Technology is increasingly being used to provide legal services, which demands a new breed of innovative lawyer for the 21st century. Law schools are launching specialist LL.M.s in response, giving students computing skills — from llm-guide.com by Seb Murray
Excerpts:
Junior lawyers at Big Law firms have long been expected to work grueling hours on manual and repetitive tasks like reviewing documents and doing due diligence. Increasingly, such work is being undertaken by machines – which can be faster, cheaper and more accurately than humans. This is the world of legal technology – the use of technology to provide legal services.
The top law schools recognize the need to train not just excellent lawyers but tech-savvy ones too, who understand the application of technology and its impact on the legal market. They are creating specialist courses for those who want to be more involved with the technology used to deliver legal advice.
“Technology is changing the way we live, work and interact,” says Alejandro Touriño, co-director of the course. “This new reality demands a new breed of lawyers who can adapt to the emerging paradigm. An innovative lawyer in the 21st century needs not only to be excellent in law, but also in the sector where their clients operate and the technologies they deal with.”
The rapid growth in Legal Tech LL.M. offerings reflects a need in the professional world. Indeed, law firms know they need to become digital businesses in order to attract and retain clients and prospective employees.
From DSC:
In case it’s helpful or interesting, a person interested in a legal career needs to first get a Juris Doctor (J.D.) Degree, then pass the Bar. At that point, if they want to expand their knowledge in a certain area or areas, they can move on to getting an LL.M. Degree if they choose to.
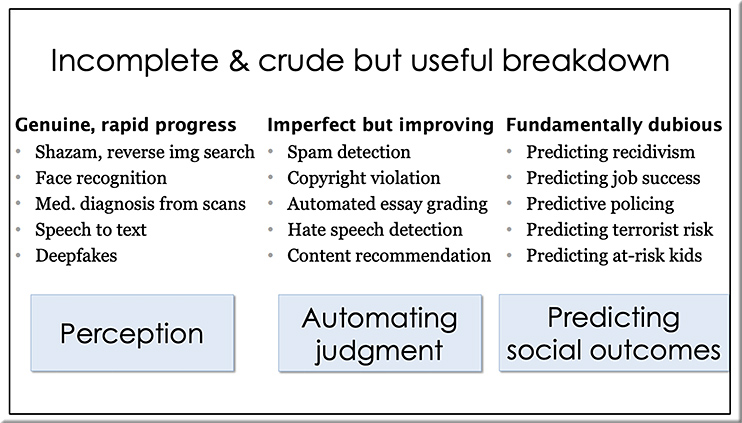
As in the world of higher ed and also in the corporate training area, I have it that the legal field will need to move more towards the use of teams of specialists. There will be several members of the team NOT having law degrees. For example, technologists, programmers, user experience designers, etc. should be teaming up with lawyers more and more these days.