Best Sites and Apps for Digital Storytelling — from techlearning.com by Diana Restifo
Digital storytelling can help boost communication and presentation skills
Excerpt:
…storytelling is a great way for kids to learn to love reading and writing. But almost any school subject can be considered through a dramatic frame, from history to geography to science. Even math can be taught through narrative (word problems, anyone?). Most importantly, storytelling gives kids the opportunity to be inventive with language, graphics, and design, and to share their creations with others.
The following sites and apps for storytelling range from basic to advanced. Many are designed for educators or include guides for use in education. And while most are paid products, the prices are generally reasonable and nearly every platform offers a free trial or free basic account.
6 best classroom noise meters for teachers — from educatorstechnology.com by Med Kharbach
Excerpt:
One of the effective ways to monitor and reduce noise levels in classrooms is by making noise visible. Enabling students to visualize their noise raises awareness to their sound levels and makes them noise conscious. There are several noise meter tools and apps to use in your classroom to bring down students noise and therefore help in creating optimal learning experiences. Below is a collection of some of the best noise meters for classroom use. They are simple, easy to use, and cost-effective.
Digital age classroom projects — from thetechedvocate.org by Matthew Lynch
Excerpt:
Classroom learning today has left the era of flipping through textbooks trying to be on the same page with the teacher, though not for every class lesson. Educators today are seizing the opportunities of digital devices and media to expand learning opportunities beyond pencil and paper homework. Also, assessment is not just a multiple-choice test.
Consider trying one of these projects:
The Education of Incarcerated Youth with Disabilities Ep.14 — from edcircuit.com
Excerpt:
The School Justice Project (SJP) champions an extremely vulnerable population: incarcerated youth with disabilities. The SJP’s mission is to ensure every learner, in or out of prison facilities, receives the education they were promised and deserve. Their current class action lawsuit against the DC prison system underscores the impact of their efforts. Featured guest, Claire Blumenson, pulls no punches as she forces us to look, and not to look away, in this pivotal moment.
We are educators, parents, siblings, and friends who aren’t satisfied with the quality of the content our students are exposed to. We know they deserve better, and are committed to bringing authentic, engaging, diverse and accessible content to all learners.

Business Leaders Say Computer Science Needs to Be A Core Subject — from edsurge.com by Daniel Mollenkamp
Excerpt:
[On July 12], a collection of more than 500 prominent business, education and nonprofit leaders called on states to update their K-12 curriculum to make computer science a core subject.
In a letter sent to governors from all fifty states, they write, “computer science provides an essential foundation—not only for careers in technology, but for every career in today’s world,” and call upon state leaders to update curriculum to ensure that all students have an opportunity to learn computer science in school.
What is Microsoft Sway and How Can it Be Used to Teach? Tips & Tricks — from techlearning.com by Luke Edwards
Microsoft Sway is a presentation tool that works really well for teaching
Excerpt:
Microsoft Sway is the company’s alternative to PowerPoint as a presentation tool that embraces collaborative working. As such, this is a powerful system for teachers and students to use in the classroom and beyond.
The idea behind Sway is to offer a super simple setup that allows anybody to create presentation slideshows. This makes it good for both younger students and teachers for in-class or online-based presenting.
For a somewhat related item, see:
Exploring some different instructional strategies and discovering how to incorporate them into the classroom process can rekindle a love affair with teaching. Finding the right instructional strategy to fit your classroom can make a world of difference to your students by allowing them to make meaningful connections with what they are learning. Take a look at a few different strategies, and see which one might suit your students this academic year.
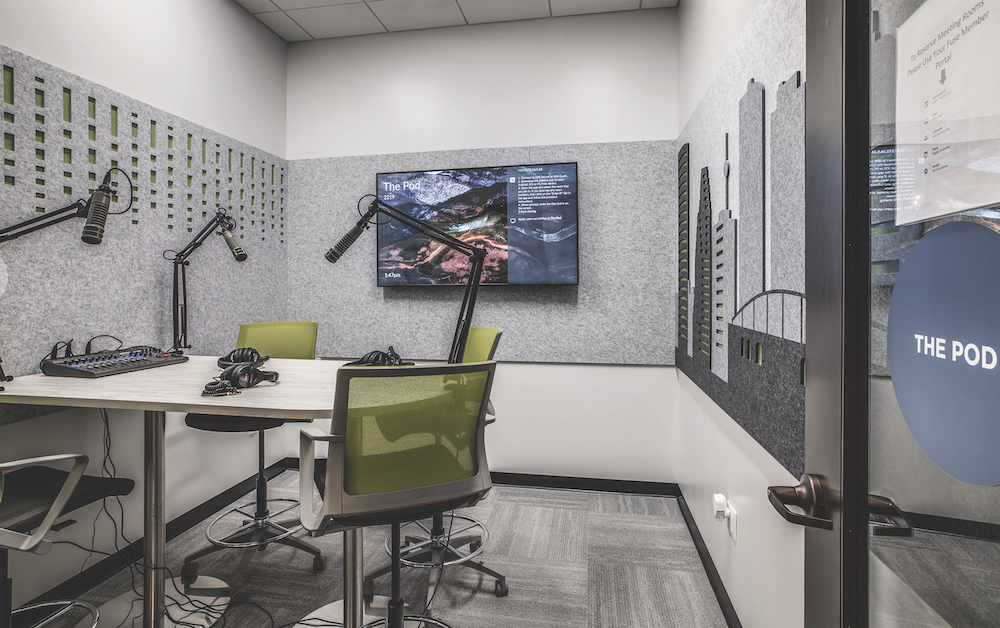
















 Podcasting studio at FUSE Workspace in Houston, TX.
Podcasting studio at FUSE Workspace in Houston, TX.