How AI could help solve some of society’s toughest problems — from technologyreview.com by Charlotte Jee
Machine learning and game theory help Carnegie Mellon assistant professor Fei Fang predict attacks and protect people.
Excerpt:
Fei Fang has saved lives. But she isn’t a lifeguard, medical doctor, or superhero. She’s an assistant professor at Carnegie Mellon University, specializing in artificial intelligence for societal challenges.
At MIT Technology Review’s EmTech conference on Wednesday, Fang outlined recent work across academia that applies AI to protect critical national infrastructure, reduce homelessness, and even prevent suicides.
How AI can be a force for good — from science.sciencemag.org by Mariarosaria Taddeo & Luciano Floridi
Excerpts:
Invisibility and Influence
AI supports services, platforms, and devices that are ubiquitous and used on a daily basis. In 2017, the International Federation of Robotics suggested that by 2020, more than 1.7 million new AI-powered robots will be installed in factories worldwide. In the same year, the company Juniper Networks issued a report estimating that, by 2022, 55% of households worldwide will have a voice assistant, like Amazon Alexa.
As it matures and disseminates, AI blends into our lives, experiences, and environments and becomes an invisible facilitator that mediates our interactions in a convenient, barely noticeable way. While creating new opportunities, this invisible integration of AI into our environments poses further ethical issues. Some are domain-dependent. For example, trust and transparency are crucial when embedding AI solutions in homes, schools, or hospitals, whereas equality, fairness, and the protection of creativity and rights of employees are essential in the integration of AI in the workplace. But the integration of AI also poses another fundamental risk: the erosion of human self-determination due to the invisibility and influencing power of AI.
…
To deal with the risks posed by AI, it is imperative to identify the right set of fundamental ethical principles to inform the design, regulation, and use of AI and leverage it to benefit as well as respect individuals and societies. It is not an easy task, as ethical principles may vary depending on cultural contexts and the domain of analysis. This is a problem that the IEEE Global Initiative on Ethics of Autonomous and Intelligent Systems tackles with the aim of advancing public debate on the values and principles that should underpin ethical uses of AI.
Who’s to blame when a machine botches your surgery? — from qz.com by Robert Hart
Excerpt:
That’s all great, but even if an AI is amazing, it will still fail sometimes. When the mistake is caused by a machine or an algorithm instead of a human, who is to blame?
This is not an abstract discussion. Defining both ethical and legal responsibility in the world of medical care is vital for building patients’ trust in the profession and its standards. It’s also essential in determining how to compensate individuals who fall victim to medical errors, and ensuring high-quality care. “Liability is supposed to discourage people from doing things they shouldn’t do,” says Michael Froomkin, a law professor at the University of Miami.
Google Cloud’s new AI chief is on a task force for AI military uses and believes we could monitor ‘pretty much the whole world’ with drones — from businessinsider.in by Greg Sandoval
Excerpt:
“We could afford if we wanted to, and if we needed, to be surveilling pretty much the whole word with autonomous drones of various kinds,” Moore said. “I’m not saying we’d want to do that, but there’s not a technology gap there where I think it’s actually too difficult to do. This is now practical.”
…
Google’s decision to hire Moore was greeted with displeasure by at least one former Googler who objected to Project Maven.
“It’s worrisome to note after the widespread internal dissent against Maven that Google would hire Andrew Moore,” said one former Google employee. “Googlers want less alignment with the military-industrial complex, not more. This hire is like a punch in the face to the over 4,000 Googlers who signed the Cancel Maven letter.”
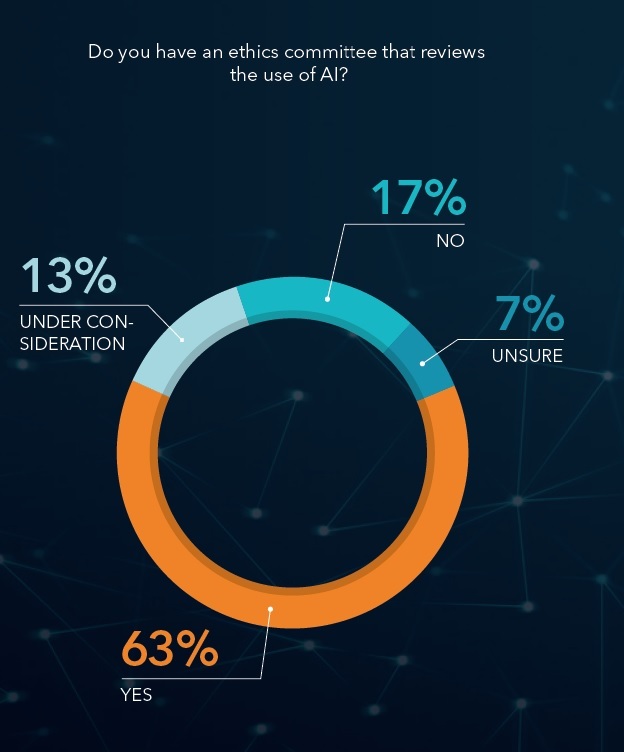
Organizations Are Gearing Up for More Ethical and Responsible Use of Artificial Intelligence, Finds Study — from businesswire.com
Ninety-two percent of AI leaders train their technologists in ethics; 74 percent evaluate AI outcomes weekly, says report from SAS, Accenture Applied Intelligence, Intel, and Forbes Insights
Excerpt:
AI oversight is not optional
Despite popular messages suggesting AI operates independently of human intervention, the research shows that AI leaders recognize that oversight is not optional for these technologies. Nearly three-quarters (74 percent) of AI leaders reported careful oversight with at least weekly review or evaluation of outcomes (less successful AI adopters: 33 percent). Additionally, 43 percent of AI leaders shared that their organization has a process for augmenting or overriding results deemed questionable during review (less successful AI adopters: 28 percent).
Do robots have rights? Here’s what 10 people and 1 robot have to say — from createdigital.org.au
When it comes to the future of technology, nothing is straightforward, and that includes the array of ethical issues that engineers encounter through their work with robots and AI.