From DSC:
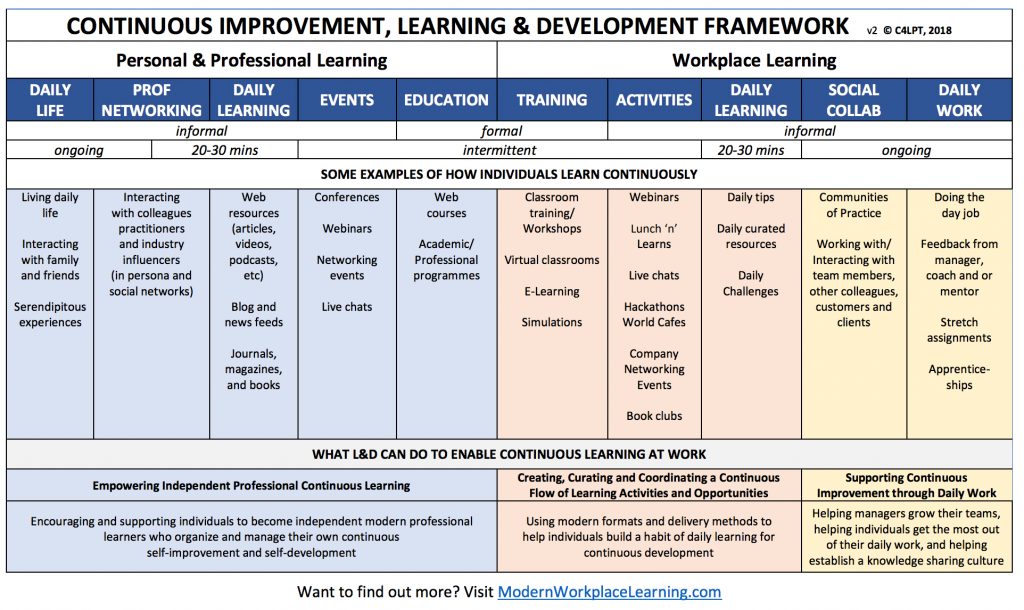
I found the following graphic out at a posting entitled, Continuous Learning & Development; more than just continuous training (from modernworkplacelearning.com/magazine). I thought it was an excellent example of a learning ecosystem!




From DSC:
I found the following graphic out at a posting entitled, Continuous Learning & Development; more than just continuous training (from modernworkplacelearning.com/magazine). I thought it was an excellent example of a learning ecosystem!
The World Will Be Painted With Data — from forbes.com by Charlie Fink
Excerpt:
The world is about to be painted with data. Every place. Every person. Every thing. In the near term this invisible digital layer will be revealed by the camera in your phone, but in the long term it will be incorporated into a wearable device, likely a head-mounted display (HMD) integrating phone, audio, and AI assistants. Users will control the system with a combination of voice, gesture and ring controller. Workers in factories use monocular displays to do this now, but it’s going to be quite some time before this benefits consumers. While this coming augmentation of man represents an evolutionary turning point, it’s adoption will resemble that of the personal computer, which took at least fifteen years. Mobile AR, on the other hand, is here now, and in a billion Android and Apple smartphones, which are about to get a lot better. Thanks to AR, we can start building the world’s digital layer for the smartphone, right now, without waiting for HMDs to unlock the benefits of an AR-enabled world.
12 hot augmented reality ideas for your business — from information-age.com
Augmented reality is one of the most exciting technologies that made its way into the mass market in the recent years.
Excerpt:
In this article we will tell you about other ways to use this technology in a mobile app except for gaming and give you some augmented reality business ideas.
Google Maps is getting augmented reality directions and recommendation features — from theverge.com by Chaim Gartenberg
Plus, the ability to vote on restaurants with friends
Excerpt:
The new AR features combine Google’s existing Street View and Maps data with a live feed from your phone’s camera to overlay walking directions on top of the real world and help you figure out which way you need to go.
VR Travel: Virtual Reality Can Show You The World — from appreal-vr.com by Yariv Levski
Excerpt:
The VR travel industry may be in its infancy, but if you expect to see baby steps leading to market adoption, think again. Digital travel sales are expected to reach $198 billion this year, with virtual reality travel apps and VR tours capturing a good share of market revenue.
Of course, this should come as no surprise. Consumers increasingly turn to digital media when planning aspects of their lives, from recreational activities to retirement. Because VR has the power to engage travelers like no other technology can do, it is a natural step in the evolution of the travel industry. It is also likely to disrupt travel planning as we know it.
In this article, we will explore VR travel technology, and what it means for business in 2018.
From Inside VR & AR
HP Inc. is teaming up with DiSTI to create VR training programs for enterprise customers. DiSTI is a platform for user interface software and custom 3D training solutions. The companies are partnering to create maintenance and operations training in VR for vehicle, aircraft and industrial equipment systems. DiSTI’s new VE Studio software lets customers develop their own virtual training applications or have DiSTI and HP professional services teams assist in designing and building the program. — TECHRADAR
HP and DiSTI to enhance enterprise training through VR solutions — from techradar.com by Nick Rego
Global alliance will combine HP’s VR solutions with DiSTI’s advanced development platform
Excerpt:
HP Inc. today announced an alliance with the DiSTI Corporation, a leading global provider of VR and advanced human machine interface development solutions, to address the growing demand for high-impact, cost-effective VR training.
The two companies will work together to develop unique VR training solutions for enterprise customers, with a specific focus on maintenance and operations training for complex systems such as vehicle, aircraft and industrial equipment.
Addendum:
Google’s robot assistant now makes eerily lifelike phone calls for you — from theguardian.com by Olivia Solon
Google Duplex contacts hair salon and restaurant in demo, adding ‘er’ and ‘mmm-hmm’ so listeners think it’s human
Excerpt:
Google’s virtual assistant can now make phone calls on your behalf to schedule appointments, make reservations in restaurants and get holiday hours.
The robotic assistant uses a very natural speech pattern that includes hesitations and affirmations such as “er” and “mmm-hmm” so that it is extremely difficult to distinguish from an actual human phone call.
The unsettling feature, which will be available to the public later this year, is enabled by a technology called Google Duplex, which can carry out “real world” tasks on the phone, without the other person realising they are talking to a machine. The assistant refers to the person’s calendar to find a suitable time slot and then notifies the user when an appointment is scheduled.
Google employees quit over the company’s military AI project — from thenextweb.com by Tristan Greene
Excerpt:
About a dozen Google employees reportedly left the company over its insistence on developing AI for the US military through a program called Project Maven. Meanwhile 4,000 others signed a petition demanding the company stop.
It looks like there’s some internal confusion over whether the company’s “Don’t Be Evil” motto covers making machine learning systems to aid warfare.
The link between big tech and defense work — from wired.com by Nitasha Tiku
Except:
FOR MONTHS, A growing faction of Google employees has tried to force the company to drop out of a controversial military program called Project Maven. More than 4,000 employees, including dozens of senior engineers, have signed a petition asking Google to cancel the contract. Last week, Gizmodo reported that a dozen employees resigned over the project. “There are a bunch more waiting for job offers (like me) before we do so,” one engineer says. On Friday, employees communicating through an internal mailing list discussed refusing to interview job candidates in order to slow the project’s progress.
Other tech giants have recently secured high-profile contracts to build technology for defense, military, and intelligence agencies. In March, Amazon expanded its newly launched “Secret Region” cloud services supporting top-secret work for the Department of Defense. The same week that news broke of the Google resignations, Bloomberg reported that Microsoft locked down a deal with intelligence agencies. But there’s little sign of the same kind of rebellion among Amazon and Microsoft workers.
Amazon urged not to sell facial recognition tool to police — from wpxi.com by Gene Johnson
Excerpt:
Facebook SEATTLE (AP) – The American Civil Liberties Union and other privacy advocates are asking Amazon to stop marketing a powerful facial recognition tool to police, saying law enforcement agencies could use the technology to “easily build a system to automate the identification and tracking of anyone.”
The tool, called Rekognition, is already being used by at least one agency – the Washington County Sheriff’s Office in Oregon – to check photographs of unidentified suspects against a database of mug shots from the county jail, which is a common use of such technology around the country.
From DSC:
Google’s C-Suite — as well as the C-Suites at Microsoft, Amazon, and other companies — needs to be very careful these days, as they could end up losing the support/patronage of a lot of people — including more of their own employees. It’s not an easy task to know how best to build and use technologies in order to make the world a better place…to create a dream vs. a nightmare for our future. But just because we can build something, doesn’t mean we should.
The Complete Guide to Conversational Commerce | Everything you need to know. — from chatbotsmagazine.com by Matt Schlicht
Excerpt:
What is conversational commerce? Why is it such a big opportunity? How does it work? What does the future look like? How can I get started? These are the questions I’m going to answer for you right now.
…
The guide covers:
Definition: Conversational commerce is an automated technology, powered by rules and sometimes artificial intelligence, that enables online shoppers and brands to interact with one another via chat and voice interfaces.
Notes from the AI frontier: Applications and value of deep learning — from mckinsey.com by Michael Chui, James Manyika, Mehdi Miremadi, Nicolaus Henke, Rita Chung, Pieter Nel, and Sankalp Malhotra
Excerpt:
Artificial intelligence (AI) stands out as a transformational technology of our digital age—and its practical application throughout the economy is growing apace. For this briefing, Notes from the AI frontier: Insights from hundreds of use cases (PDF–446KB), we mapped both traditional analytics and newer “deep learning” techniques and the problems they can solve to more than 400 specific use cases in companies and organizations. Drawing on McKinsey Global Institute research and the applied experience with AI of McKinsey Analytics, we assess both the practical applications and the economic potential of advanced AI techniques across industries and business functions. Our findings highlight the substantial potential of applying deep learning techniques to use cases across the economy, but we also see some continuing limitations and obstacles—along with future opportunities as the technologies continue their advance. Ultimately, the value of AI is not to be found in the models themselves, but in companies’ abilities to harness them.
It is important to highlight that, even as we see economic potential in the use of AI techniques, the use of data must always take into account concerns including data security, privacy, and potential issues of bias.
AI for Good — from re-work.co by Ali Shah, Head of Emerging Technology and Strategic Direction – BBC
Excerpt:
What AI for good is really trying to ask is how we might develop and apply AI so that it makes a positive difference to society. Since the material question is about the change in society we would like to see, then we must first define the change we are hoping for before we can judge how AI might help. There are many areas of society that we might choose to consider, but I will focus on two interrelated issues.
Algorithms are making the same mistakes assessing credit scores that humans did a century ago — from qz.com by Rachel O’Dwyer
Educause Releases 2018 Horizon Report Preview — from campustechnology.com by Rhea Kelly
Excerpt:
After acquiring the rights to the New Media Consortium’s Horizon project earlier this year, Educause has now published a preview of the 2018 Higher Education Edition of the Horizon Report — research that was in progress at the time of NMC’s sudden dissolution. The report covers the key technology trends, challenges and developments expected to impact higher ed in the short-, mid- and long-term future.
Also see:
Creating continuous, frictionless learning with new technologies — from clomedia.com by Karen Hebert-Maccaro
Point-of-need and on-the-job learning experiences are about to get a lot more creative.
Excerpt:
Technology has conditioned workers to expect quick and easy experiences — from Google searches to help from voice assistants — so they can get the answers they need and get back to work. While the concept of “on-demand” learning is not new, it’s been historically tough to deliver, and though most learning and development departments have linear e-learning modules or traditional classroom experiences, today’s learners are seeking more performance-adjacent, “point-of-need” models that fit into their busy, fast-paced work environments.
Enter emerging technologies. Artificial intelligence, voice interfaces and augmented reality, when applied correctly, have the potential to radically change the nature of how we learn at work. What’s more, these technologies are emerging at a consumer-level, meaning HR’s lift in implementing them into L&D may not be substantial. Consider the technologies we already use regularly — voice assistants like Alexa, Siri and Google Assistant may be available in 55 percent of homes by 2022, providing instant, seamless access to information we need on the spot. While asking a home assistant for the weather, the best time to leave the house to beat traffic or what movies are playing at a local theater might not seem to have much application in the workplace, this nonlinear, point-of-need interaction is already playing out across learning platforms.
Artificial intelligence, voice interfaces and augmented reality, when applied correctly, have the potential to radically change the nature of how we learn at work.
The rise of newsroom smart machines: Optimizing workflow with artificial intelligence — from mediablog.prnewswire.com by Julian Dossett
Excerpts:
As computer algorithms become more advanced, artificial intelligence (AI) increasingly has grown prominent in the workplace. Top news organizations now use AI for a variety of newsroom tasks.
…
But current AI systems largely are still dependent on humans to function correctly, and the most pressing concern is understanding how to correctly operate these systems as they continue to thrive in a variety of media-related industries.
…
So, while [Machine Learning] systems soon will become ubiquitous in many professions, they won’t replace the professionals working in those fields for some time — rather, they will become an advanced tool that will aid in decision making. This is not to say that AI will never endanger human jobs. Automation always will find a way.
AI and Chatbots in Education: What Does The FutureHold? — from chatbotsmagazine.com by Robin Singh
From DSC:
While I don’t find this article to be exemplary, I post this one mainly to encourage innovative thinking about how we might use some of these technologies in our future learning ecosystems.
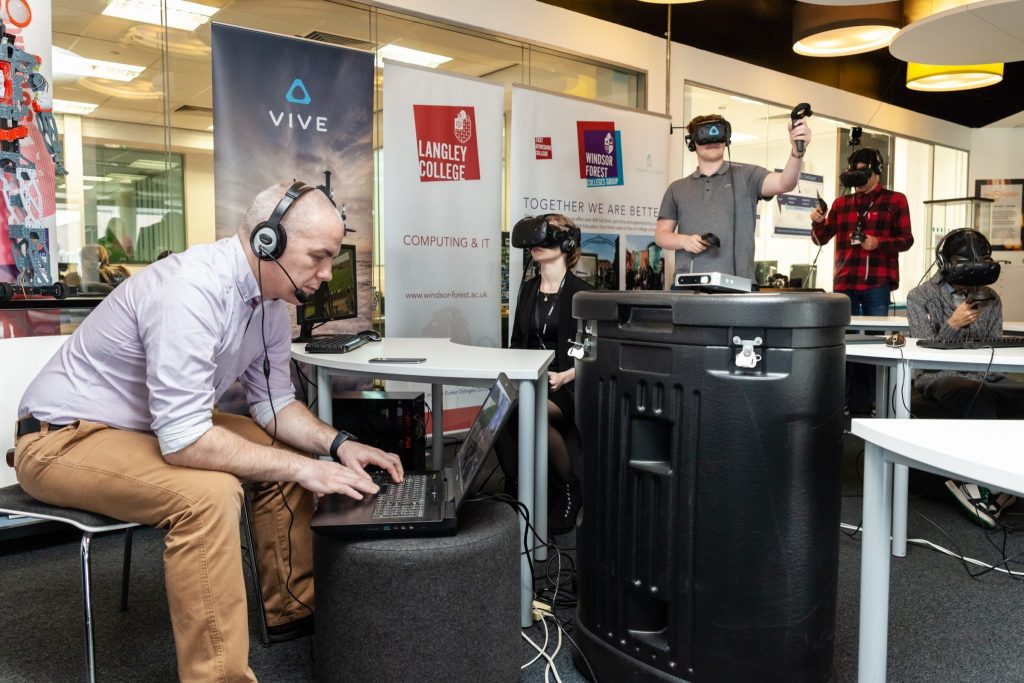
Immersive VR Education showcases the power of learning through virtual reality — from vrfocus.com by Nina Salomons
Pixar co-founder Loren Carpenter was ‘teleported’ live into a virtual classroom in the UK.
Excerpt:
Virtual reality (VR) has often been mentioned as the empathy machine, however it has many use cases. When it comes to memory and retention it looks like VR is not only useful for simulation but for education as well. Immersive VR Education teamed up with HTC Vive and Windsor Forest Colleges Group to create a memorable experience of virtual teaching.
On the April 25th ten students from Windsor Forest Colleges Group in the UK put on an HTC Vive headset and guided by David Whelan CEO & Founder of Immersive VR Education and Mike Armstrong, Senior/Lead Developer of Immersive VR Education using the free VR social education and presentation platform ENGAGE. ENGAGE allows users to hold meetings, classes, private lessons and presentations. Users can record, create their own lessons and presentations as well as allow users to interact with virtual objects.
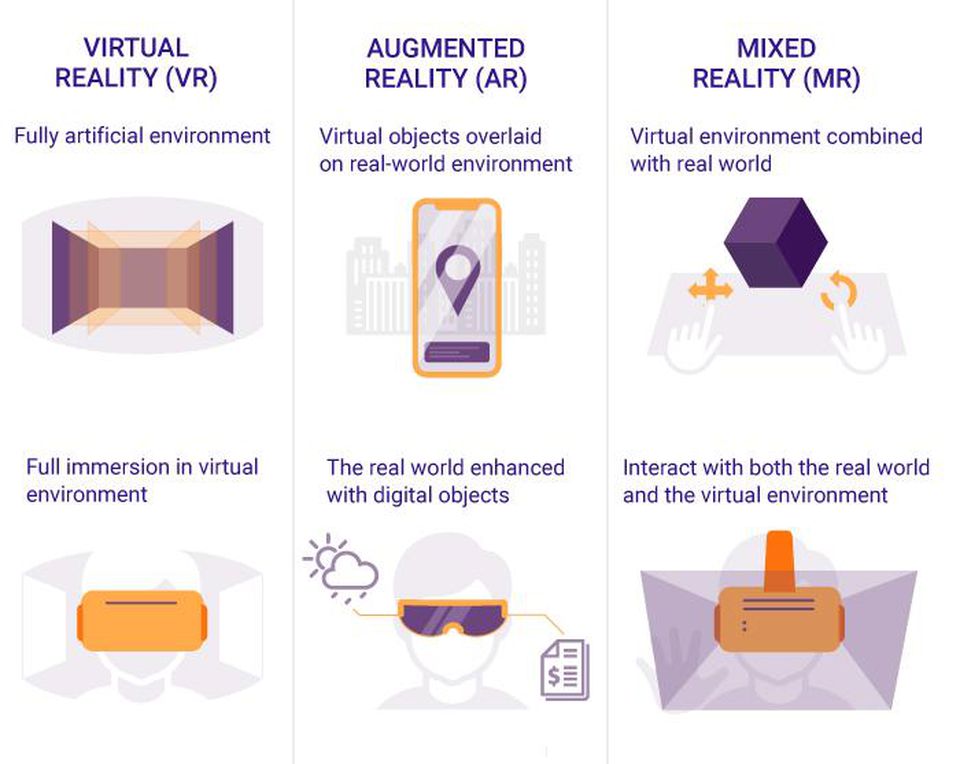
The difference between Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality and Mixed Reality — from forbes.com Julia Tokareva
Addendum on 5/5/18
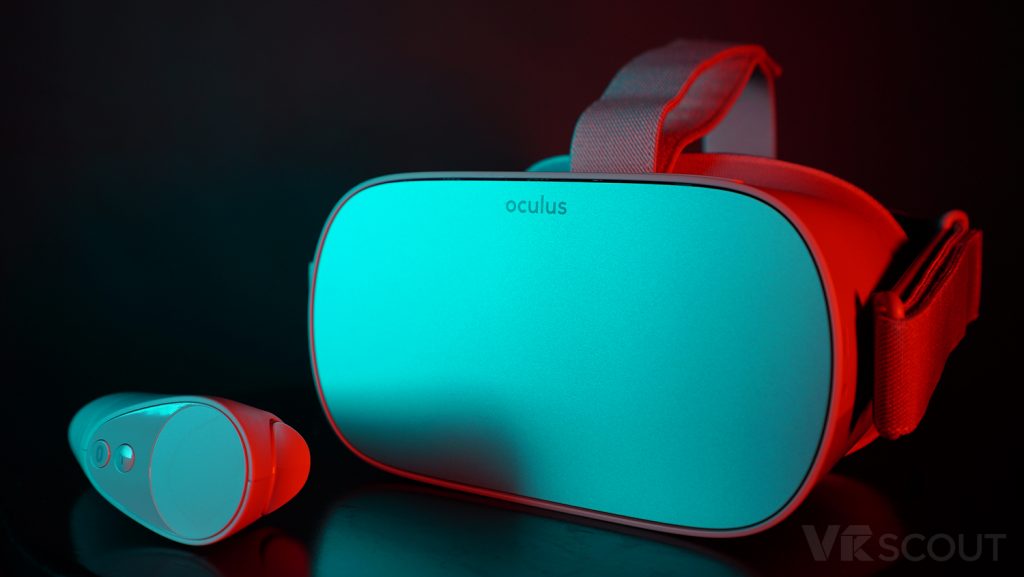
Oculus Go Has Arrived and It’s a Big Deal — from vrscout.com by Jonathan Nafarrete
Excerpt:
The $200 Oculus Go is the most accessible VR headset today.
Up until now, one of the biggest barriers to entry for VR has been price. Headset adoption has taken a conservative growth path, mostly due in part to high prices of PC-required systems or just requiring consumers to own a specific line of VR compatible phones to pair with mobile headsets.
But now the Oculus Go is finally here and it’s a big deal, especially for the millions of iPhone users out there who up until today have had limited options to get into VR.
Starting today, the Oculus Go standalone VR headset is available for purchase for $199. Available for sale on Oculus.com in 23 countries, you can also pick up one online from Amazon or in Best Buy Stores in the U.S. The Oculus companion app used for initial setup is available for both iPhone or Android devices.
From DSC regarding Virtual Reality-based apps:
If one can remotely select/change their seat at a game or change seats/views at a concert…how soon before we can do this with learning-related spaces/scenes/lectures/seminars/Active Learning Classrooms (ALCs)/stage productions (drama) and more?
Talk about getting someone’s attention and engaging them!
Excerpt:
(MAY 2, 2018) MelodyVR, the world’s first dedicated virtual reality music platform that enables fans to experience music performances in a revolutionary new way, is now available.
The revolutionary MelodyVR app offers music fans an incredible selection of immersive performances from today’s biggest artists. Fans are transported all over the world to sold-out stadium shows, far-flung festivals and exclusive VIP sessions, and experience the music they love.
What MelodyVR delivers is a unique and world-class set of original experiences, created with multiple vantage points, to give fans complete control over what they see and where they stand at a performance. By selecting different Jump Spots, MelodyVR users can choose to be in the front row, deep in the crowd, or up-close-and-personal with the band on stage.
With standalone VR headsets like the Oculus Go now available at an extremely accessible price point ($199), the already vibrant VR market is set to grow exponentially over the coming years. Current market forecasts suggest over 350 million users by 2021 and last year saw $3 billion invested in virtual and alternative reality.

Amazon CEO Jeff Bezos’ personal AV tech controls the future of AV and doesn’t even realize it — from ravepubs.com by Gary Kayye
Excerpt:
But it dawned on me today that the future of our very own AV market may not be in the hands of any new product, new technology or even an AV company at all. In fact, there’s likely one AV guy (or girl) out there, today, that controls the future of AV for all of us, but doesn’t even know it, yet.
I’m talking about Jeff Bezos’ personal AV technician. Yes, that Jeff Bezos — the one who started Amazon.
Follow my logic.
The Amazon Alexa is AMAZING. Probably the most amazing thing since Apple’s iPhone. And, maybe even more so. The iPhone was revolutionary as it was a handheld phone, an email client, notes taker, voice recorder, calendar, to-do list, wrist watch and flashlight — all in one. It replaced like 10 things I was using every single day. And I didn’t even mention the camera!
…
Alexa seamlessly and simply connects to nearly everything you want to connect it to. And, it’s updated weekly — yes, weekly — with behind-the-scenes Friday-afternoon firmware and software upgrades. So, just when you think Alexa doesn’t do something you want it to do, she can — you just have to wait until an upcoming Friday — as someone will add that functionality. And, at any time, you can add Alexa SKILLS to yours and have third-party control of your Lutron lighting system, your shades and blinds, your HVAC, your TV, your DVR, your CableTV box, your SONOS, your home security system, your cameras and even your washer and dryer (yes, I have that functionality — even though I can’t find a use for it yet). It can even call people, play any radio station in the world, play movie previews, play Jeopardy!, play Sirius/XM radio — I mean, it can do nearly anything. It’s squarely aimed at the average consumer or home application — all to simplify your life.
But it could EASILY be upgraded to control everything. I mean everything. Projectors, digital signage networks, AV-over-IP systems, scalers, switchers, audio systems, commercial-grade lighting systems, rooms, buildings, etc. — you get the idea.
From DSC:
By the way, I wouldn’t be so sure that Bezos doesn’t realize this; there’s very little that gets by that guy.
Also see:
Crestron to Ship AirBoard Whiteboarding Solution — from ravepubs.com by Sara Abrons
Excerpt:
Crestron will soon be shipping the Crestron AirBoard PoE electronic whiteboard technology. Crestron AirBoard enables viewing of electronic whiteboard content on any display device, thereby solving the problem of meeting participants — remote participants, especially — not being able to see the whiteboard unless they’re seated with a direct line of sight.
…
With Crestron AirBoard, annotations can be saved and then posted, emailed, or texted to either a central web page (education applications) or to invited participants (corporate applications). Meeting participants simply choose “whiteboard” as a source on the in-room Crestron TSW or Crestron Mercury touch screen to start the session. When “end meeting” is selected, the user is prompted to save and send the file.
An AI Bot for the Teacher — with thanks to Karthik Reddy for this resource
Artificial intelligence is the stuff of science fiction – if you are old enough, you will remember those Terminator movies a good few years ago, where mankind was systematically being wiped out by computers.
The truth is that AI, though not quite at Terminator level yet, is already a fact and something that most of us have encountered already. If you have ever used the virtual assistant on your phone or the Ask Google feature, you have used AI.
Some companies are using it as part of their sales and marketing strategies. An interesting example is Lowe’s Home Improvement that, instead of chatbots, uses actual robots into their physical stores. These robots are capable of helping customers locate products that they’re interested in, taking a lot of the guesswork out of the entire shopping experience.
Of course, there are a lot of different potential applications for AI that are very interesting. Imagine an AI teaching assistant, for example. They could help grade papers, fact check and assist with lesson planning, etc., all to make our harassed teachers’ lives a little easier.
Chatbots could be programmed as tutors to help kids better understand core topics if they are struggling with them, ensuring that they don’t hold the rest of the class up. And, for kids who have a real affinity with the subject, help them learn more about what they are interested in.
It could also help enhance long distance training. Imagine if your students could get instant answers to basic questions through a simple chatbot. Sure, if they were still not getting it, they would come through to you – the chatbot cannot replace a real, live, teacher after all. But it could save you a lot of time and frustration.
Here, of course, we have only skimmed the surface of what artificial intelligence is capable of. Why not look through this infographic to see how different brands have been using this tech, and see what possible applications of it we might expect.
Brands that use AI to enhance marketing (infographic) 2018
From 16best.net with thanks to Karthik Reddy for this resource
50 animation tools and resources for digital learners — from teachthought.com by Lisa Chesser, opencolleges.edu.au
Excerpt:
Some of the animation links cataloged here will give educators very basic tools and histories of animation while others have the animation already created and set in motion, it’s just a matter of sharing it with students. Educators need to decide which tool is best for them. If you want to create your own animation from scratch, then you want to go to sites such as Animwork. If you want to select from an animation that’s already set up, for you then perhaps Explainia makes more sense. One of the easiest ways to animate, however, isn’t with your own camera and modeling clay, it’s with your links to sites that hand you everything within their own forums. Use the first part of this list for creating original animation or using animation tools to create lessons. Use the second part to select animated lessons that are already completed and set to share.
Click on the image to get a larger image in a PDF file format.
From DSC:
So regardless of what was being displayed up on any given screen at the time, once a learner was invited to use their devices to share information, a graphical layer would appear on the learner’s mobile device — as well as up on the image of the screens (but the actual images being projected on the screens would be shown in the background in a muted/pulled back/25% opacity layer so the code would “pop” visually-speaking) — letting him or her know what code to enter in order to wirelessly share their content up to a particular screen. This could be extra helpful when you have multiple screens in a room.
For folks at Microsoft: I could have said Mixed Reality here as well.
#ActiveLearning #AR #MR #IoT #AV #EdTech #M2M #MobileApps
#Sensors #Crestron #Extron #Projection #Epson #SharingContent #Wireless
FLGI Publishes the Top 100 Educators Leading Flipped Learning in 2018
The Flipped Learning Global Initiative identifies the movement’s leading educators, administrators, and technologists worldwide
CHICAGO, April 16, 2018 /PRNewswire/ — Today, the Flipped Learning Global Initiative (FLGI), a worldwide coalition of educators, researchers, technologists, professional development providers and education leaders, announced the publication of the FLGI 100. The annual list identifies the top 100 K-12 educators who are driving the adoption of the flipped classroom around the world. The list is compiled by the FLGI executive committee – led by Jon Bergmann, Chief Academic Officer and one of the pioneers of the flipped classroom movement. Educators from around the globe are represented, including Flipped Learning practitioners from Brazil, Australia, New Zealand, Italy, China, Taiwan,
“The global Flipped Learning community continues to grow, introducing us to fresh ideas, new innovations, and emerging leaders. The 2018 FLGI Flipped Learning leaders lists include veterans from prior years, and many new names and faces. The FLGI 100 list, along with the two FLGI 50 lists, represent the practitioners who are showing us the connection between Flipped Learning, active learning, and world-class learners,” said Jon Bergmann.
The FLGI Flipped Learning leaders lists are updated annually, and all three lists are published in the April issue of Flipped Learning Review (FLR): the Flipped Learning 3.0 magazine. FLR is the first digital magazine dedicated to covering the ideas and people driving the global Flipped Learning movement. The issue features an insightful interview with one of the leading voices in the Flipped Learning community: Dr. Eric Mazur at Harvard University. Bergmann and Mazur discuss how Flipped Learning has evolved over the last decade and why group space mastery is the next frontier for this instructional model. The April issue also includes the full list of global delegates participating in the project to establish international standards for Flipped Learning. The 2018 FLGI 100 list, the Bergmann/Mazur interview, and the global delegates lists are accessible at http://flr.flglobal.org/
About the Flipped Learning Global Initiative
The Flipped Learning Global Initiative, (FLGI), was created to support the rapidly expanding adoption of Flipped Learning all over the world in countries including China, Taiwan,
FLGI serves as a global hub for coordinating, orchestrating and scaling the key elements required to expand Flipped Learning successfully around the world. FLGI is home to the Flipped Learning International Faculty, the Flipped Learning Innovation Center, the Flipped Learning Global Standards project, and Flipped Learning Review (FLR).
For more information, contact: Errol St.Clair Smith, Director of Global Development at 949-677-7381, 193454@email4pr.
Also see this page, which states:
On Monday, April 16, 2018 The Flipped Learning Global Initiative (FLGI) will publish the 2018 FLGI 100. The annual list identifies the top 100 K-12 educators who are driving the adoption of Flipped Learning around the world. The list is compiled by the FLGI executive committee, led by Jon Bergmann, Chief Academic Officer. Educators from around the globe are represented, including Flipped Learning practitioners from Italy, China, Taiwan, Spain, UAE, the United Kingdom, Turkey, Italy, Korea, Argentina, Iceland, Sweden, India, and the United States. The initiative also identified the top 50 Flipped Learning leaders in higher education and the top 50 Flipped Learning administrators and tech coaches.
The 50 Best Augmented Reality Apps for iPhone, iPad & Android Devices — from next.reality.news by Tommy Palladino
Excerpt:
Complete Anatomy 2018 +Courses (iOS): Give your preschoolers a head start on their education! Okay, clearly this app is meant for more advanced learners. Compared to the average app, you’ll end up paying through the nose with in-app purchases, but it’s really a drop in the bucket compared to the student loans students will accumulate in college. Price: Free with in-app purchases ranging from $0.99 to $44.99.
SkyView (iOS & Android): If I can wax nostalgic for a bit, I recall one of the first mobile apps that wowed me being Google’s original SkyView app. Now you can bring back that feeling with some augmented reality. With SkyView, you can point your phone to the sky and the app will tell you what constellations or other celestial bodies you are looking at. Price: $1.99, but there’s a free version for iOS and Android.
JigSpace (iOS): JigSpace is an app dedicated to showing users how things work (the human body, mechanical objects, etc.). And the app recently added how-to info for those who WonderHowTo do other things as well. JigSpace can now display its content in augmented reality as well, which is a brilliant application of immersive content to education. Price: Free.
NY Times (iOS & Android): The New York Times only recently adopted augmented reality as a means for covering the news, but already we’ve had the chance to see Olympic athletes and David Bowie’s freaky costumes up close. That’s a pretty good start! Price: Free with in-app purchases ranging from $9.99 to $129.99 for subscriptions.
BBC Civilisations (iOS & Android): Developed as a companion to the show of the same name, this app ends up holding its own as an AR app experience. Users can explore digital scans of ancient artifacts, learn more about their significance, and even interact with them. Sure, Indiana Jones would say this stuff belongs in a museum, but augmented reality lets you view them in your home as well. Price: Free.
SketchAR (iOS, Android, & Windows): A rare app that works on the dominant mobile platforms and HoloLens, Sketch AR helps users learn how to draw. Sketch AR scans your environment for your drawing surface and anchors the content there as you draw around it. As you can imagine, the app works best on HoloLens since it keeps users’ hands free to draw. Price: Free.
Sun Seeker (iOS & Android): This app displays the solar path, hour intervals, and more in augmented reality. While this becomes a unique way to teach students about the Earth’s orbit around the sun (and help refute silly flat-earthers), it can also be a useful tool for professionals. For instance, it can help photographers plan a photoshoot and see where sunlight will shine at certain times of the day. Price: $9.99.
Froggipedia (iOS): Dissecting a frog is basically a rite of passage for anyone who has graduated from primary school in the US within the past 50 years or so. Thanks to augmented reality, we can now save precious frog lives while still learning about their anatomy. The app enables users to dissect virtual frogs as if they are on the table in front of them, and without the stench of formaldehyde. Price: $3.99.
GeoGebra Augmented Reality (iOS): Who needs a graphing calculator when you can visualize equations in augmented reality. That’s what GeoGebra does. The app is invaluable for visualizing graphs. Price: Free.
Addendum:
VR Lab! — from thejournal.com by Joshua Bolkan
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
When Tampa Preparatory School launched decided to turn a closet into a virtual reality lab, they had no idea how far their students would run with the tools, but that’s exactly what they did, sitting down to build their own educational apps to help visualize concepts in astronomy, chemistry and physics. In addition to the educational apps, built by students on their own initiative, the VR lab is also used for art classes and more.
Chad Lewis, director of technology at Tampa Prep, recently sat down with THE Journal to talk about the school’s experience with VR as an educational tool.
Tell me a little about having students design their own VR apps. Are there any benefits to it that surprised you?
Chad Lewis: Some surprising benefits included branching out beyond computer science into areas like chemistry and physics. This is an example of the amazing things students can do if given the opportunity to pursue their passions. They need time, space and resources as well as support and encouragement.
The main thing is that they’re learning coding, 3D modeling, game development, collaboration, design thinking, etc.
In the process, one of our computer science students came up to me and said, “Mr. Lewis do you mind if I try to create some virtual reality apps using Unity?” and it really took off from there. The lab was a student-driven initiative.
From DSC:
This application looks to be very well done and thought out! Wow!
Check out the video entitled “Interactive Ink – Enables digital handwriting“ — and you may also wonder whether this could be a great medium/method of having to “write things down” for better information processing in our minds, while also producing digital work for easier distribution and sharing!
Wow! Talk about solid user experience design and interface design! Nicely done.
Below is an excerpt of the information from Bella Pietsch from anthonyBarnum Public Relations
Imagine a world where users interact with their digital devices seamlessly, and don’t suffer from lag and delayed response time. I work with MyScript, a company whose Interactive Ink tech creates that world of seamless handwritten interactivity by combining the flexibility of pen and paper with the power and productivity of digital processing.
According to a recent forecast, the global handwriting recognition market is valued at a trillion-plus dollars and is expected to grow at an almost 16 percent compound annual growth rate by 2025. To add additional context, the new affordable iPad with stylus support was just released, allowing users to work with the $99 Apple Pencil, which was previously only supported by the iPad Pro.
Check out the demo of Interactive Ink using an Apple Pencil, Microsoft Surface Pen, Samsung S Pen or Google Pixelbook Pen here.
Interactive Ink’s proficiencies are the future of writing and equating. Developed by MyScript Labs, Interactive Ink is a form of digital ink technology which allows ink editing via simple gestures and providing device reflow flexibility. Interactive Ink relies on real-time predictive handwriting recognition, driven by artificial intelligence and neural network architectures.