Google Glass wasn’t a failure. It raised crucial concerns. — from wired.com by Rose Eveleth
Excerpts:
So when Google ultimately retired Glass, it was in reaction to an important act of line drawing. It was an admission of defeat not by design, but by culture.
These kinds of skirmishes on the front lines of surveillance might seem inconsequential — but they can not only change the behavior of tech giants like Google, they can also change how we’re protected under the law. Each time we invite another device into our lives, we open up a legal conversation over how that device’s capabilities change our right to privacy. To understand why, we have to get wonky for a bit, but it’s worth it, I promise.
But where many people see Google Glass as a cautionary tale about tech adoption failure, I see a wild success. Not for Google of course, but for the rest of us. Google Glass is a story about human beings setting boundaries and pushing back against surveillance…
IN THE UNITED States, the laws that dictate when you can and cannot record someone have a several layers. But most of these laws were written when smartphones and digital home assistants weren’t even a glimmer in Google’s eye. As a result, they are mostly concerned with issues of government surveillance, not individuals surveilling each other or companies surveilling their customers. Which means that as cameras and microphones creep further into our everyday lives, there are more and more legal gray zones.
From DSC:
We need to be aware of the emerging technologies around us. Just because we can, doesn’t mean we should. People need to be aware of — and involved with — which emerging technologies get rolled out (or not) and/or which features are beneficial to roll out (or not).
One of the things that’s beginning to alarm me these days is how the United States has turned over the keys to the Maserati — i.e., think an expensive, powerful thing — to youth who lack the life experiences to know how to handle such power and, often, the proper respect for such power. Many of these youthful members of our society don’t own the responsibility for the positive and negative influences and impacts that such powerful technologies can have.
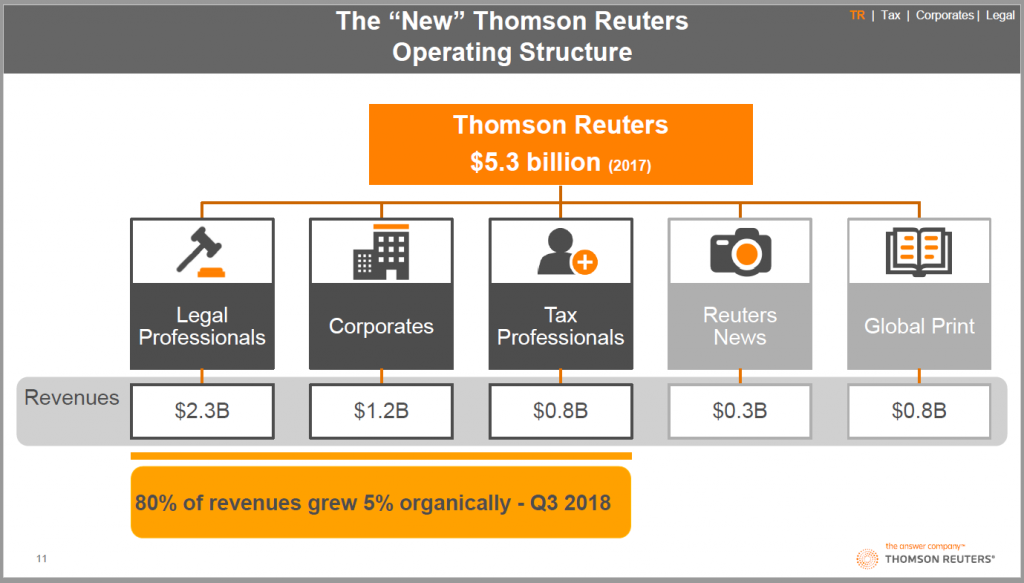
If you owned the car below, would you turn the keys of this ~$137,000+ car over to your 16-25 year old? Yet that’s what America has been doing for years. And, in some areas, we’re now paying the price.

The corporate world continues to discard the hard-earned experience that age brings…as they shove older people out of the workforce. (I hesitate to use the word wisdom…but in some cases, that’s also relevant/involved here.) Then we, as a society, sit back and wonder how did we get to this place?
Even technologists and programmers in their 20’s and 30’s are beginning to step back and ask…WHY did we develop this application or that feature? Was it — is it — good for society? Is it beneficial? Or should it be tabled or revised into something else?
Below is but one example — though I don’t mean to pick on Microsoft, as they likely have more older workers than the Facebooks, Googles, or Amazons of the world. I fully realize that all of these companies have some older employees. But the youth-oriented culture in American today has almost become an obsession — and not just in the tech world. Turn on the TV, check out the new releases on Netflix, go see a movie in a theater, listen to the radio, cast but a glance at the magazines in the check out lines, etc. and you’ll instantly know what I mean.
In the workplace, there appears to be a bias against older employees as being less innovative or tech-savvy — such a perspective is often completely incorrect. Go check out LinkedIn for items re: age discrimination…it’s a very real thing. But many of us over the age of 30 know this to be true if we’ve lost a job in the last decade or two and have tried to get a job that involves technology.
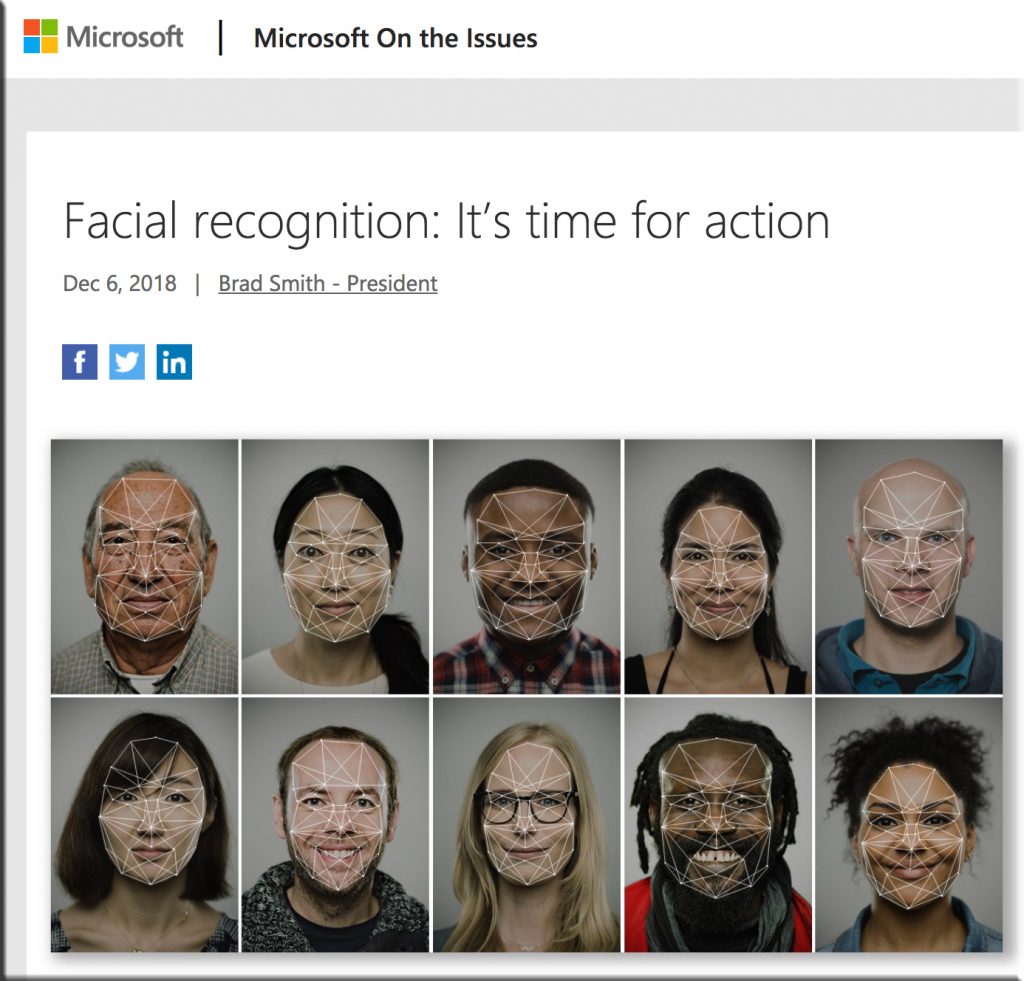
Microsoft argues facial-recognition tech could violate your rights — from finance.yahoo.com by Rob Pegoraro
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
On Thursday, the American Civil Liberties Union provided a good reason for us to think carefully about the evolution of facial-recognition technology. In a study, the group used Amazon’s (AMZN) Rekognition service to compare portraits of members of Congress to 25,000 arrest mugshots. The result: 28 members were mistakenly matched with 28 suspects.
The ACLU isn’t the only group raising the alarm about the technology. Earlier this month, Microsoft (MSFT) president Brad Smith posted an unusual plea on the company’s blog asking that the development of facial-recognition systems not be left up to tech companies.
Saying that the tech “raises issues that go to the heart of fundamental human rights protections like privacy and freedom of expression,” Smith called for “a government initiative to regulate the proper use of facial recognition technology, informed first by a bipartisan and expert commission.”
But we may not get new laws anytime soon.

Just because we can…

Addendum on 12/27/18: — also related/see:
‘We’ve hit an inflection point’: Big Tech failed big-time in 2018 — from finance.yahoo.com by JP Mangalindan
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
2018 will be remembered as the year the public’s big soft-hearted love affair with Big Tech came to a screeching halt.
For years, lawmakers and the public let massive companies like Facebook, Google, and Amazon run largely unchecked. Billions of people handed them their data — photos, locations, and other status-rich updates — with little scrutiny or question. Then came revelations around several high-profile data breaches from Facebook: a back-to-back series of rude awakenings that taught casual web-surfing, smartphone-toting citizens that uploading their data into the digital ether could have consequences. Google reignited the conversation around sexual harassment, spurring thousands of employees to walk out, while Facebook reminded some corners of the U.S. that racial bias, even in supposedly egalitarian Silicon Valley, remained alive and well. And Amazon courted well over 200 U.S. cities in its gaudy and protracted search for a second headquarters.
“I think 2018 was the year that people really called tech companies on the carpet about the way that they’ve been behaving conducting their business,” explained Susan Etlinger, an analyst at the San Francisco-based Altimeter Group. “We’ve hit an inflection point where people no longer feel comfortable with the ways businesses are conducting themselves. At the same time, we’re also at a point, historically, where there’s just so much more willingness to call out businesses and institutions on bigotry, racism, sexism and other kinds of bias.”
The public’s love affair with Facebook hit its first major rough patch in 2016 when Russian trolls attempted to meddle with the 2016 U.S. presidential election using the social media platform. But it was the Cambridge Analytica controversy that may go down in internet history as the start of a series of back-to-back, bruising controversies for the social network, which for years, served as the Silicon Valley poster child of the nouveau American Dream.