The Broken Higher Education System: Addressing Stakeholder Needs for a More Adaptive Model — from educationoneducation.substack.com
Excerpt:
Higher education Chief Academic Officers (CAOs) must shift their perspective and strive to increase customer satisfaction to ensure the highest quality of educational products. A recent survey by Higher Education found that only 25% of customers were satisfied with the results higher education provided, contradicting the satisfaction differences of 99% of CAOs. Clearly, a disconnect exists between what higher education leaders deliver and what students, employers, and the changing labor market requirements are. To bridge this gap, higher education must develop products focusing on stakeholder feedback in product design, job requirements, and practical skills development.
From DSC:
So in terms of Design Thinking for reinventing lifelong learning, it seems to me that we need much more collaboration between the existing siloes. That is, we need students, educators, administrators, employers, and other stakeholders at the (re)design table. More experiments and what I call TrimTab Groups are needed.
But I think that the culture of many institutions of traditional higher education will prevent this from occurring. Many in academia shy away from (to put it politely) the world of business (even though they themselves ARE a business). I know, it’s not fair nor does it make sense. But many faculty members lean towards much more noble purposes, while never seeing the mounting gorillas of debt that they’ve heaped upon their students’/graduates’ backs. Those in academia shouldn’t be so quick to see themselves as being so incredibly different from those working in the corporate/business world.
The following quote seems appropriate to place here:
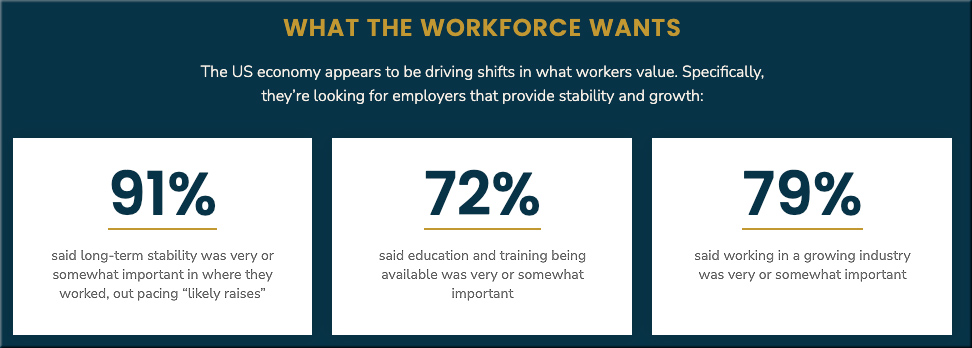
Along the lines of other items in the higher education space, see:
New Data Shows Emergency Pandemic Aid Helped Keep 18 Million Students Enrolled — from forbes.com by Edward Conroy
Excerpt:
The Department of Education (ED) has released new data showing that 18 million students were helped by emergency aid for colleges and universities throughout the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, more than half of which was used to provide emergency grants to students. These funds were provided through three rounds of Higher Education Emergency Relief Funds (HEERF) In total, $76.2 billion was provided, with half of those funds going to support students directly. Unusually for funding in higher education, the money was not heavily means-tested, and was distributed very quickly.
The report indicates that the funds were used for several essential purposes, including student basic needs, keeping staff employed, and helping keep students enrolled. For example, students used funds to cover things like food and housing at a time when employment was drying up for many students, ensuring that the Pandemic did not plunge students who already had limited funds deeper into basic needs insecurity.
Flagships prosper, while regionals suffer — from chronicle.com by Lee Gardner
Competition is getting fierce, and the gap is widening
Excerpts:
Some key numbers are moving in the right direction at the University of Oregon. The flagship institution enrolled 5,338 freshmen in the fall of 2022, its largest entering class ever. First-year enrollment increased 16 percent over 2021, which was also a record year. Meanwhile, Western Oregon University, a regional public institution an hour’s drive north, just outside Salem, lost nearly 7 percent of its enrollment over the same period.
…
In 28 states, flagships have seen enrollment rise between 2010 to 2021, while regionals have trended down, according to a Chronicle analysis of U.S. Education Department data. Across all states, enrollment at 78 public flagships rose 12.3 percent from 2010 to 2021, the most recent year for which data is available. Enrollment at 396 public regional universities slumped more than 4 percent during the same period.
A Chronicle analysis of federal data showed, for example, that in Michigan, a state being hit hard by demographic shifts and with no central higher-ed authority, the flagship University of Michigan at Ann Arbor saw undergraduate enrollment rise 16 percent between 2010 and 2020. Over the same period, it fell at 11 of the state’s 12 other four-year public campuses.