C-Suite TV debuts, offers advice for the boardroom — from streamingmedia.com by Troy Dreier
Business leaders now have an on-demand video network to call their own, thanks to one Bloomberg host’s online venture.
Excerpt:
Bringing some business acumen to the world of online video, C-Suite TV is launching today. Created by Bloomberg TV host and author Jeffrey Hayzlett, the on-demand video network offers interviews with and shows about business execs. It promises inside information on business trends and the discussions taking place in the biggest boardrooms.
The Future of TV is here for the C-Suite — from hayzlett.com by Jeffrey Hayzlett
Excerpt:
Rather than wait for networks or try and gain traction through the thousands of cat videos, we went out and built our own network.
See also:
- Mind your own business
From the About page:
C-Suite TV is a web-based digital on-demand business channel featuring interviews and shows with business executives, thought leaders, authors and celebrities providing news and information for business leaders. C-Suite TV is your go-to resource to find out the inside track on trends and discussions taking place in businesses today. This online channel will be home to such shows as C-Suite with Jeffrey Hayzlett, MYOB – Mind Your Own Business and Bestseller TV with more shows to come.
From DSC:
The above items took me back to the concept of Learning from the Living [Class] Room.
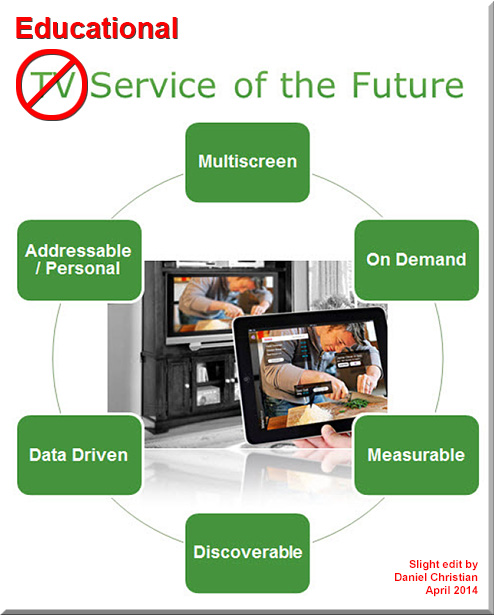
Many of the following bullet points are already happening — but what I’m trying to influence/suggest is to bring all of them together in a powerful, global, 24 x 7 x 365, learning ecosystem:
- When our “TVs” become more interactive…
- When our mobile devices act as second screens and when second screen-based apps are numerous…
- When discussion boards, forums, social media, assignments, assessments, and videoconferencing capabilities are embedded into our Smart/Connected TVs and are also available via our mobile devices…
- When education is available 24 x 7 x 365…
- When even the C-Suite taps into such platforms…
- When education and entertainment are co-mingled…
- When team-based educational content creation and delivery are mainstream…
- When self-selecting Communities of Practice thrive online…
- When Learning Hubs combine the best of both worlds (online and face-to-face)…
- When Artificial Intelligence, powerful cognitive computing capabilities (i.e., IBM’s Watson), and robust reporting mechanisms are integrated into the backends…
- When lifelong learners have their own cloud-based profiles…
- When learners can use their “TVs” to tap into interactive, multimedia-based streams of content of their choice…
- When recommendation engines are offered not just at Netflix but also at educationally-oriented sites…
- When online tutoring and intelligent tutoring really take off…
…then I’d say we’ll have a powerful, engaging, responsive, global education platform.









![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)