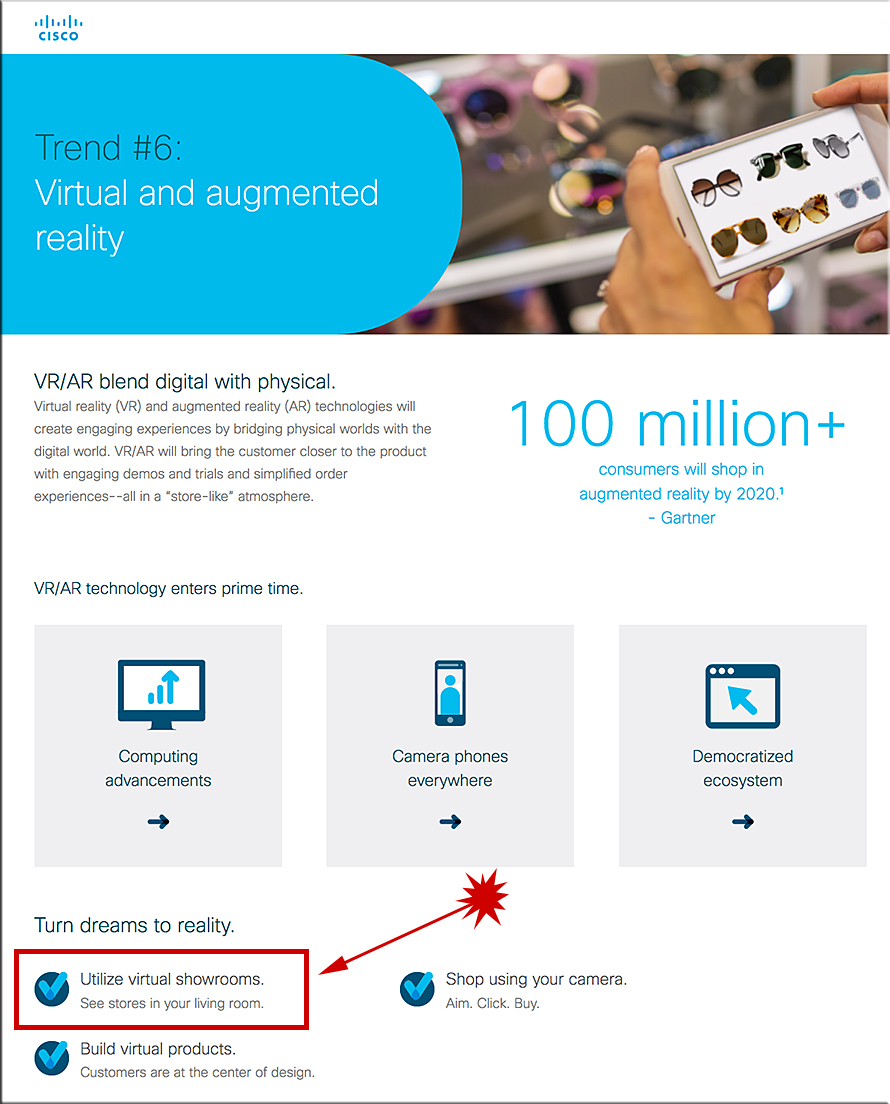
3 ways augmented reality will find its way into your life in 2018 and beyond — from entrepreneur.com by Han-Gwon Lung
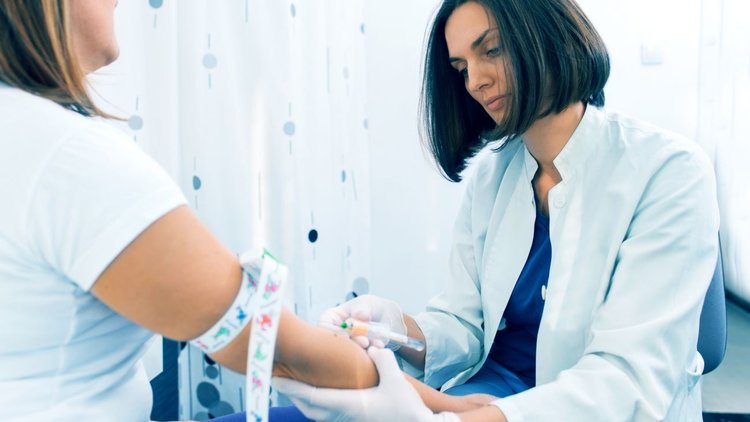
Up to 40 percent of nurses miss the patient’s vein on their first attempt at taking blood. That’s changing, because of augmented reality.
Excerpt:
- A pair of glasses you can’t live without
- More immersive (and personalized) marketing
- Less guesswork in health care
The race for AR glasses starts now — from wired.com by Steven Levy
Excerpt:
Though the Next Big Thing won’t appear for a while, we know pretty much what it will look like: a lightweight, always-on wearable that obliterates the divide between the stuff we see on screens and the stuff we see when we look up from our screens.
…
Not every company working on post-reality glasses shares an identical vision; some have differing views of how immersive it should be. But all have quietly adopted the implicit assumption that a persistent, wearable artificial reality is the next big thing. The pressure of the competition has forced them to begin releasing interim products, now.
And he added that “these glasses will offer AR, VR, and everything in between, and we’ll wear them all day and we’ll use them in every aspect of our lives.”
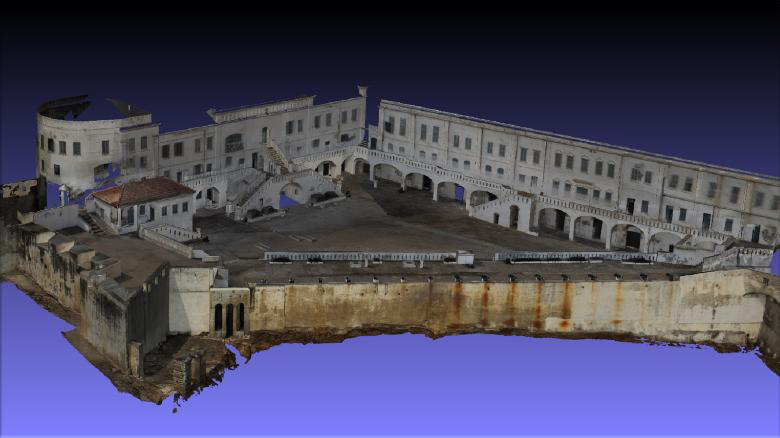
Meet the scientists immortalizing African heritage in virtual reality — from by Chris Giles
Excerpt:
Concerned with the decay of African heritage sites, The Zamani Project, based at the University of Cape Town, South Africa, is seeking to immortalize historic spots in three-dimensional, virtual reality-ready models.
Professor Heinz Ruther steers the project. He ventures up and down the continent — visiting Ghana, Tanzania, Mali, Ethiopia, Kenya and elsewhere — recording in remarkable detail the structure and condition of tombs, churches and other buildings.
“I’ve seen how sites are deteriorating visibly,” Ruther told CNN.
The project’s aim is to build a database of complex, lifelike 3-D models. Presently, they’ve mapped around 16 sites including Lalibela in Ethiopia, Timbuktu in Mali and Kilwa in Tanzania.
4 augmented and virtual reality projects that point to the future of education — from edsurge.com by Justin Hendrix
Excerpt:
Education has been a recurring theme throughout the many programs of the NYC Media Lab, a public-private partnership where I serve as an Executive Director. How will virtual and augmented reality change the classroom? How can teachers use immersive media to educate citizens and keep our communities vibrant? In what ways can enterprises leverage innovation to better train employees and streamline workflows?
These are just a few of the top-of-mind questions that NYC Media Lab’s consortium is thinking about as we enter the next wave of media transformation.
Researchers and professionals at work across the VR/AR community in New York City are excited for what comes next. At NYC Media Lab’s recent Exploring Future Reality conference, long-time educators including Agnieszka Roginska of New York University and Columbia University’s Steven Feiner pointed to emerging media as a way to improve multi-modal learning for students and train computer systems to understand the world around us.
NYC Media Lab merges engineering and design research happening at the city’s universities with resources and opportunities from the media and technology industry—to produce new prototypes, launch new companies and advocate for the latest thinking.
In the past year, the Lab has completed dozens of rapid prototyping projects; exhibited hundreds of demos from the corporate, university and entrepreneurship communities; helped new startups make their mark; and hosted three major events, all to explore emerging media technologies and their evolving impact.
4 virtual reality desktops for Vive, Rift, and Windows VR compared — from roadtovr.com by Dominic Brennan
Excerpt:
While it’s all too easy to lose ourselves in the countless VR worlds at our fingertips, sometimes we just need to access the desktop and get things done in Windows. Thanks to a few innovative apps, this is possible without removing your headset.













![The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)