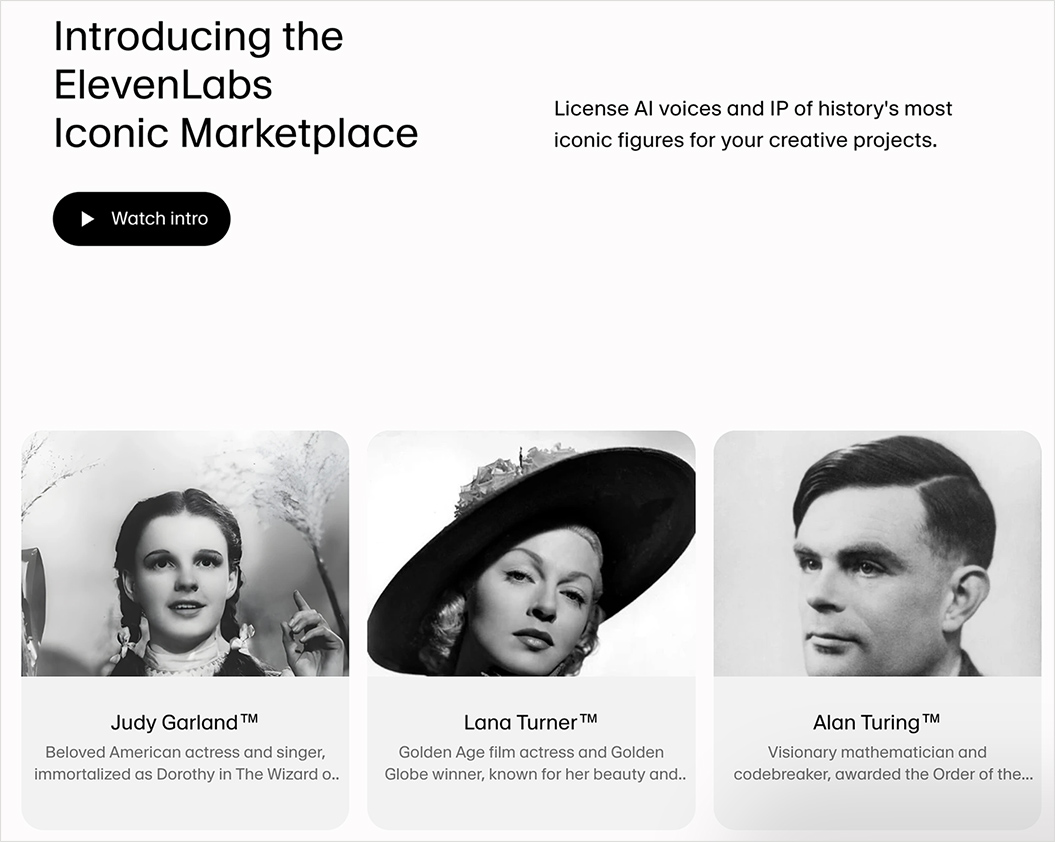
ElevenLabs just launched a voice marketplace — from elevenlabs.io; via theaivalley.com
Via the AI Valley:
Why does it matter?
AI voice cloning has already flooded the internet with unauthorized imitations, blurring legal and ethical lines. By offering a dynamic, rights-secured platform, ElevenLabs aims to legitimize the booming AI voice industry and enable transparent, collaborative commercialization of iconic IP.
.
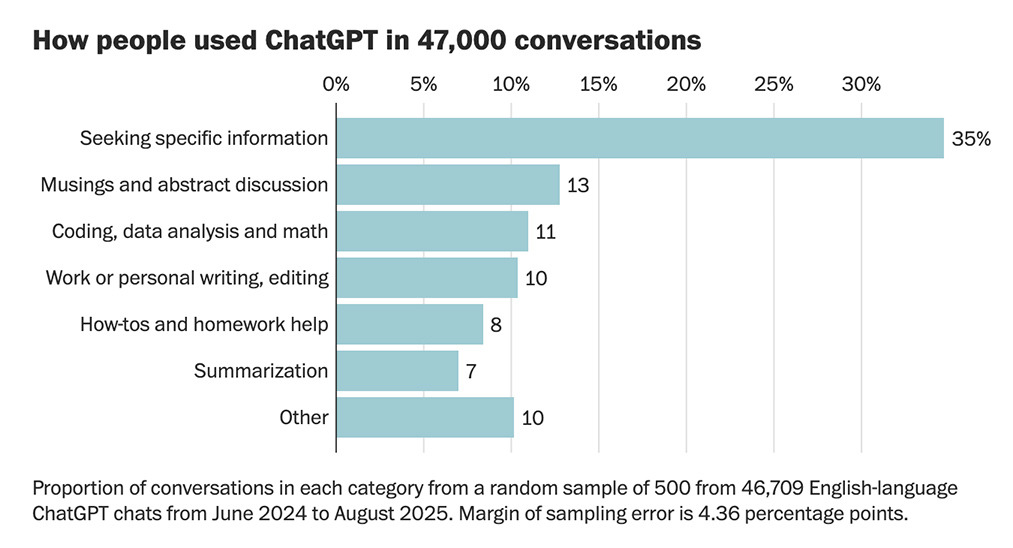
[GIFTED ARTICLE] How people really use ChatGPT, according to 47,000 conversations shared online — from by Gerrit De Vynck and Jeremy B. Merrill
What do people ask the popular chatbot? We analyzed thousands of chats to identify common topics discussed by users and patterns in ChatGPT’s responses.
.
Data released by OpenAI in September from an internal study of queries sent to ChatGPT showed that most are for personal use, not work.
Emotional conversations were also common in the conversations analyzed by The Post, and users often shared highly personal details about their lives. In some chats, the AI tool could be seen adapting to match a user’s viewpoint, creating a kind of personalized echo chamber in which ChatGPT endorsed falsehoods and conspiracy theories.
Lee Rainie, director of the Imagining the Digital Future Center at Elon University, said his own research has suggested ChatGPT’s design encourages people to form emotional attachments with the chatbot. “The optimization and incentives towards intimacy are very clear,” he said. “ChatGPT is trained to further or deepen the relationship.”
Per The Rundown: OpenAI just shared its view on AI progress, predicting systems will soon become smart enough to make discoveries and calling for global coordination on safety, oversight, and resilience as the technology nears superintelligent territory.
The details:
- OpenAI said current AI systems already outperform top humans in complex intellectual tasks and are “80% of the way to an AI researcher.”
- The company expects AI will make small scientific discoveries by 2026 and more significant breakthroughs by 2028, as intelligence costs fall 40x per year.
- For superintelligent AI, OAI said work with governments and safety agencies will be essential to mitigate risks like bioterrorism or runaway self-improvement.
- It also called for safety standards among top labs, a resilience ecosystem like cybersecurity, and ongoing tracking of AI’s real impact to inform public policy.
Why it matters: While the timeline remains unclear, OAI’s message shows that the world should start bracing for superintelligent AI with coordinated safety. The company is betting that collective safeguards will be the only way to manage risk from the next era of intelligence, which may diffuse in ways humanity has never seen before.
Which linked to:
- AI progress and recommendations — from openai.com
AI is unlocking new knowledge and capabilities. Our responsibility is to guide that power toward broad, lasting benefit.
From DSC:
I hate to say this, but it seems like there is growing concern amongst those who have pushed very hard to release as much AI as possible — they are NOW worried. They NOW step back and see that there are many reasons to worry about how these technologies can be negatively used.
Where was this level of concern before (while they were racing ahead at 180 mph)? Surely, numerous and knowledgeable people inside those organizations warned them about the destructive/downside of these technologies. But their warnings were pretty much blown off (at least from my limited perspective).
The state of AI in 2025: Agents, innovation, and transformation — from mckinsey.com
Key findings
- Most organizations are still in the experimentation or piloting phase: Nearly two-thirds of respondents say their organizations have not yet begun scaling AI across the enterprise.
- High curiosity in AI agents: Sixty-two percent of survey respondents say their organizations are at least experimenting with AI agents.
- Positive leading indicators on impact of AI: Respondents report use-case-level cost and revenue benefits, and 64 percent say that AI is enabling their innovation. However, just 39 percent report EBIT impact at the enterprise level.
- High performers use AI to drive growth, innovation, and cost: Eighty percent of respondents say their companies set efficiency as an objective of their AI initiatives, but the companies seeing the most value from AI often set growth or innovation as additional objectives.
- Redesigning workflows is a key success factor: Half of those AI high performers intend to use AI to transform their businesses, and most are redesigning workflows.
- Differing perspectives on employment impact: Respondents vary in their expectations of AI’s impact on the overall workforce size of their organizations in the coming year: 32 percent expect decreases, 43 percent no change, and 13 percent increases.
Marble: A Multimodal World Model — from worldlabs.ai
Spatial intelligence is the next frontier in AI, demanding powerful world models to realize its full potential. World models should reconstruct, generate, and simulate 3D worlds; and allow both humans and agents to interact with them. Spatially intelligent world models will transform a wide variety of industries over the coming years.
Two months ago we shared a preview of Marble, our World Model that creates 3D worlds from image or text prompts. Since then, Marble has been available to an early set of beta users to create 3D worlds for themselves.
Today we are making Marble, a first-in-class generative multimodal world model, generally available for anyone to use. We have also drastically expanded Marble’s capabilities, and are excited to highlight them here: