How artificial intelligence could transform government — from Deloitte University Press
Cognitive technologies have the potential to revolutionize the public sector—and save billions of dollars
Excerpt:
The rise of more sophisticated cognitive technologies is, of course, critical to that third era, aiding advances in several categories:
- Rules-based systems capture and use experts’ knowledge to provide answers to tricky but routine problems. As this decades-old form of AI grows more sophisticated, users may forget they aren’t conversing with a real person.
- Speech recognition transcribes human speech automatically and accurately. The technology is improving as machines collect more examples of conversation. This has obvious value for dictation, phone assistance, and much more.
- Machine translation, as the name indicates, translates text or speech from one language to another. Significant advances have been made in this field in only the past year.8 Machine translation has obvious implications for international relations, defense, and intelligence as well as, in our multilingual society, numerous domestic applications.
- Computer vision is the ability to identify objects, scenes, and activities in naturally occurring images. It’s how Facebook sorts millions of users’ photos, but it can also scan medical images for indications of disease and identify criminals from surveillance footage. Soon it will allow law enforcement to quickly scan license plate numbers of vehicles stopped at red lights, identifying suspects’ cars in real time.
- Machine learning takes place without explicit programming. By trial and error, computers learn how to learn, mining information to discover patterns in data that can help predict future events. The larger the datasets, the easier it is to accurately gauge normal or abnormal behavior. When your email program flags a message as spam, or your credit card company warns you of a potentially fraudulent use of your card, machine learning may be involved. Deep learning is a branch of machine learning involving artificial neural networks inspired by the brain’s structure and function.9
- Robotics is the creation and use of machines to perform automated physical functions. The integration of cognitive technologies such as computer vision with sensors and other sophisticated hardware has given rise to a new generation of robots that can work alongside people and perform many tasks in unpredictable environments. Examples include drones, robots used for disaster response, and robot assistants in home health care.
- Natural language processing refers to the complex and difficult task of organizing and understanding language in a human way. This goes far beyond interpreting search queries, or translating between Mandarin and English text. Combined with machine learning, a system can scan websites for discussions of specific topics even if the user didn’t input precise search terms. Computers can identify all the people and places mentioned in a document or extract terms and conditions from contracts. As with all AI-enabled technology, these become smarter as they consume more accurate data—and as developers integrate complementary technologies such as machine translation and natural language processing.
…
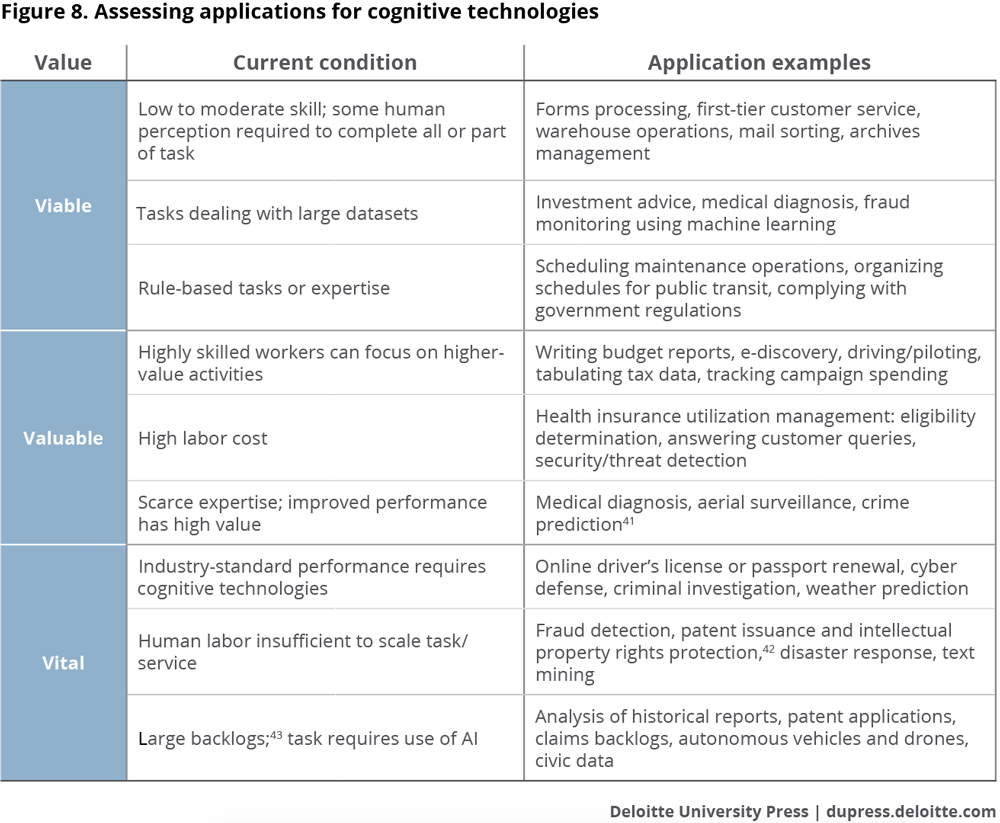
We’ve developed a framework that can help government agencies assess their own opportunities for deploying these technologies. It involves examining business processes, services, and programs to find where cognitive technologies may be viable, valuable, or even vital. Figure 8 summarizes this “Three Vs” framework. Government agencies can use it to screen the best opportunities for automation or cognitive technologies.