From DSC:
Christin Bohnke raises a great and timely question out at edsurge.com in her article entitled:
Do We Really Want Academic Permanent Records to Live Forever on Blockchain?
Christin does a wonderful job of addressing the possibilities — but also the challenges — of using blockchain for educational/learning-related applications. She makes a great point that the time to look at this carefully is now:
Yet as much as unchangeable education records offer new chances, they also create new challenges. Setting personal and academic information in stone may actually counter the mission of education to help people evolve over time. The time to assess the benefits and drawbacks of blockchain technology is right now, before adoption in schools and universities is widespread.
As Christin mentions, blockchain technology can be used to store more than formal certification data. It could also store such informal certification data such as “research experience, individual projects and skills, mentoring or online learning.”
The keeping of extensive records via blockchain certainly raises numerous questions. Below are a few that come to my mind:
- Will this type of record-keeping help or hurt in terms of career development and moving to a different job?
- Will — or should — CMS/LMS vendors enable this type of feature/service in their products?
- Should credentials from the following sources be considered relevant?
- Microlearning-based streams of content
- Data from open courseware/courses
- Learning that we do via our Personal Learning Networks (PLNs) and social networks
- Learning that we get from alternatives such as bootcamps, coding schools, etc.
- Will the keeping of records impact the enjoyment of learning — or vice versa? Or will it depend upon the person?
- Will there be more choice, more control — or less so?
- To what (granular) level of competency-based education should we go? Or from project-based learning?
- Could instructional designers access learners’ profiles to provide more personalized learning experiences?
- …and I’m certain there are more questions than these.
All that said…
To me, the answers to these questions — and likely other questions as well — lie in:
- Giving a person a chance to learn, practice, and then demonstrate the required skills (regardless of the data the potential employer has access to)
.
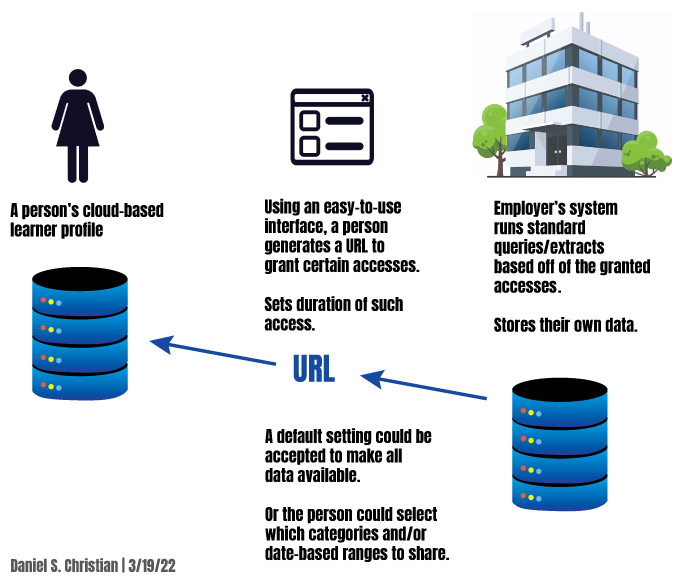
- Giving each user the right to own their own data — and to release it as they see fit. Each person should have the capability of managing their own information/data without having to have the skills of a software engineer or a database administrator. When something is written to a blockchain, there would be a field for who owns — and can administer — the data.
In the case of finding a good fit/job, a person could use a standardized interface to generate a URL that is sent out to a potential employer. That URL would be good for X days. The URL gives the potential employer the right to access whatever data has been made available to them. It could be full access, in which case the employer is able to run their own queries/searches on the data. Or the learner could restrict the potential employer’s reach to a more limited subset of data.
Visually, speaking:
I still have a lot more thinking to do about this, but that’s where I’m at as of today. Have a good one all!