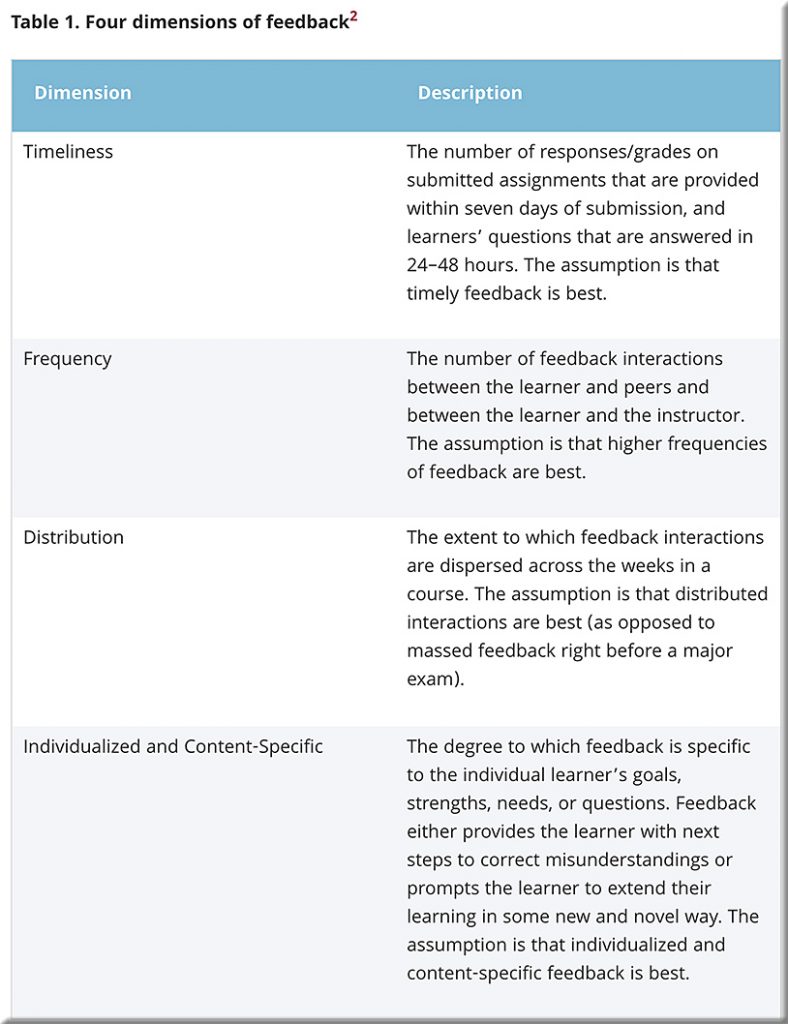
Below is a snapshot from a video that Kim O’Leary, Professor at the WMU-Cooley Law School did regarding the topic of giving (and receiving) individualized feedback.
As a relevant aside here, I want to send a shout out to Kim, as she is incredibly devoted to the craft of teaching and learning and to developing solid, competent learners and lawyers. She is a fantastic professor, as well as a caring, hard-working person — an excellent colleague whom I’m very grateful to have the privilege of working alongside.

When I saw this quote from Thomas Friedman, I wondered…
- Are our school systems creating students who are self-motivated?
Sorry…but my answer (based on what my own learning experiences in K-16 were like as well as from having observed the learning experiences of our three kids) was, “No way…at least not yet.” And the ramifications of this are getting increasingly serious as our kids need to be able to navigate an often chaotic, quickly-changing world from here on out.
- We don’t offer nearly enough learner agency.
- We create gameplayers who only focus on grades.
- We tell students what to learn.
- We don’t offer nearly enough choice and control to students.