AI-Powered Lawyering: AI Reasoning Models, Retrieval Augmented Generation, and the Future of Legal Practice
Minnesota Legal Studies Research Paper No. 25-16; March 02, 2025; from papers.ssrn.com by:
Daniel Schwarcz
University of Minnesota Law School
Sam Manning
Centre for the Governance of AI
Patrick Barry
University of Michigan Law School
David R. Cleveland
University of Minnesota Law School
J.J. Prescott
University of Michigan Law School
Beverly Rich
Ogletree Deakins
Abstract
Generative AI is set to transform the legal profession, but its full impact remains uncertain. While AI models like GPT-4 improve the efficiency with which legal work can be completed, they can at times make up cases and “hallucinate” facts, thereby undermining legal judgment, particularly in complex tasks handled by skilled lawyers. This article examines two emerging AI innovations that may mitigate these lingering issues: Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), which grounds AI-powered analysis in legal sources, and AI reasoning models, which structure complex reasoning before generating output. We conducted the first randomized controlled trial assessing these technologies, assigning upper-level law students to complete six legal tasks using a RAG-powered legal AI tool (Vincent AI), an AI reasoning model (OpenAI’s o1-preview), or no AI. We find that both AI tools significantly enhanced legal work quality, a marked contrast with previous research examining older large language models like GPT-4. Moreover, we find that these models maintain the efficiency benefits associated with use of older AI technologies. Our findings show that AI assistance significantly boosts productivity in five out of six tested legal tasks, with Vincent yielding statistically significant gains of approximately 38% to 115% and o1-preview increasing productivity by 34% to 140%, with particularly strong effects in complex tasks like drafting persuasive letters and analyzing complaints. Notably, o1-preview improved the analytical depth of participants’ work product but resulted in some hallucinations, whereas Vincent AI-aided participants produced roughly the same amount of hallucinations as participants who did not use AI at all. These findings suggest that integrating domain-specific RAG capabilities with reasoning models could yield synergistic improvements, shaping the next generation of AI-powered legal tools and the future of lawyering more generally.
Guest post: How technological innovation can boost growth — from legaltechnology.com by Caroline Hill
One key change is the growing adoption of technology within legal service providers, and this is transforming the way firms operate and deliver value to clients.
The legal services sector’s digital transformation is gaining momentum, driven both by client expectations as well as the potential for operational efficiency. With the right support, legal firms can innovate through tech adoption and remain competitive to deliver strong client outcomes and long-term growth.
AI Can Do Many Tasks for Lawyers – But Be Careful — from nysba.org by Rebecca Melnitsky

Artificial intelligence can perform several tasks to aid lawyers and save time. But lawyers must be cautious when using this new technology, lest they break confidentiality or violate ethical standards.
The New York State Bar Association hosted a hybrid program discussing AI’s potential and its pitfalls for the legal profession. More than 300 people watched the livestream.
For that reason, Unger suggests using legal AI tools, like LexisNexis AI, Westlaw Edge, and vLex Fastcase, for legal research instead of general generative AI tools. While legal-specific tools still hallucinate, they hallucinate much less. A legal tool will hallucinate 10% to 20% of the time, while a tool like ChatGPT will hallucinate 50% to 80%.
Fresh Voices on Legal Tech with Nikki Shaver — from legaltalknetwork.com by Dennis Kennedy, Tom Mighell, and Nikki Shaver
Determining which legal technology is best for your law firm can seem like a daunting task, so Legaltech Hub does the hard work for you! In another edition of Fresh Voices, Dennis and Tom talk with Nikki Shaver, CEO at Legaltech Hub, about her in-depth knowledge of technology and AI trends. Nikki shares what effective tech strategies should look like for attorneys and recommends innovative tools for maintaining best practices in modern law firms. Learn more at legaltechnologyhub.com.
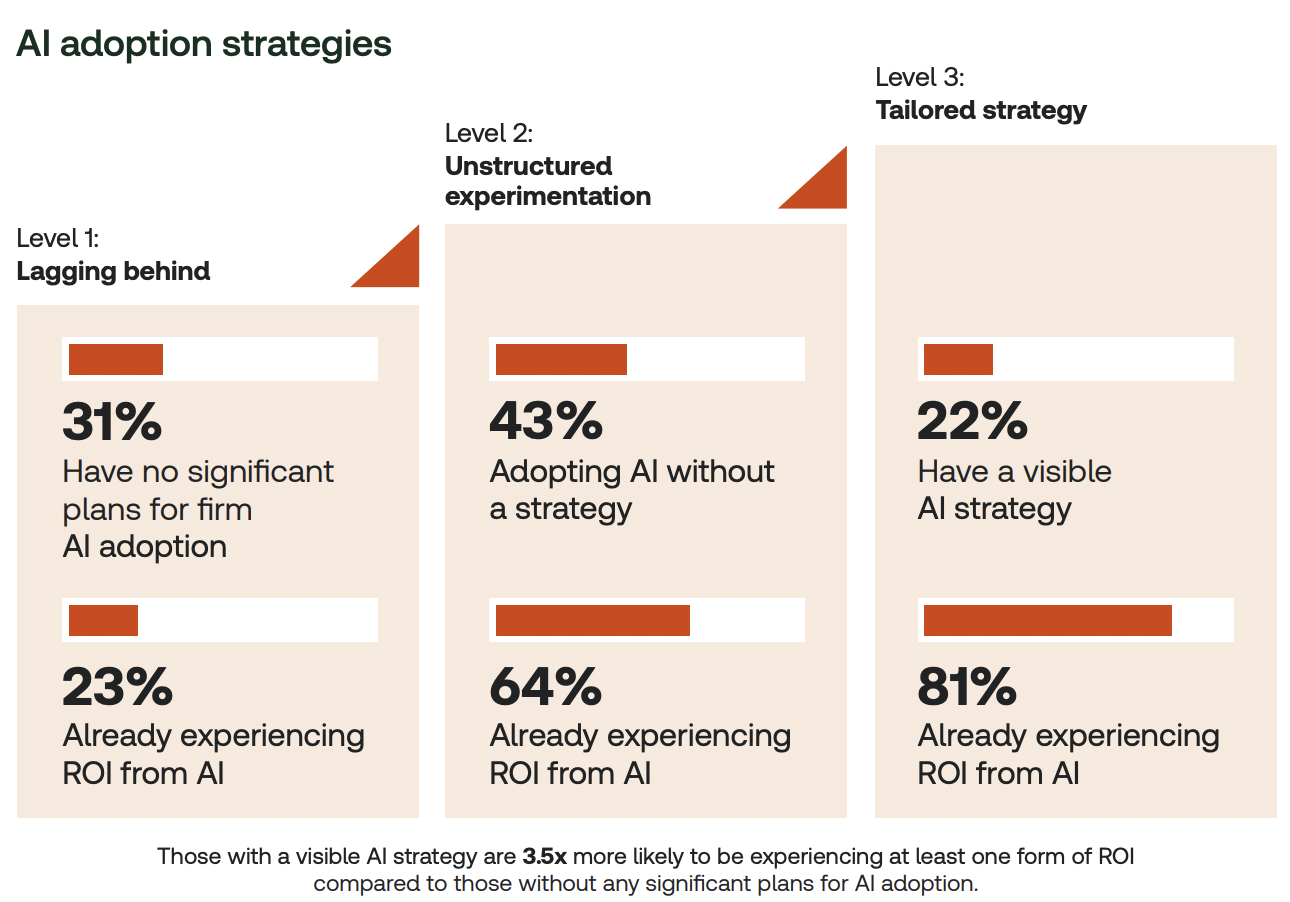
AI for in-house legal: 2025 predictions — from deloitte.com
Our expectations for AI engagement and adoption in the legal Market over the coming year.
AI will continue to transform in-house legal departments in 2025
As we enter 2025, over two-thirds of organisations plan to increase their Generative AI (GenAI) investments, providing legal teams with significant executive support and resources to further develop this Capabilities. This presents a substantial opportunity for legal departments, particularly as GenAI technology continues to advance at an impressive pace. We make five predictions for AI engagement and adoption in the legal Market over the coming year and beyond.
Navigating The Fine Line: Redefining Legal Advice In The Age Of Tech With Erin Levine And Quinten Steenhuis — from abovethelaw.com by Olga V. Mack
The definition of ‘practicing law’ is outdated and increasingly irrelevant in a tech-driven world. Should the line between legal advice and legal information even exist?
Practical Takeaways for Legal Leaders
- Use Aggregated Data: Providing consumers with benchmarks (e.g., “90% of users in your position accepted similar settlements”) empowers them without giving direct legal advice.
- Train and Supervise AI Tools: AI works best when it’s trained on reliable, localized data and supervised by legal professionals.
- Partner with Courts: As Quinten pointed out, tools built in collaboration with courts often avoid UPL pitfalls. They’re also more likely to gain the trust of both regulators and consumers.
- Embrace Transparency: Clear disclaimers like “This is not legal advice” go a long way in building consumer trust and meeting ethical standards.











-p-3200.png)