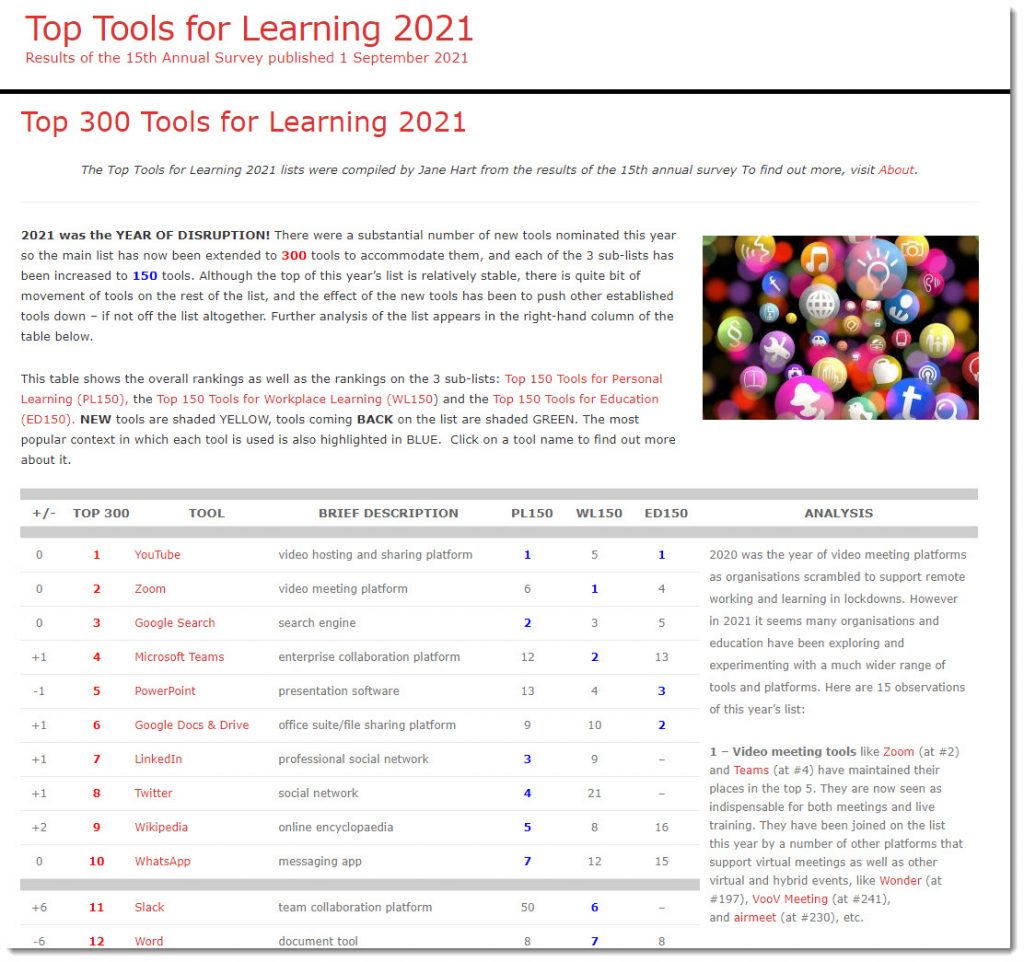
Top 300 Tools for Learning 2021 — from toptools4learning.com by Jane Hart
Excerpt:
2021 was the YEAR OF DISRUPTION! There were a substantial number of new tools nominated this year so the main list has now been extended to 300 tools to accommodate them, and each of the 3 sub-lists has been increased to 150 tools. Although the top of this year’s list is relatively stable, there is quite bit of movement of tools on the rest of the list, and the effect of the new tools has been to push other established tools down – if not off the list altogether. Further analysis of the list appears in the right-hand column of the table below.
This table shows the overall rankings as well as the rankings on the 3 sub-lists: Top 150 Tools for Personal Learning (PL150), the Top 150 Tools for Workplace Learning (WL150) and the Top 150 Tools for Education (ED150). NEW tools are shaded YELLOW, tools coming BACK on the list are shaded GREEN. The most popular context in which each tool is used is also highlighted in BLUE. Click on a tool name to find out more about it.