Being a new teacher is hard. Having a good mentor can help — from npr.org by Cory Turner
Excerpt:
[Besides this article’s focus on mentorship]
In March, I reported a pair of stories from Jackson, Miss., where the school district is paying for unlicensed classroom aides to go back to school and get their master’s degrees.
In April, I told the story of a remarkable idea: A new high school in San Antonio dedicated entirely to training high-schoolers in the art and science of good teaching.
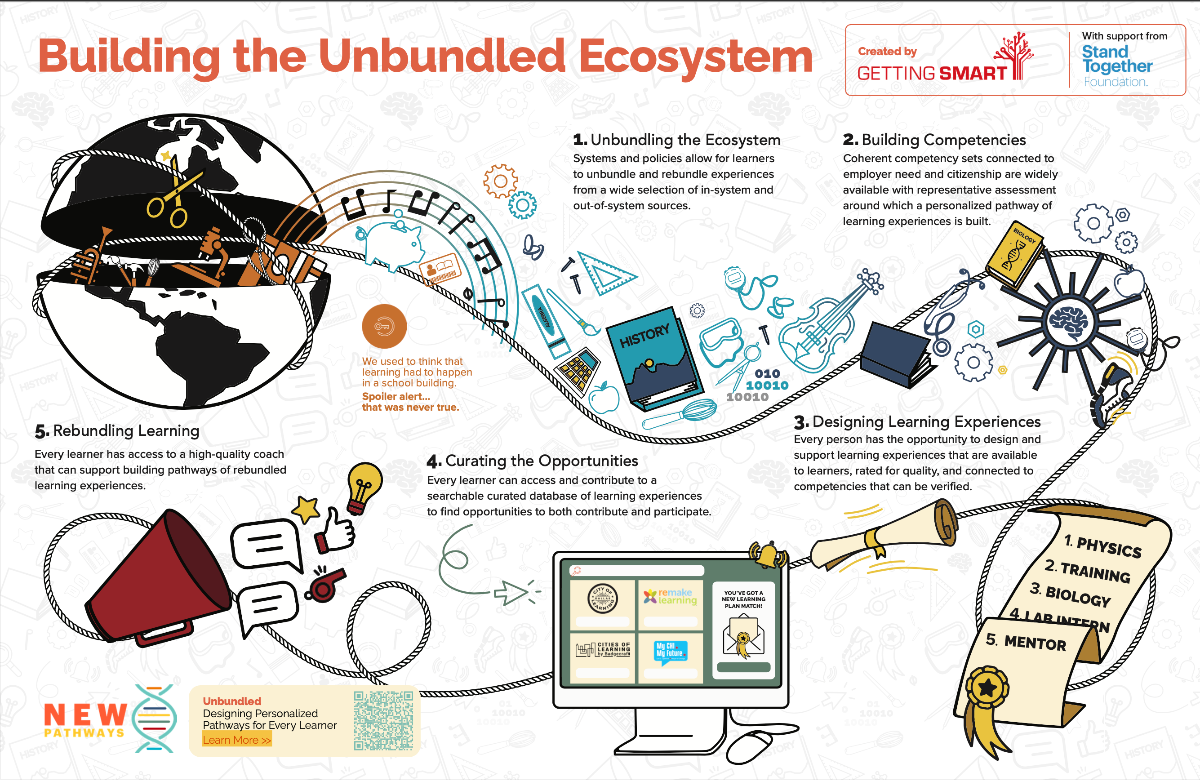
From DSC:
I would add a few more items:
- Significantly reduce the impact of legislators on K-12. If they do vote on something that would impact schools, each legislator that votes on such legislation must first spend at least ___ week(s) observing in some of the schools that would be impacted before even starting to draft legislation and/or debate on the topic(s).
- Instead, turn over more control and power to the students, teachers, K12 administrators, parents, and school boards.
- Provide more choice, more control as each student can handle it.
- Stop the one-size fits all system. Instead use AI-based systems to provide more personalized learning.
- Develop more hybrid programs — but this time I’m talking mixing what we’ve known as public education with homeschooling and smaller learning pods. Let’s expand what’s included when we discuss “learning spaces.”
- Strive for a love of learning — vs. competition and developing gameplayers
- Support makerspaces, entrepreneurship, and experiments
- Speaking of experiments, I would recommend developing more bold experiments outside of the current systems.
Along the lines of potential solutions/visions, see:
Why ‘System Transformation’ Is Likely A Pipe Dream — from michaelbhorn.substack.com by Michael Horn
But I’m for System Replacement
Excerpt:
Foremost among them is this: Despite all the fancy models and white papers around what are all the levers to pull in order to transform a system, system transformation almost never happens by changing the fundamental tenets of the system itself. Instead, it comes from replacing the system with a brand-new system.
To start to understand why, consider the complicated system in which public schools find themselves. As Thomas Arnett explained, they are one part of a vast value network of federal, state, and local regulators, voters and taxpayers, parents and students, teachers, administrators, unions, curriculum providers, school vendors, public infrastructure, higher education institutions, and more.
New ideas, programs, or entities that don’t fit into these processes, priorities, and cost structures are simply not plug-compatible into that value network. They consequently get rejected, tossed to the fringe, or altered to meet the needs of the existing actors in the value network.