From DSC:
It seems to me that we are right on the precipice of major changes — throughout the globe — that are being introduced by the growing use and presence of automation, robotics, and artificial intelligence/machine learning/deep learning, as well as other emerging technologies. But it’s not just the existence of these technologies, but it’s also that the pace of adoption of these technologies continues to increase.
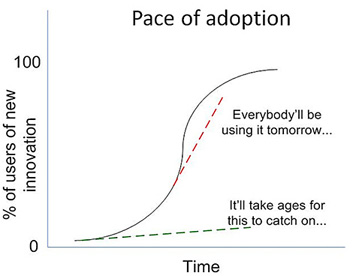
These things made me wonder….what are the ramifications of the graphs below — and this new trajectory/pace of change that we’re on — for how we accredit new programs within higher education?
For me, it speaks to the need for those of us who are working within higher education to be more responsive, and we need to increase our efforts to provide more lifelong learning opportunities. People are going to need to reinvent themselves over and over again. In order for higher education to be of the utmost service to people, the time that it takes to accredit a program must be greatly reduced in cost and in time.

Somewhat relevant addendums:
A quote from “Response: What Teaching in the Year 2047 Might Look Like“
To end the metaphor, what I am simply trying to say is that schools cannot afford to evolve at ¼ of the pace the world is around it and not face the possibility of becoming dangerously irrelevant. So, to answer the question – do I think the classrooms of 2040 look like the classrooms of today? Yes, I think they look more like them than they do not. Unfortunately, in my opinion, that is not the way to best serve our kids in our ever-changing world. Let me be clear, great teaching and instruction has not fundamentally changed in the past 2000 years and will not in the next 30. The context of learning and doing our best to meet the needs of the society we are preparing kids for is how and why schools must be revolutionized, not simply evolve at their own pace.
An excerpt from “The global forces inspiring a new narrative of progress” (from mckinsey.com by Ezra Greenberg, Martin Hirt, and Sven Smit; emphasis DSC):
The next three tensions highlight accelerating industry disruption. Digitization, machine learning, and the life sciences are advancing and combining with one another to redefine what companies do and where industry boundaries lie. We’re not just being invaded by a few technologies, in other words, but rather are experiencing a combinatorial technology explosion. Customers are reaping some of the rewards, and our notions of value delivery are changing. In the words of Alibaba’s Jack Ma, B2C is becoming “C2B,” as customers enjoy “free” goods and services, personalization, and variety. And the terms of competition are changing: as interconnected networks of partners, platforms, customers, and suppliers become more important, we are experiencing a business ecosystem revolution.
38% of American Jobs Could be Replaced by Robots, According to PwC Report — from bigthink.com by David Ryan Polgar
Excerpt:
Nearly 4 out of 10 American jobs may be replaced through automation by the early 2030s, according to a new report by Price Waterhouse Cooper (PwC). In the report, the United States was viewed as the country most likely to lost jobs through automation–ahead of the UK, Germany, and Japan. This is probably not what the current administration had in mind with an “America First” policy.









