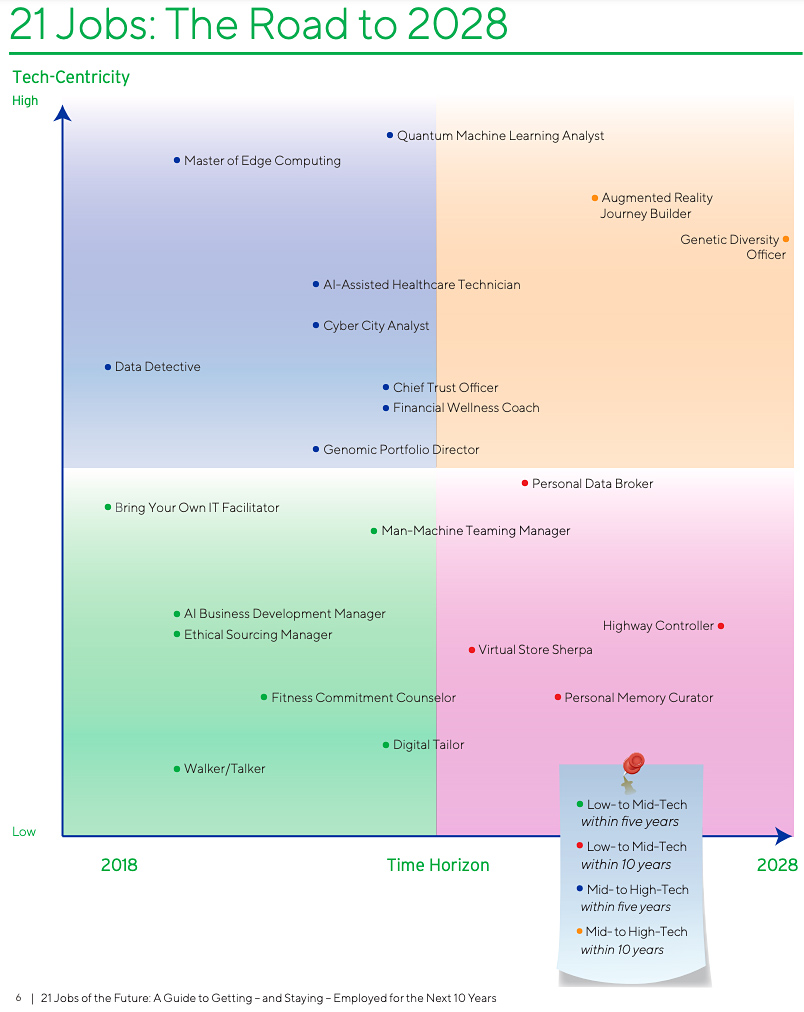
21 jobs of the future: A guide to getting — and staying — employed over the next 10 years — from cognizant.com and the Center for The Future of Work
Excerpt:
WHAT THE NEXT 10 YEARS WILL BRING: NEW JOBS
In this report, we propose 21 new jobs that will emerge over the next 10 years and will become cornerstones of the future of work. In producing this report, we imagined hundreds of jobs that could emerge within the major macroeconomic, political, demographic, societal, cultural, business and technology trends observable today, e.g., growing populations, aging populations, populism, environmentalism, migration, automation, arbitrage, quantum physics, AI, biotechnology, space exploration, cybersecurity, virtual reality.
Among the jobs we considered, some seemed further out on the horizon and are not covered here: carbon farmers, 3-D printing engineers, avatar designers, cryptocurrency arbitrageurs, drone jockeys, human organ developers, teachers of English as a foreign language for robots, robot spa owners, algae farmers, autonomous fleet valets, Snapchat addiction therapists, urban vertical farmers and Hyperloop construction managers. These are jobs that younger generations may do in the further off future.
Also see:
Here are the top 10 jobs of the future — from bigthink.com by Robert Brown
Say hello to your new colleague, the Workplace Environment Architect.
Excerpt:
6. Algorithm Bias Auditor – “All online, all the time” lifestyles for work and leisure accelerated the competitive advantage derived from algorithms by digital firms everywhere. But from Brussels to Washington, given the increasing statutory scrutiny on data, it’s a near certainty that when it comes to how they’re built, verification through audits will help ensure the future workforce is also the fair workforce.