Gen Z is about to take over higher education—here’s what to expect — from ecampusnews.com by Lisa Malat
Survey finds digital natives “Gen Z” set to reshape higher ed landscape with focus on careers, dependence on technology.
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
Educators take note: it’s time to make way for Generation Z (Gen Z).
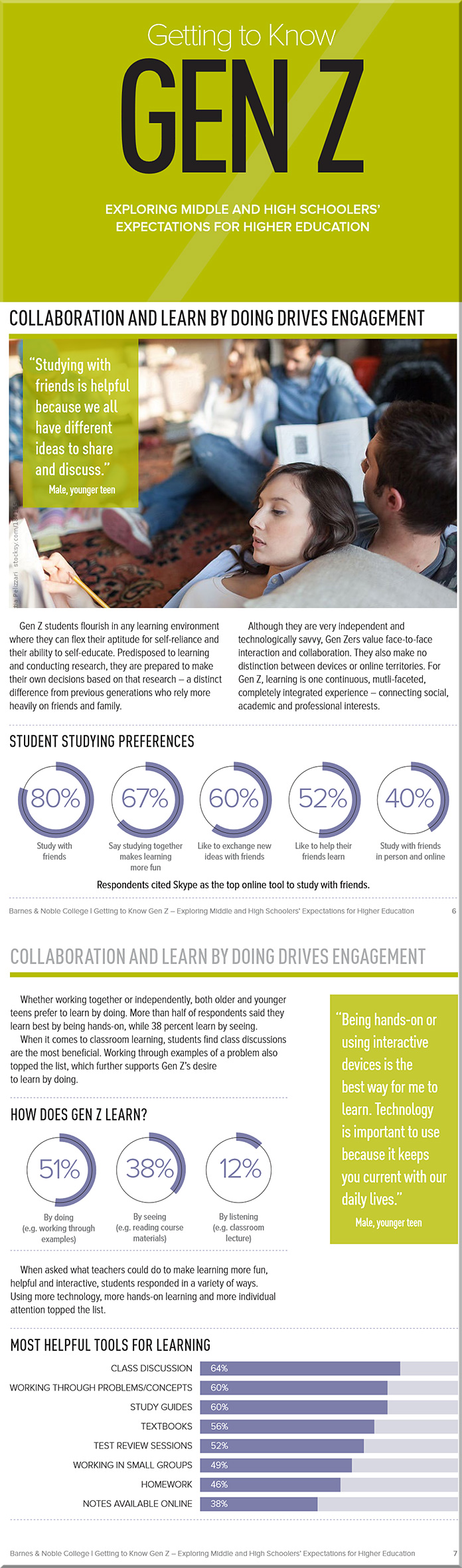
In a recent study by Barnes & Noble College, 1,300 middle-school and high school students ages 13-18 from 49 different states shared their attitudes, preferences and expectations regarding their educational and learning experiences. The findings from the study are clear: Gen Z is significantly different than previous generations, and these students will bring both challenges and opportunities for the future of higher education.
…
With Gen Z being a generation of “digital natives,” it stands to reason that the future of educational technology is now. Technology is embraced almost universally by Gen Z. In fact, the students surveyed shared that they are apt to regularly use five different computer tools for their social and educational purposes: laptops, desktops, tablets, smartphones and video game consoles.
Unlike Millennials, who have broadly adopted technology, Gen Z has adopted a technology-centric lifestyle. They define themselves in online, digital terms. Gen Z doesn’t distinguish between devices or online territories. It is one continuous, multi-faceted, completely integrated experience – connecting social, academic and professional interests.
…
Gen Z also has different learning style preferences from past generations. While they are very into DIYL (do-it-yourself-learning), these students also embrace peer-to-peer learning, with 80 percent reporting that they study with their friends and classmates. Fifty percent said they enjoy the element of leadership it presents, and 60 percent reported that it gives them the perfect way to exchange ideas and consider new perspectives.
From DSC:
The article/report above prompted me to reflect…
Many throughout higher education are responding to change. But many are not. We aren’t nearly as nimble as we need to be.
I hope that the faculty, staff, boards, administrations, and the heavy-hitting donors at colleges and universities throughout the U.S. appreciate how important it is to be aware of — and respond to — changes within the K-12 world, changes in today’s students, changes within the higher ed landscape, and to changes within the corporate/business world.
We operate in a continuum.
With all of those changes, maintaining the status quo seems to be a dangerous experiment to me. We are not in control. Rather, we all need to adapt and to respond.
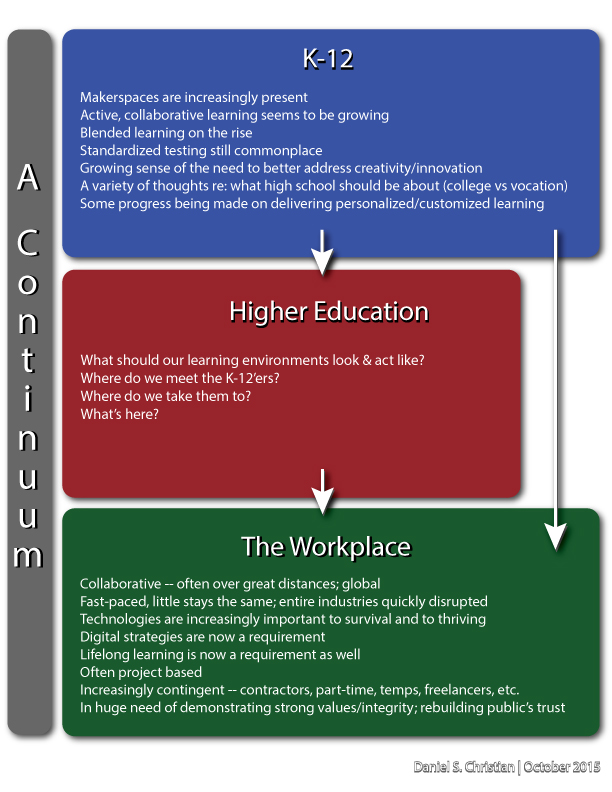
Along these lines, maintaining the status quo shows a blatant disregard of our customers’ preferences — an unwise strategy to take. (And for those of you who don’t like the word customer here, bear with me…because in my mind, any person who pays anywhere near the price of a house to obtain their education has earned the right to be called a customer. Today’s students are paying a heck of a lot more than we did.)
Also, maintaining the status quo seems like a dangerous strategy when we’re talking about recruitment and retention. Remember, we are talking about depending upon the decisions of 18 year olds here.
So as I:
- Read the above article and the report that it refers to
- Consider the higher ed landscape that continues to encounter new alternatives
- Observe that different pathways that are cropping up all the time
- See that the federal government is moving towards funding such alternative methods
…I am forced to ask myself, “Given all of this, will maintaining the status quo suffice? Really?“
This report should encourage us to:
- Seek to do a better job of pulse checking the K-12 world and the students’ learning preferences coming out of that world — and to develop our responses to those changing preferences.
- Pursue more instances of blended/hybrid learning and active learning-based classrooms
- Provide a variety of delivery mechanisms to meet our students’ needs — including a solid line up of online-based courses and programs. Students are often having to work in order to get through college, and they need flexible solutions.
- Better address our physical learning spaces, which should offer strong/secure wireless networks and means of quickly collaborating via BYOD-based devices.
- Continue to invest in selecting and investigating how best to use a variety of educationally-related technologies (something which, in my mind, invites the use of teams of specialists).
(I could, and probably should, think bigger here, but I’ll stop at these reflections.)
I’ll leave you with the following graphic, relaying that often times members of Gen Z tend to prefer active learning-based classrooms: