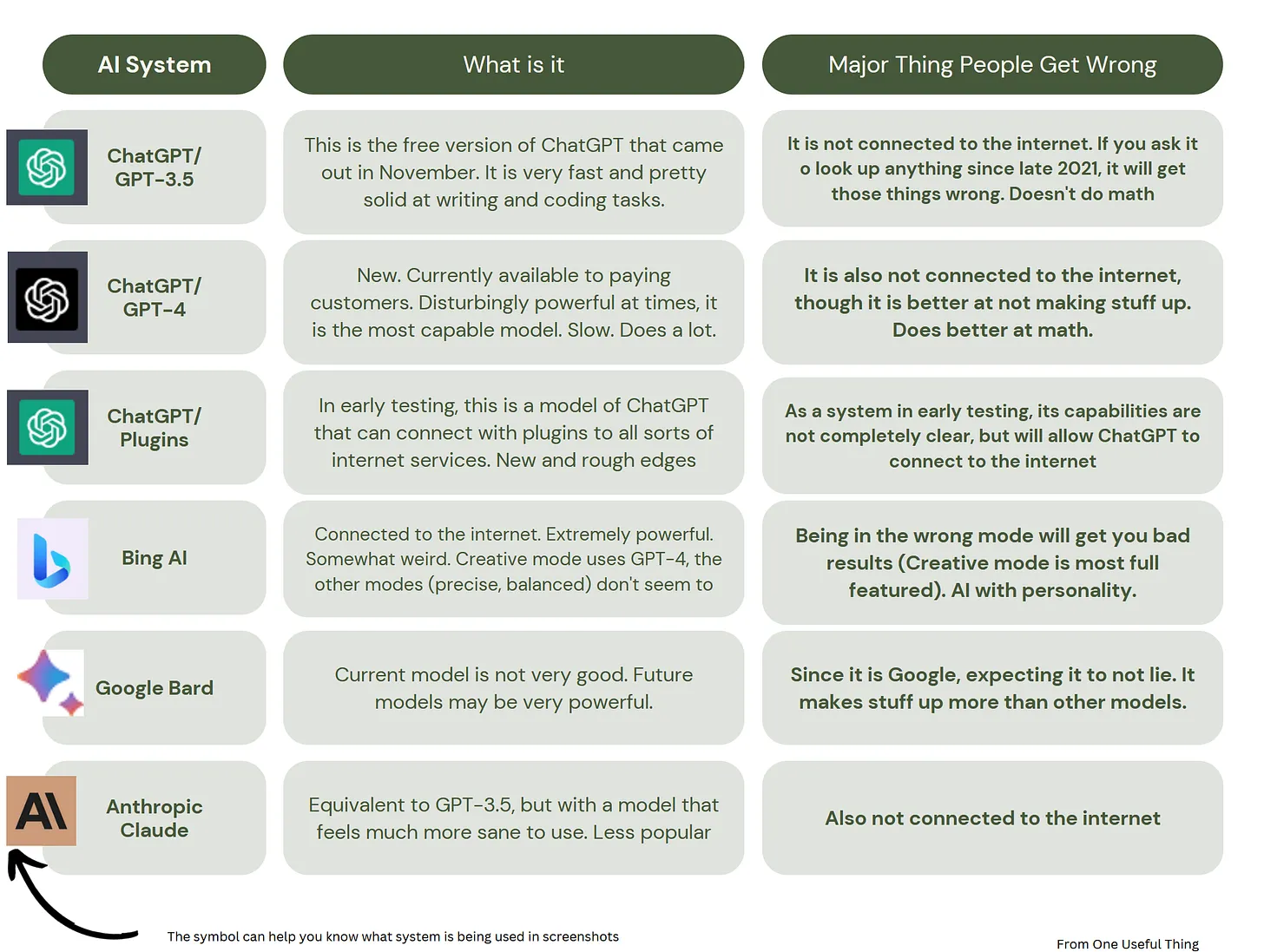
From DSC:
Before we get to Scott Belsky’s article, here’s an interesting/related item from Tobi Lutke:
I just clued in how insane text2vid will get soon. As crazy as this sounds, we will be able to generate movies from just minor prompts and the path there is pretty clear.
— tobi lutke (@tobi) March 29, 2023
Our World Shaken, Not Stirred: Synthetic entertainment, hybrid social experiences, syncing ourselves with apps, and more. — from implications.com by Scott Belsky
Things will get weird. And exciting.
Excerpts:
Recent advances in technology will stir shake the pot of culture and our day-to-day experiences. Examples? A new era of synthetic entertainment will emerge, online social dynamics will become “hybrid experiences” where AI personas are equal players, and we will sync ourselves with applications as opposed to using applications.
Unauthorized sequels, spin-offs, some amazing stuff, and a legal dumpster fire: Now lets shift beyond Hollywood to the fast-growing long tail of prosumer-made entertainment. This is where entirely new genres of entertainment will emerge including the unauthorized sequels and spinoffs that I expect we will start seeing.
Also relevant/see:
Digital storytelling with generative AI: notes on the appearance of #AICinema — from bryanalexander.org by Bryan Alexander
Excerpt:
This is how I viewed a fascinating article about the so-called #AICinema movement. Benj Edwards describes this nascent current and interviews one of its practitioners, Julie Wieland. It’s a great example of people creating small stories using tech – in this case, generative AI, specifically the image creator Midjourney.
Bryan links to:
Artists astound with AI-generated film stills from a parallel universe — from arstechnica.com by Benj Edwards
A Q&A with “synthographer” Julie Wieland on the #aicinema movement.
From DSC:
How will text-to-video impact the Learning and Development world? Teaching and learning? Those people communicating within communities of practice? Those creating presentations and/or offering webinars?
Hmmm…should be interesting!