US College Closures Are Expected to Soar, Fed Research Says — from bloomberg.com
- Fed research created predictive model of college stress
- Worst-case scenario forecasts 80 additional closures
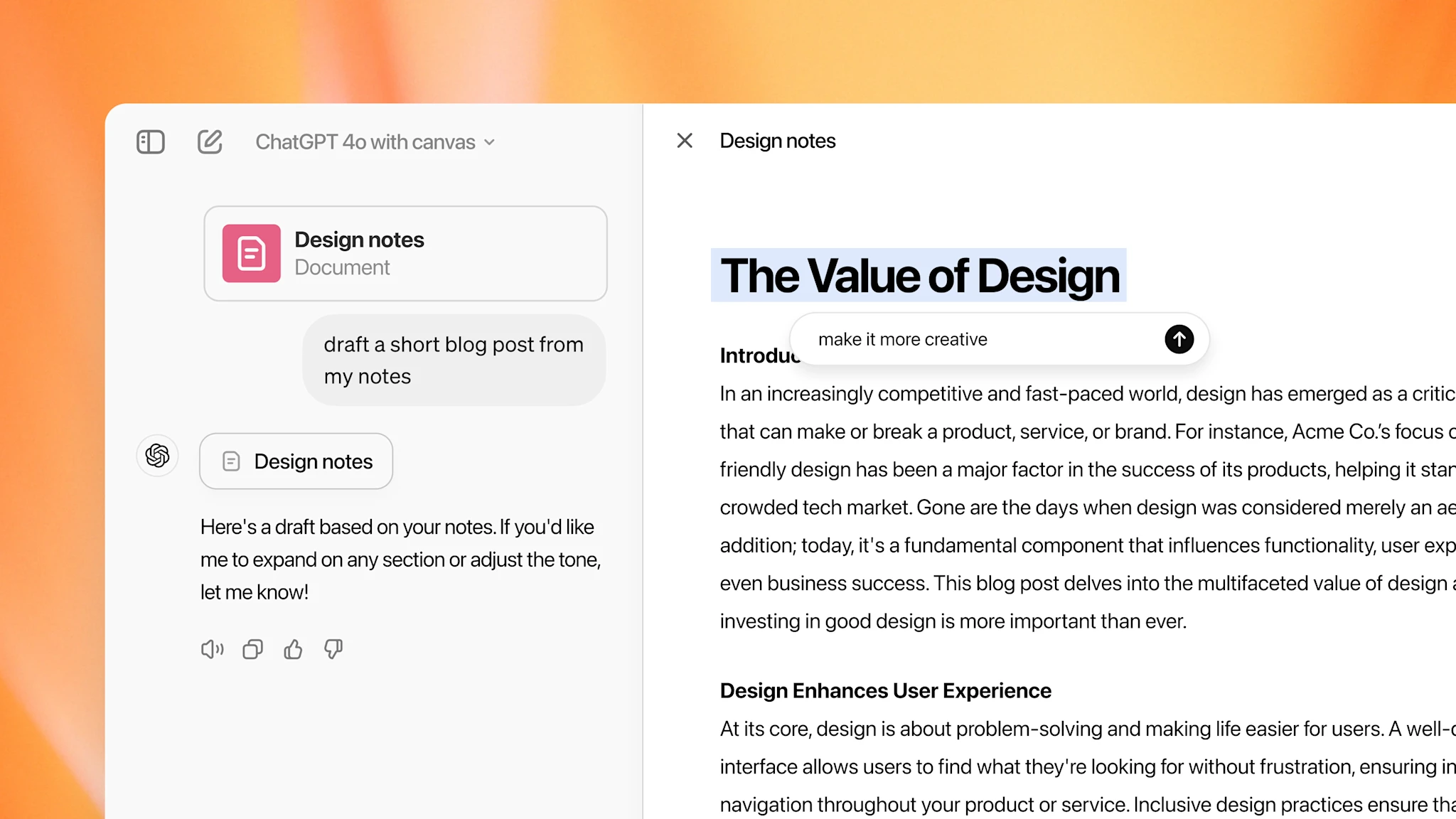
The number of colleges that close each year is poised to significantly increase as schools contend with a slowdown in prospective students.
That’s the finding of a new working paper published by the Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia, where researchers created predictive models of schools’ financial distress using metrics like enrollment and staffing patterns, sources of revenue and liquidity data. They overlayed those models with simulations to estimate the likely increase of future closures.
Excerpt from the working paper:
We document a high degree of missing data among colleges that eventually close and show that this is a key impediment to identifying at risk institutions. We then show that modern machine learning techniques, combined with richer data, are far more effective at predicting college closures than linear probability models, and considerably more effective than existing accountability metrics. Our preferred model, which combines an off-the-shelf machine learning algorithm with the richest set of explanatory variables, can significantly improve predictive accuracy even for institutions with complete data, but is particularly helpful for predicting instances of financial distress for institutions with spotty data.
From DSC:
Questions that come to my mind here include:
- Shouldn’t the public — especially those relevant parents and students — be made more aware of these types of papers and reports?
. - How would any of us like finishing up 1-3 years of school and then being told that our colleges or universities were closing, effective immediately? (This has happened many times already.) and with the demographic cliff starting to hit higher education, this will happen even more now.
.
Adding insult to injury…when we transfer to different institutions, we’re told that many of our prior credits don’t transfer — thus adding a significant amount to the overall cost of obtaining our degrees.
.
- Would we not be absolutely furious to discover such communications from our prior — and new — colleges and universities?
. - Will all of these types of closures move more people to this vision here?
Relevant excerpts from Ray Schroeder’s recent articles out at insidehighered.com:
Winds of Change in Higher Ed to Become a Hurricane in 2025
A number of factors are converging to create a huge storm. Generative AI advances, massive federal policy shifts, broad societal and economic changes, and the demographic cliff combine to create uncertainty today and change tomorrow.
Higher Education in 2025: AGI Agents to Displace People
The anticipated enrollment cliff, reductions in federal and state funding, increased inflation, and dwindling public support for tuition increases will combine to put even greater pressure on university budgets.
On the positive side of things, the completion rates have been getting better:
National college completion rate ticks up to 61.1% — from highereddive.com by Natalie Schwartz
Those who started at two-year public colleges helped drive the overall increase in students completing a credential.
Dive Brief:
- Completion rates ticked up to 61.1% for students who entered college in fall 2018, a 0.5 percentage-point increase compared to the previous cohort, according to data released Wednesday by the National Student Clearinghouse Research Center.
- The increase marks the highest six-year completion rate since 2007 when the clearinghouse began tracking the data. The growth was driven by fewer students stopping out of college, as well as completion gains among students who started at public two-year colleges.
- “Higher completion rates are welcome news for colleges and universities still struggling to regain enrollment levels from before the pandemic,” Doug Shapiro, the research center’s executive director, said in a statement dated Wednesday.
Addendum:
Attention Please: Professors Struggle With Student Disengagement — from edsurge.com
The stakes are huge, because the concern is that maybe the social contract between students and professors is kind of breaking down. Do students believe that all this college lecturing is worth hearing? Or, will this moment force a change in the way college teaching is done?