaching? — from hechingerreport.org by Nirvi Shah
We tracked down nearly 90 members of the University of Maryland College of Education’s 2020 class. Their experiences suggest the field isn’t doing enough to adapt to a new, more difficult era for educators
The number of people studying for careers in education has been declining for years. At the same time, schools have struggled to hold on to new teachers: Studies indicate that about 44 percent of teachers leave the profession within their first five years.
Then the pandemic came along, hammering teachers and the profession as a whole.
“The first three years of teaching are really, really hard even in a perfect school system,” said Randi Weingarten, president of the American Federation of Teachers. So for teachers who entered the teaching profession at any point during the pandemic, “this has been a helluva ride.”

As Back-to-School Costs Soar, More Parents & Teachers Turn to Charities for Help — from the74million.org by Sierra Lyons
But as the need increases, inflation makes it harder for nonprofits to meet this year’s demand.
A study from World Remit shows that the cost of school supplies in the United States has increased by over 25% compared with 2022.
Though inflation is the lowest it has been since March 2021, high prices are still stressing shoppers and increasing their reliance on local and national back-to-school drives. The nonprofit organizations that sponsor those drives, in turn, are struggling to meet the growing demand.
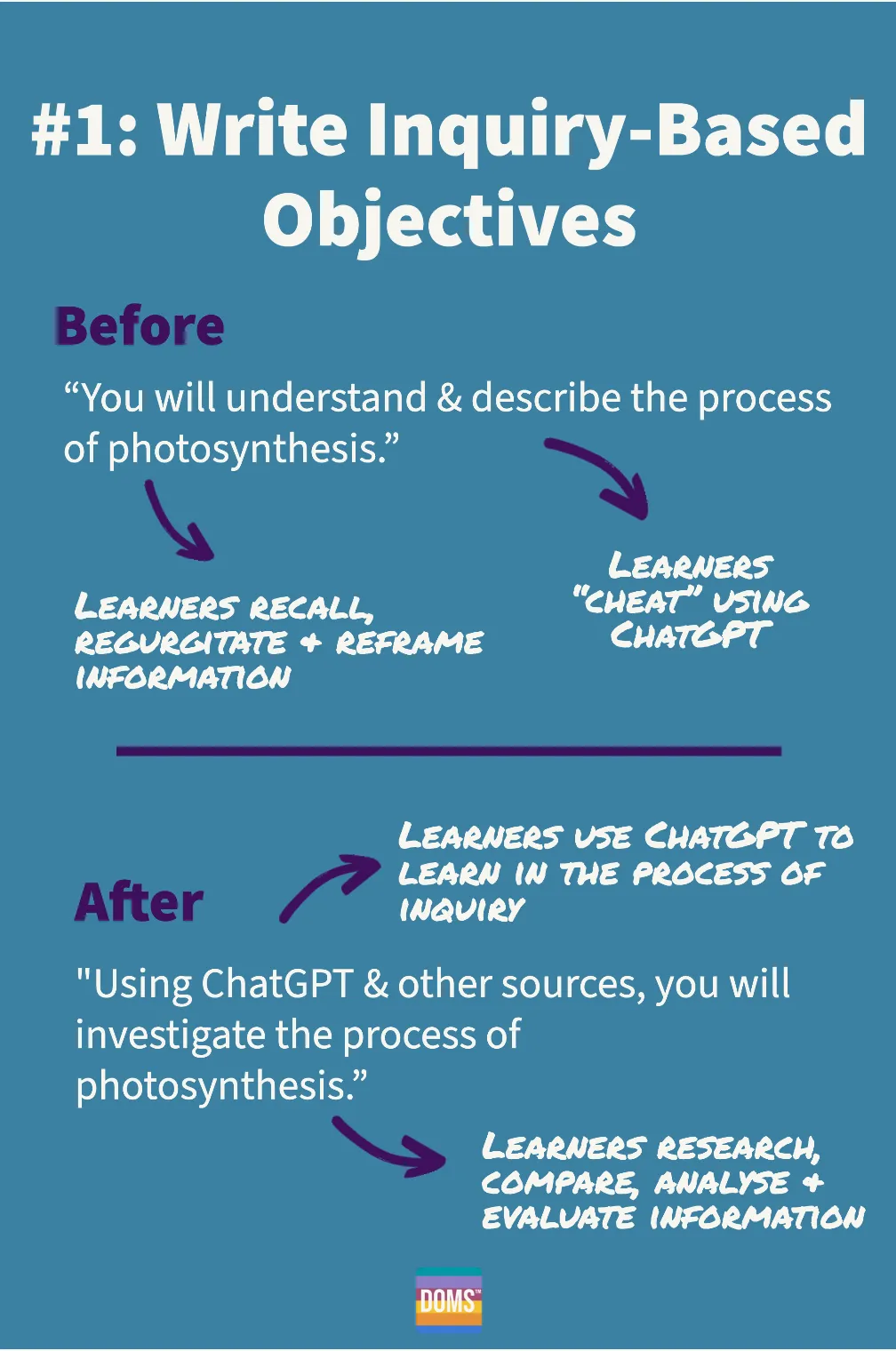
Excerpt from Tom Barrett’s Dialogic #329: The Transformative Power of Compassionate Leadership
Your Next Steps: ?Commit to action and turn words into works
- Reflect on your current leadership style and identify opportunities to incorporate more compassionate practices. Consider the Appreciative Inquiry model to guide this process.
- Develop an empathy-driven approach to problem-solving and team dynamics, focusing on fostering a culture of understanding, collaboration, and mutual respect.
- Revisit your feedback mechanisms and explore how they can be made more compassionate. Consider how critique can be delivered with kindness to empower, rather than tear down.
What Defines a Next-Gen High School? — from michaelbhorn.substack.com by Michael B. Horn
Against that backdrop, Ken Montgomery, co-founder of Design Tech High, known as D-Tech, and Keeanna Warren, who just became the CEO of the Purdue Polytechnic High School network, joined me to talk about their school designs, in particular the importance of:
- helping students connect to something bigger than the school itself;
- offering competency-based learning pathways with a transformed assessment system;
- allowing students to find their creative purpose aligned to the common good;
- and building a more permeable school that is connected to the community and offers a deep sense of belonging.
They also talked about the role of AI (artificial intelligence) and the anxiety that their students feel around its emergence, as well as the barriers that arise to building school models that break the traditional molds—from policy to human capital.