Best Month Of Code 2020 Coding Kit Products — from techlearning.com by Luke Edwards
The best kits to get the most out of the Month of Code 2020




Best Month Of Code 2020 Coding Kit Products — from techlearning.com by Luke Edwards
The best kits to get the most out of the Month of Code 2020
From DSC:
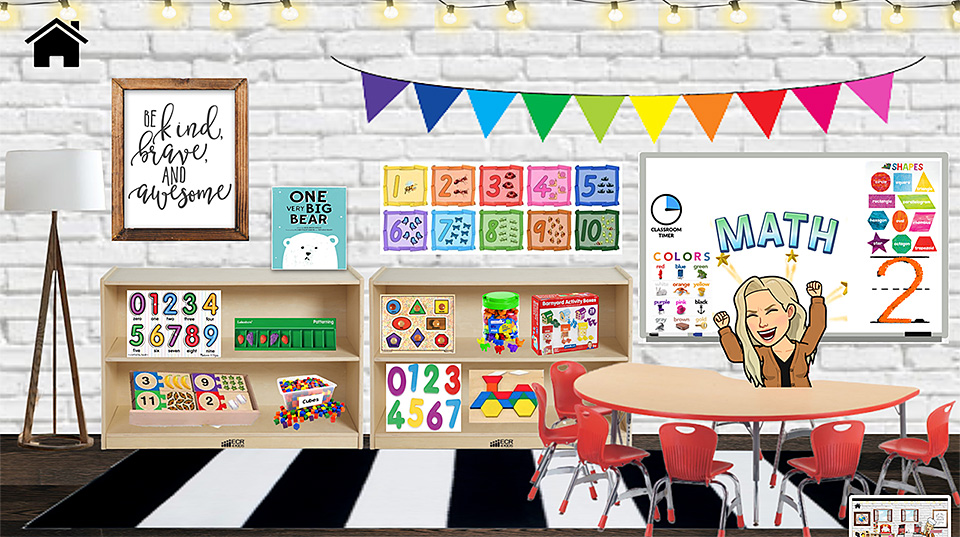
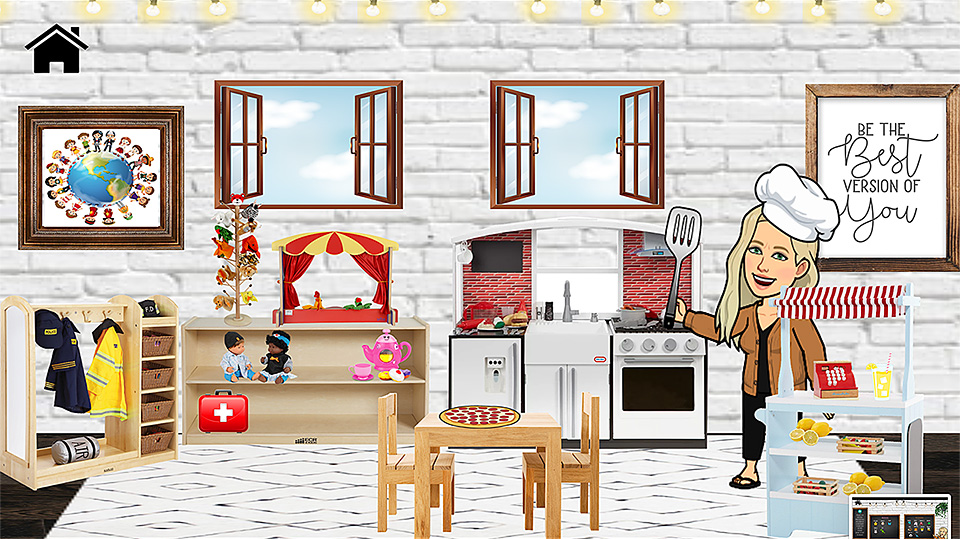
Our oldest daughter showed me a “Bitmoji Classroom” that her mentor teacher — Emily Clay — uses as her virtual classroom. Below are some snapshots of the Google Slides that Emily developed based on the work of:
My hats off to all of these folks whose work laid the foundations for this creative, fun, engaging, easy-to-follow virtual classroom for a special education preschool classroom — complete with ties to videoconferencing functionalities from Zoom. Emily’s students could click on items all over the place — they could explore, pursue their interests/curiosities/passions. So the snapshots below don’t offer the great interactivity that the real deal does.
Nice work Emily & Company! I like how you provided more choice, more control to your students — while keeping them engaged!


From DSC:
I also like the idea of presenting this type of slide (immediately below, and students’ names have been blurred for privacy’s sake) prior to entering a videoconferencing session where you are going to break out the students into groups. Perhaps that didn’t happen in Emily’s class…I’m not sure, but in other settings, it would make sense to share one’s screen right before sending the students to those breakout rooms and show them that type of slide (to let them know who will be in their particular breakout group).
The students in the different breakout sessions could then collaboratively work on Google Docs, Sheets, or Slides and you could watch their progress in real-time!




Also see:
3 educational websites for history and social studies — from educatorstechnology.com
Excerpt:
Below are three websites we are featuring in our blog for the first time. These are platforms where teachers (and students) can access resources and teaching materials to help them with their history teaching (learning). We invite you to check them out and share with us your feedback.
New York, NY – November 26, 2020 – The Intercept has published a video investigation by filmmaker Emily Cohen Ibañez on the impact of the switch to remote learning –– and the Coronavirus pandemic –– on students in an agro-industrial town (Watsonville, CA) and an affluent Bay Area suburb (Pine Hills, CA).
The Intercept: https://
YouTube link: https://youtu.be/7_YoSFNe2lM
“Life at Watsonville High was fast-paced, full of a lot of energy, a lot of really amazing students,” said Dr. Sara Roe, an English Learner Coach at Watsonville High. “Watsonville High is 98 percent Latinx, Latino, Latina. We are made up of a higher percentage of first-generation students. Socioeconomically, we’re predominantly a low-income area, so 100 percent of our students receive free and reduced lunch, and most likely, their parents or someone in their family has worked in the fields or is currently working in the fields.”
“If we thought then that kids had social, emotional challenges, their needs weren’t being met in particular ways,” said Dr. Roe, “If we thought there were issues then, I don’t think we could have ever imagined what the implications of going online would uncover for us in terms of issues for students.”
#digitaldivide #education #remotelearning #K12 #edtech #digitalequity
Saving — and Enhancing — Music Education With Online Learning — from edcircuit.com by D. Travis Washington
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
I teach Choir and lead the Young Vocal Scholars Program, and before COVID arrived, we were excited to move forward on the culmination of learning through live performances. With school closure, all that changed, and we were forced to adapt to virtual learning. Through the initial transition, we discovered that online learning options such as Soundtrap could not only extend projects we were currently working on but expand music learning to previously unimaginable heights.
…
When Covid hit and we couldn’t continue with the traditional choir program, my school looked for remote solutions. Soundtrap was exactly what we needed. We began conducting Young Vocal Scholars choir sessions remotely through Soundtrap and filled our extra Soundtrap seats with students from the District 8 Choir who weren’t being served music at all — doing similar projects that we had been creating previously in my classes. It was incredible to suddenly recognize that there were far more students interested in music who could connect via their laptops and tablets at home.
Also see:
Soundtrap revolutionized my classroom in a virtual setting. Students became more engaged than ever before. My “4-star artists,” as I refer to my highly motivated students, kept making songs. I recall one of them saying to me, “Music class was cool because we sang together, but Soundtrap is cooler because it allows us to make projects together and they sound good.”
Librarians become go-to resource during school closures — from educationdive.com by Shawna De La Rosa
Dive Brief:
https://www.kxan.com/pass-or-fail/students-meet-in-austin-churches-for-free-virtual-learning-pods-during-pandemic/
Ann Arbor church transformed into schoolhouse so immigrant children don’t fall behind — from mlive.com by Martin Slagter
Understanding the learning pods landscape — from crpe.org by Ashley Jochim and Robin Lake
Mapping the Pandemic Learning Landscape — from medium.com by Carolyn Gramstorff
Today we launched a national database that will catalogue and make sense of #learningpod initiatives across the country, with an eye toward equity.
Explore data on the 160 pods and hubs we've found so far: https://t.co/uAINWVPdqr
Read the blog: https://t.co/2yGqKVgSdL pic.twitter.com/Ts3Q9YiIYx
— Center on Reinventing Public Education (@CRPE_UW) November 19, 2020

Purdue Project Tackles AR/VR for Workforce Ed — from campustechnology.com by Dian Schaffhauser
Excerpt:
Purdue University has received a $3 million grant from the National Science Foundation to continue development of a prototype that will facilitate workforce education being done through augmented reality and virtual reality.
How Can Schools Prepare for VR/AR Integration? https://t.co/X3FhkUPyfZ via @VRScout
— Daniel Christian (he/him/his) (@dchristian5) November 15, 2020
Pushback is growing against automated proctoring services. But so is their use — from edsurge.com by Jeffrey R. Young
Excerpt:
Many students have pushed back, arguing that remote proctoring tools result in a serious invasion of privacy and create stress that can hinder academic performance. More than 60,000 students across the U.S. have signed petitions calling on their colleges to stop using automated proctoring tools, meaning that the technology has become arguably the most controversial tool of the pandemic at colleges.
From DSC:
We have an issue oftentimes within higher education — including graduate schools/professional schools as well — where the student and the professor aren’t always on the same team (or at least that’s the percaption). To me, the professors need to be saying (and living out the message that), “We ARE on your team. We are working to help make you successful in the future that you have chosen for yourself. We’re here to help you…not monitor you.”
It’s like I feel when I walk into so many public places these days (and even out on the roadways as well). When I walk into a store, it’s like the security cameras are whispering to me and to others…”We don’t trust you. Some of you have stolen in the past. so we’re going to carefully watch every single one of you. And we aren’t just going to watch you, we’re going to record you as well.”
The message? We don’t trust you.
This severely hampers the relationships involved.
And I’m sure that cheating is going on. But then, that makes me think that perhaps it’s time to change the way we assess students — and to help them see assessments as opportunities to learn, not to cheat.
Lower the stakes. Offer tests more frequently. Provide more opportunities to practice recall. And be on their team.
Temperament-Inclusive Pedagogy: Helping Introverted and Extraverted Students Thrive in a Changing Educational Landscape — from onlinelearningconsortium.org by Mary R. Fry
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
So how do we take these different approaches to learning into account and foster a classroom environment that is more inclusive of the needs of both extraverts and introverts? Let’s first distinguish between how extraverts and introverts most prefer to learn, and then discuss ways to meet the needs of both. Extraverts tend to learn through active and social engagement with the material (group work, interactive learning experiences, performing and discussing). Verbalizing typically helps extraverts to think through their ideas and to foster new ones. They often think quickly on their feet and welcome working in large groups. It can be challenging for extraverts to generate ideas in isolation (talking through ideas is often needed) and thus working on solitary projects and writing can be challenging.
In contrast, introverts thrive with solitary/independent work and typically need this time to sort through what they are learning before they can formulate their thoughts and articulate their perspectives. Introverted learners often dislike group work (or at least the group sizes and structures that are often used in the classroom (more on this in a moment)) and find their voice drowned out in synchronous discussions as they don’t typically think as fast as their extroverted counterparts and don’t often speak until they feel they have something carefully thought out to share. Introverted learners are often quite content, and can remain attentive, through longer lectures and presentations and prefer engaging with the material in a more interactive way only after a pause or break.
From DSC:
Could/would a next-generation learning platform that has some Artificial Intelligence (AI) features baked into it — working in conjunction with a cloud-based learner profile — be of assistance here?
That is, maybe a learner could self-select the type of learning that they are: introverted or extroverted. Or perhaps they could use a sliding scaled to mix learning activities up to a certain degree. Or perhaps if one wasn’t sure of their preferences, they could ask the AI-backed system to scan for how much time they spent doing learning activities X, Y, and Z versus learning activities A, B, and C…then AI could offer up activities that meet a learner’s preferences.
(By the way, I love the idea of the “think-ink-pair-share” — to address both extroverted and introverted learners. This can be done digitally/virtually as well as in a face-to-face setting.)
All of this would further assist in helping build an enjoyment of learning. And wouldn’t that be nice? Now that we all need to learn for 40, 50, 60, 70, or even 80 years of our lives?
Virtual Reality: Realizing the Power of Experience, Excursion and Immersion in the Classroom — from nytimes.com
A framework for teaching with New York Times 360 V.R. videos, plus eight lesson plans for STEM and the humanities.
A Guide for Using NYT VR With Students
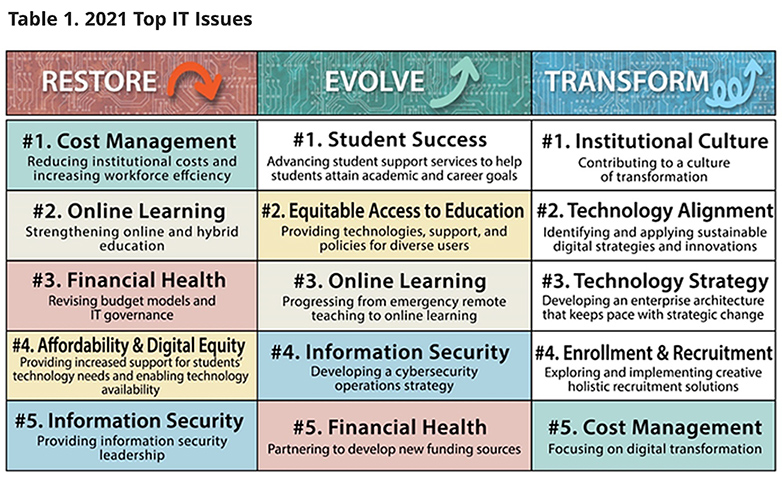
Top IT Issues, 2021: Emerging from the Pandemic — from educause.edu
Excerpt:
The EDUCAUSE Top IT Issues list has been refactored for 2021 to help higher education shape the role technology will play in the recovery from the pandemic. What different directions might institutional leaders take in their recovery strategy? How can technology help our ecosystem emerge stronger and fitter for the future?
The 2021 EDUCAUSE IT Issues project explores these questions using a very different approach from previous years. Anticipating potential ways institutions might emerge from the pandemic, this year we offer three Top IT Issues lists and examine the top 5 issues within three scenarios that may guide institutional leaders’ use of technology: restore, evolve, and transform.
Also see:
OPM Market Landscape and Dynamics: Fall 2020 updates — from philonedtech.com by Phil Hill; with thanks to Edsurge.com for this resource
Excerpt:
There has been growing interest in the Online Program Management (OPM) market, as more schools try to develop a strategy and revenue model for online programs (particularly for master’s level). In addition, there has been a broad question to what degree schools would turn to OPM partners to help out with the Covid-driven move to online education in 2020 and beyond. We’re in the middle of the chaotic period of the pandemic, so there are no clear answers yet, but the consistent message is that OPM vendors are seeing a marked increase in interest from colleges and universities this year.