The 11 coolest announcements Google made at its biggest product event of the year — from businessinsider.com by Dave Smith
Excerpt:
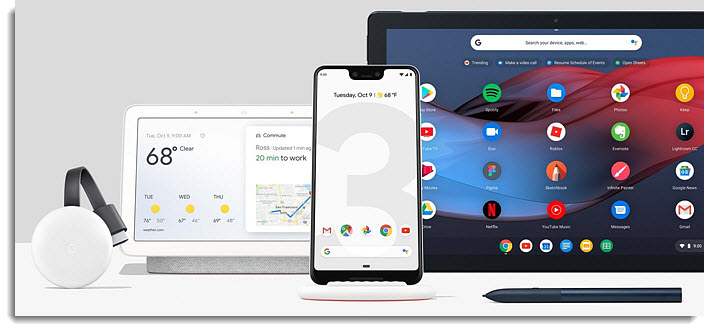
On Tuesday (10/9), Google invited journalists to New York City to debut its newest smartphone, the Pixel 3, among several other hardware goodies.
Google made dozens of announcements in its 75-minute event, but a handful of “wow” moments stole the show.
Here are the 11 coolest announcements Google made at its big hardware event…
Google’s Pixel 3 event in 6 minutes — from businessinsider.com
Google unveiled its new Home Hub but it might be ‘late to the market’ — from barrons.com by Emily Bary
Excerpt:
Alphabet ’s Google has sold millions of voice-enabled speakers, but it inched toward the future at a Tuesday launch event when it introduced the Home Hub smart screen.
Google isn’t the first company to roll out a screen-enabled home device with voice-assistant technology— Amazon.com released its Echo Show in July 2017. Meanwhile, Lenovo has gotten good reviews for its Smart Display, and Facebook introduced the Portal on Monday.
For the most part, though, consumers have stuck to voice-only devices, and it will be up to Google and its rivals to convince them that an added screen is worth paying for. They’ll also have to reassure consumers that they can trust big tech to maintain their privacy, an admittedly harder task these days after recent security issues at Google and Facebook.
Amazon was right to realize early on that consumers aren’t always comfortable buying items they can’t even see pictures of, and that it’s hard to remember directions you’ve heard but not seen.
Google has announced its first smart speaker with a screen — from businessinsider.com by Brandt Ranj
- Google has announced the Google Hub, its first smart home speaker with a screen. It’s available for pre-order at Best Buy, Target, and Walmart for $149. The Hub will be released on October 22.
- The Hub has a 7″ touchscreen and sits on a base with a built-in speaker and microphones, which you can use to play music, watch videos, get directions, and control smart home accessories with your voice.
- Its biggest advantage is its ability to hook into Google’s first-party services, like YouTube and Google Maps, which none of its competitors can use.
- If you’re an Android or Chromecast user, trust Google more than Amazon, or want a smaller smart home speaker with a screen, the Google Hub is now your best bet.
Google is shutting down Google+ for consumers following security lapse — from theverge.com by Ashley Carman
Excerpt:
Google is going to shut down the consumer version of Google+ over the next 10 months, the company writes in a blog post today. The decision follows the revelation of a previously undisclosed security flaw that exposed users’ profile data that was remedied in March 2018.
Google shutters Google+ after users’ personal data exposed — from cbsnews.com
Google+ is shutting down, and the site’s few loyal users are mourning – from cnbc.com by Jillian D’Onfro
- Even though Google had diverted resources away from Google+, there’s a small loyal base of users devastated to see it go away.
- One fan said the company is using its recently revealed security breach as an excuse to shutter the site.
- Google said it will be closing Google+ in the coming months.