DC: So how might this impact the learning ecosystems out there?https://t.co/tMl5ouSX1x#learningecosystems #learningfromthelivingclassroom #careers #careerdevelopment #education #highereducation #change
— Daniel Christian (he/him/his) (@dchristian5) November 25, 2020
Employers May Drastically Change Benefits in 2021 — from insights.dice.com by Leslie Stevens-Huffman
Excerpts:
As employers continue to rethink all aspects of business and strategy in the wake of COVID-19, many are also exploring major changes to benefit programs and perks for 2021.
…
After access to routine health services became an issue during the lockdown, some 32 percent of employers are planning to add virtual care or telehealth services to existing health coverage, according to a study by Mercer, an HR consulting firm.
Bloomberg Law 2021 — from pro.bloomberglaw.com
Excerpt:
Our Bloomberg Law 2021 series sets the stage for a new year, previewing the themes and topics that our experts will be watching closely, so you can effectively navigate the dynamic legal landscape. Our team of experienced legal analysts leverages the latest data and technology to deliver expert perspectives on the legal market to the legal market.

Digital transformation: 5 ways to balance creativity and productivity — from enterprisersproject.com by Andrew Parker
Creativity and productivity shouldn’t be opposing forces in your digital transformation efforts. Consider these tips to tap the power of both
Excerpt:
Creativity and productivity might sound like they’re poles apart: One is about thinking in new ways; the other is about making things happen.
But in successful digital transformation programs, the two go hand in hand – a perfect marriage of creative thinking that takes the latest technology innovations into account and productive action that brings those new ideas to life.
Today, creativity is more important than ever. As a result of the pandemic, organizations have been forced to think differently and to adapt quickly in order to stay relevant and survive. It’s a case of do or die.
In the wake of the pandemic, creativity is more important than ever.
From DSC:
Another important element here is developing/establishing a culture that is willing to innovate, adapt, experiment, and change. That is SO key in this type of transformation.
It’s clear to me that our people, and their willingness to be agile, innovate, test, and learn, were one of the “secrets” behind those successes. (source)
Also see:
- Remote work: How the pandemic is reshaping the office of the future — from enterprisersproject.com by Raju Vegesna
Having shifted to remote work, more businesses are considering a future with lower-cost office models that give employees choice in how and where they work. Good news: It’s a win-win.
By decentralizing the workforce, companies can attract talent anywhere in the world.
From DSC:
This means that our students must be able to collaborate and to create their deliverables — digitally/virtually/online.
The Gap Between What C-Suite Leaders Think And What HR Executives And Employees Know About Their Workplaces — from forbes.com by Kathy Caprino
Excerpt:
- C-suite executives now rank organizational complexity, inadequate skills and employee burnout as the top 3 greatest challenges their businesses will face in the next 2 years, and 84% of CHROs say over the next two years they will prioritize agility and flexibility in the workforce. Yet only 19% of HR executives say their HR function has the proper business acumen or capabilities to do so
- 74% of executives believe they’re helping their employees learn new skills needed to work during the pandemic yet only 38% of their employees believe the same
- Despite nearly 80% of C-suite executives say they’re supporting the physical and emotional health of their workers right now, only 46% of employees agree
Important New Report on Essential Lawyering Skills — from bestpracticeslegaled.com by John Lande
Excerpt:
Ohio State Professor Deborah Jones Merritt and Institute for the Advancement of the American Legal System Research Director Logan Cornett just published an important report, Building a Better Bar: The Twelve Building Blocks of Minimum Competence, based on insights from 50 focus groups.
They found that minimum competence consists of 12 interlocking “building blocks,” including the ability to interact effectively with clients, communicate as a lawyer, and see the “big picture” of client matters.
They propose 10 recommendations that courts, law schools, bar associations, bar examiners, and other stakeholders should consider in their efforts to move towards better, evidence-based lawyer licensing.
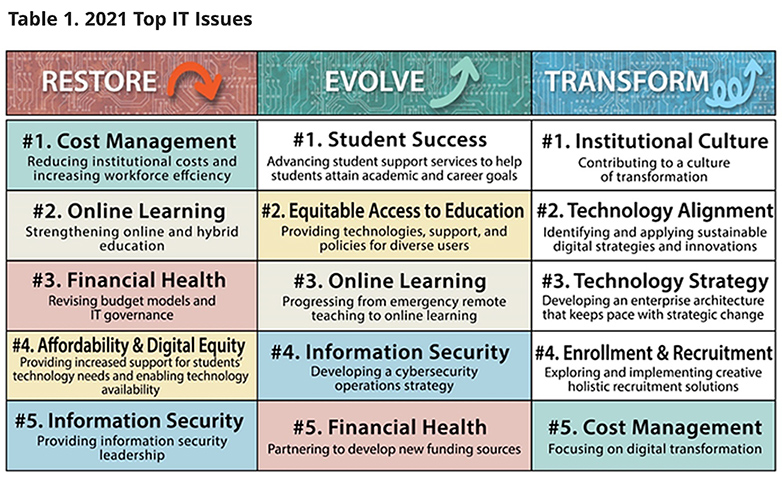
Top IT Issues, 2021: Emerging from the Pandemic — from educause.edu
Excerpt:
The EDUCAUSE Top IT Issues list has been refactored for 2021 to help higher education shape the role technology will play in the recovery from the pandemic. What different directions might institutional leaders take in their recovery strategy? How can technology help our ecosystem emerge stronger and fitter for the future?
The 2021 EDUCAUSE IT Issues project explores these questions using a very different approach from previous years. Anticipating potential ways institutions might emerge from the pandemic, this year we offer three Top IT Issues lists and examine the top 5 issues within three scenarios that may guide institutional leaders’ use of technology: restore, evolve, and transform.
Also see:
- Educause Identifies Top IT Issues for an Uncertain Future — from campustechnology.com by Dian Schaffhauser