Per Kim O’Leary, here are some resources re: the topic of giving/receiving feedback:
Other items re: feedback worth checking out:
How ‘Learning Engineering’ Hopes to Speed Up Education — from edsurge.com by Jeff Young
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
One insight Lepper brought is that when education software tools simply list all the errors students made and points out what they should have done instead, what many end up hearing is, “You’re wrong, you’re wrong, you’re wrong.” For students, this is a discouraging engagement, Lepper says.
“That kind of feedback would be perfect if you had a robot learner on the other end,” he says. “The robot learner would be delighted to have you say, ‘Okay, you made three errors in problem number one,’ and being a robot learner, they’d be able to take out those bugs and do better the next time. Real kids, especially real kids who are kind of phobic about math and who think they can’t do it, they leave and say, ‘See I can’t do it.’”
Don’t water down feedback to your student — from teachingprofessor.com by John Orlando
RetrievalPractice.org/feedback
From OLC session “Carl Rogers, Teaching Presence, and Student Engagement in Online Learning” Cheng-Chia (Brian) Chen, Denise Bockmier-Sommers, & Karen Swan (emphasis DSC)
- Use student’s first name in feedback
- Speak directly to them
- Paraphrase their words
- Provide video feedback
- Sandwich method — Include the strengths of student’s reasoning or responses in addition to your constructive critique(s)
- Acknowledge student contributions
- Let them know you care and appreciate them
- What’s timely feedback? The quicker the better, but whatever your availability is, tell what students can expect, and stick to that. Put that into your syllabus along with communication methods (email, LMS message, phone, other)
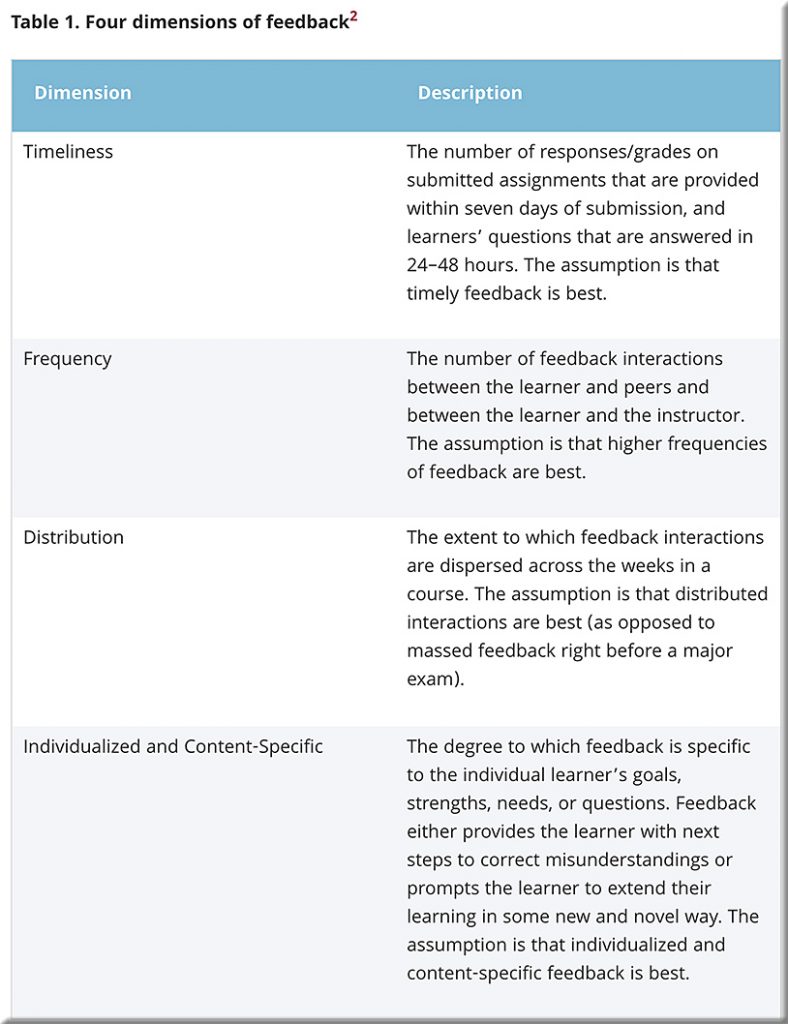
Leveraging Feedback Experiences in Online Learning — from er.educause.edu by Erin Crisp
Here are some design tips to increase the probability for success.
- Structure the course so that there are opportunities for instructors and peers to provide formative feedback several weeks before final projects/papers are due.
- Identify key time frames in the course when instructors will be heavily engaged in providing written or video feedback that is individualized and moves the learning forward.
- Create a bank of content-specific feedback comments that instructors can use for common issues and errors.
- If end-of-course survey evaluations are low, implement strategies to provide feedback that directly connects to learners as individuals.
- If you teach and grade papers in a professional discipline, provide feedback related to the course and program learning outcomes, and focus less on grammar and language usage.