Sleek Furniture Collection by Hilla Shamia Harmonizes Cast Aluminum and Natural Wood — from thisiscolossal.com by Grace Ebert
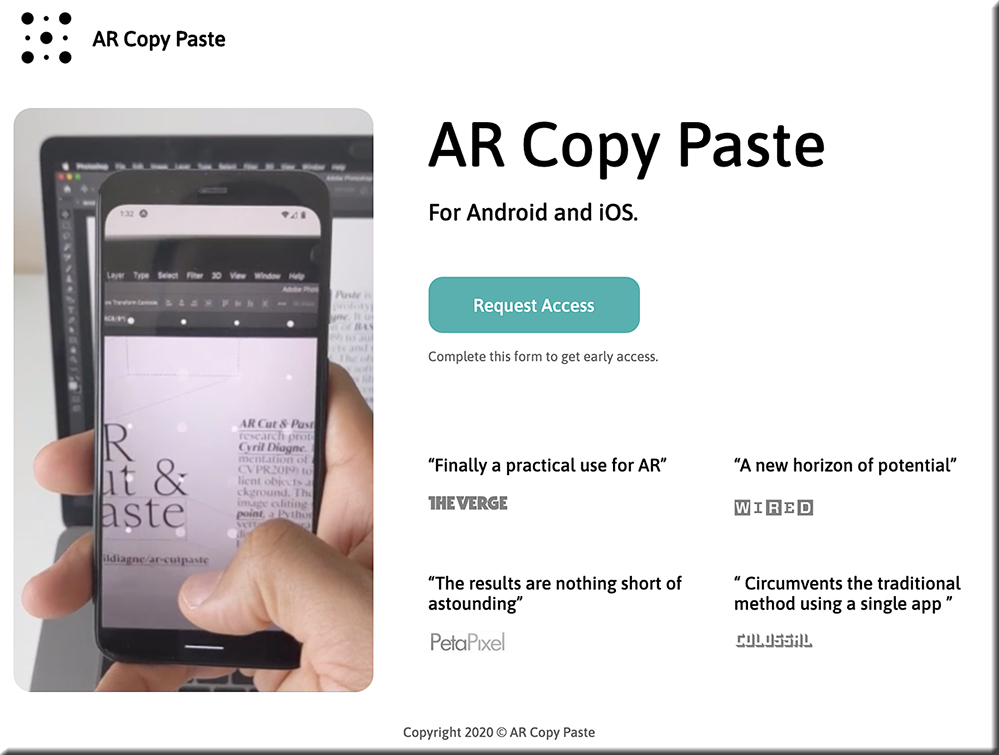
This magical interface will let you copy and paste the real world into your computer — from fastcompany.com by Mark Wilson
Wowza.
Excerpt:
But a new smartphone and desktop app coming from Cyril Diagne, an artist-in-residence at Google, greatly simplifies the process. Called AR Copy Paste, it can literally take a photo of a plant, mug, person, newspaper—whatever—on your phone, then, through a magical bit of UX, drop that object right onto your canvas in Photoshop on your main computer.
…
“It’s not so hard to open the scope of its potential applications. First of all, it’s not limited to objects, and it works equally well with printed materials like books, old photo albums, and brochures,” says Diagne. “Likewise, the principle is not limited to Photoshop but can be applied to any image, document, or video-editing software.”
4/10 – Cut & paste your surroundings to Photoshop
Code: https://t.co/cVddH3u3ik
Book: @HOLOmagazine
Garment: SS17 by @thekarentopacio
Type: Sainte Colombe by @MinetYoann @ProductionType
Technical Insights: ?#ML #AR #AI #AIUX #Adobe #Photoshop pic.twitter.com/LkTBe0t0rF— Cyril Diagne (@cyrildiagne) May 3, 2020
Setting Expectations for Remote Learning — from evoLLLution.com (where LLL stands for lifelong learning) by Robin Robinson
Excerpt:
Evo: How important is it to clearly differentiate remote learning and online education?
RR: You need to set expectations. Normally, if someone is going to produce an online course, they’re going to spend at least a semester building out the appropriate course map and alignments to their course objectives. In this situation, with remote learning, you’re trying to meet the same objective as you would in a regular face-to-face class, but online learning is completely different. Your head space needs to reflect that, and you need to consider the things in this environment that can’t be done in a face-to-face environment. We’re drawing on what people understand as good teaching and trying to emulate that experience online as much as possible.
Remote delivery requires using a lot of the synchronous tools. Online learning is about combining the best of both worlds.
Faculty who were skeptical have now adopted online learning. Many of them are amazed at how well they can get to know their students and how well they can track their performances in school.
…
What I’m concerned about is the digital divide. We want a very inclusive and diverse university, but that means recognizing that there are students at a disadvantage.
Law by Design — a book by Margaret Hagan
Excerpt:
Why combine law with design? Even if these two fields have traditionally not intersected, I see three main points of value in bringing them together.
- Experimental Culture: To be more forward-thinking in how we as legal professionals generate solutions for problems in the legal sector;
- User Centered Innovation: To put greater focus on the client and the lay person who has to use legal systems, to deliver them better services tailored their function and their experiential needs;
- New Paths for Legal Work & Serving Justice: To build a new set of professional paths and opportunities for people who want to work in law — and especially those who see that traditional ways of being law students and lawyers do not enable them to make the positive changes in society that originally drove them into law.
Also see:
The latest research for web designers, February 2020 — from webdesignerdepot.com by Suzanne Scacca
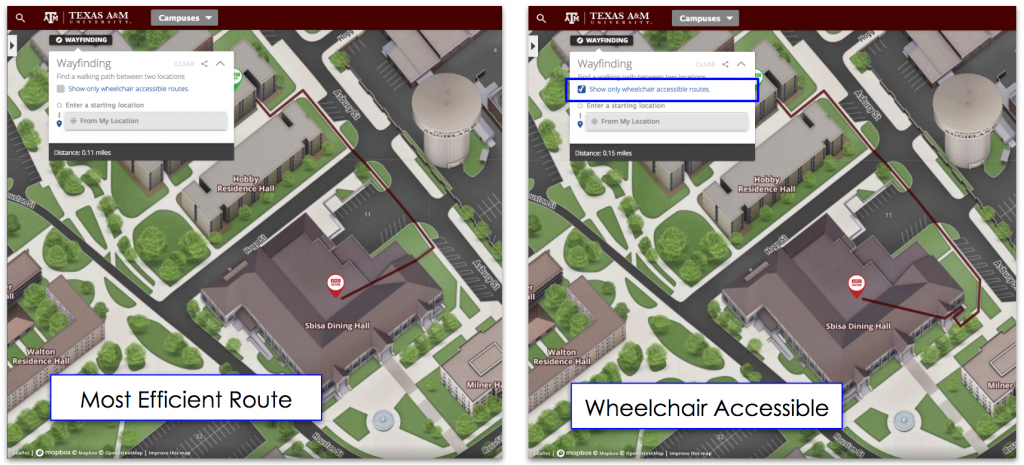
Concept3D introduces wheelchair wayfinding feature to support campus accessibility — from concept3d.echoscomm.com with thanks to Delaney Lanker for this resource
System makes wheelchair friendly campus routes easy to find and follow
Excerpt:
Concept3D, a leader in creating immersive online experiences with 3D modeling, interactive maps and virtual tour software, today announced the launch of a new wheelchair wayfinding feature that adds a new level of accessibility to the company’s interactive map and tour platform.
With the new wheelchair accessible route functionality, Concept3D clients are able to offer a separate set of wayfinding routes specifically designed to identify the most efficient and easiest routes.
Concept3D’s wayfinding system uses a weighted algorithm to determine the most efficient route between start and end points, and the new system was enhanced to factor in routing variables like stairs, curb cuts, steep inclines, and other areas that may impact accessibility.
Also see:
Wayfinding :: Wheelchair Accessible Routes — from concept3d.com
Making Waves — from provideocoalition.com by Woody Woodhall
Interview with Midge Costin
Excerpt:
Making Waves – The Art of Cinematic Sound, is an outstanding achievement not only as a stand-alone documentary film, but also as one of the only films that is dedicated solely to the art of sound for film. As we all know, when films started, sound was either done live with musical accompaniment or was simply exhibited silently.
It is a huge challenge to tackle such a wide ranging and meaningful advancement for film storytelling and yet undeterred, Midge Costin, herself a working sound professional, took it on. We spoke at length about her work on the film and her work as a filmmaker with sound, and as an educator.









![Sleek Furniture Collection by Hilla Shamia Harmonizes Cast Aluminum and Natural Wood [Ebert]](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/shamia-1-1024x681.jpg)