18 striking AI Trends to watch in 2018 – Part 1 as well as 18 striking AI Trends to watch in 2018 – Part 2 — from datahub.packtpub.com by Sugandha Lahoti
Excerpt:
Artificial Intelligence is the talk of the town. It has evolved past merely being a buzzword in 2016, to be used in a more practical manner in 2017. As 2018 rolls out, we will gradually notice AI transitioning into a necessity. We have prepared a detailed report, on what we can expect from AI in the upcoming year. So sit back, relax, and enjoy the ride through the future. (Don’t forget to wear your VR headgear! )
Here are 18 things that will happen in 2018 that are either AI driven or driving AI:
- Artificial General Intelligence may gain major traction in research.
- We will turn to AI enabled solution to solve mission-critical problems.
- Machine Learning adoption in business will see rapid growth.
- Safety, ethics, and transparency will become an integral part of AI application design conversations.
- Mainstream adoption of AI on mobile devices
- Major research on data efficient learning methods
- AI personal assistants will continue to get smarter
- Race to conquer the AI optimized hardware market will heat up further
- We will see closer AI integration into our everyday lives.
- The cryptocurrency hype will normalize and pave way for AI-powered Blockchain applications.
- Advancements in AI and Quantum Computing will share a symbiotic relationship18 striking AI Trends to watch in 2018 – Part 1
- Deep learning will continue to play a significant role in AI development progress.
- AI will be on both sides of the cybersecurity challenge.
- Augmented reality content will be brought to smartphones.
- Reinforcement learning will be applied to a large number of real-world situations.
- Robotics development will be powered by Deep Reinforcement learning and Meta-learning
- Rise in immersive media experiences enabled by AI.
- A large number of organizations will use Digital Twin.
Inside AI — from inside.com
The year 2017 has been full of interesting news about Artificial Intelligence, so to close out the year, we’re doing two special retrospective issues covering the highlights.
Excerpt:
A Reality Check For IBM’s A.I. Ambitions. MIT Tech Review.
This is a must read piece about the failures, and continued promise, of Watson. Some of the press about Watson has made IBM appear behind some of the main tech leaders, but, keep in mind that Google, Amazon, Facebook, and others don’t do the kinds of customer facing projects IBM is doing with Watson. When you look at how the tech giants are positioned, I think IBM has been vastly underestimated, given that they have the one thing few others do – large scale enterprise A.I. projects. Whether it all works today, or not, doesn’t matter. The experience and expertise they are building is a competitive advantage in a market that is very young where no other companies are doing these types of projects that will soon enough be mainstream.
The Business of Artificial Intelligence. Harvard Business Review.
This cover story for the latest edition of HBR explains why artificial intelligence is the most powerful general purpose technology to come around in a long time. It also looks into some of the key ways to think about applying A.I. at work, and how to expect the next phase of this technology to play out.
The Robot Revolution Is Coming. Just Be Patient. Bloomberg.
We keep hearing that robots and A.I. are about to make us super productive. But when? Sooner than we think, according to this.
An excerpt from A2Apple.com:
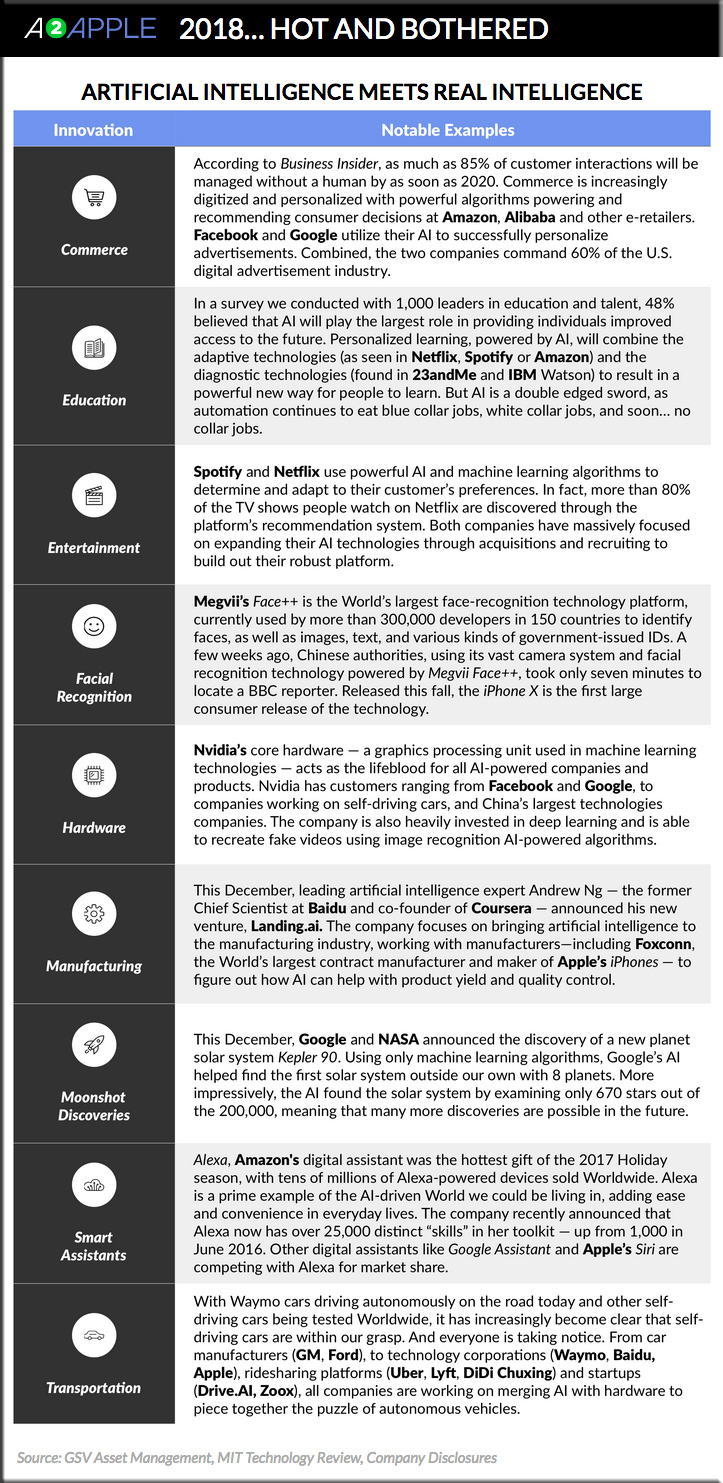
Alexa Wants You to Talk to Your Ads — from wired.com by Ricki Harris
Excerpt:
There are few electronic devices with which you cannot order a Domino’s pizza. When the craving hits, you can place an order via Twitter, Slack, Facebook Messenger, SMS, your tablet, your smartwatch, your smart TV, and even your app-enabled Ford. This year, the pizza monger added another ordering tool: If your home is one of the 20 million with a voice assistant, you can place a regular order through Alexa or Google Home. Just ask for a large extra-cheese within earshot, and voila—your pizza is in the works.
Amazon’s Alexa offers more than 25,000 skills—the set of actions that serve as applications for voice technology. Yet Domino’s is one of a relatively small number of brands that has seized the opportunity to enter your home by creating a skill of its own. Now that Amazon Echoes and Google Homes are in kitchens and living rooms across the country, they open a window into user behavior that marketers previously only dreamt of. But brands’ efforts to engage consumers directly via voice have been scattershot. The list of those that have tried is sparse: some banks; a couple of fast food chains; a few beauty companies; retailers here and there. Building a marketing plan for Alexa has been a risky venture. That’s because, when it comes to our virtual assistants, no one knows what the *&^& is going on.
But if 2017 was the year that Alexa hit the mainstream, 2018 will be the year that advertisers begin to take her seriously by investing time and money in figuring out how to make use of her.
8 emerging AI jobs for IT pros — from enterprisersproject.com by Kevin Casey
What IT jobs will be hot in the age of AI? Take a sneak peek at roles likely to be in demand
Excerpt:
If you’re watching the impact of artificial intelligence on the IT organization, your interest probably starts with your own job. Can robots do what you do? But more importantly, you want to skate where the puck is headed. What emerging IT roles will AI create? We talked to AI and IT career experts to get a look at some emerging roles that will be valuable in the age of AI.
Getting Intelligent About Artificial Intelligence: 6 Ways Executives Can Start — from forbes.comby Davia Temin
Excerpt:
This past June, Fortune Magazine asked all the CEOs of the Fortune 500 what they believed the biggest challenge facing their companies was. Their biggest concern for 2017: “The rapid pace of technological change” said 73% of those polled, up from 64% in 2016. Cyber security came in only a far second, at 61%, even after all the mega hacks of the past year.
So, what does “technological change” entail? For almost all Fortune 500 CEOs, it means, in part, artificial intelligence. And, as we wrote in our piece yesterday on Forbes.com, “Forget The Hype: What Every Business Leader Needs To Know About Artificial Intelligence Now,” AI is on the lips of almost every global CEO and Board of Directors.
But apart from the Big 8 technology companies – Google, Facebook, Microsoft, Amazon, IBM, Baidu, Tencent, and Alibaba – business leaders, especially of earlier generations, may feel they don’t know enough about AI to make informed decisions.
Artificial intelligence is helping astronomers discover new planets — from wired.co.uk
AI could help us discover planet nine, dark matter and more gravitational waves
Excerpt:
For the first time, artificial intelligence has been used to discover two new exoplanets. One of the discoveries, made by Nasa’s Kepler mission, brings the Kepler-90 solar system to a total of 8 planets – the first solar system found with the same number as our own.













![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)