From DSC:
Late last week, I ran into several items re: the state of the journalism industry in America. The bottom line is not encouraging. And this should concern every citizen who wants to see our democracy do well.
Here are some items that got me to reflect on this issue/situation:
The State of Local News — from localnewsinitiative.northwestern.edu (Northwestern University); via Ryan Craig’s Gap Letter from last week
Executive Summary (emphasis DSC)
There was both good news and bad news for local journalism this past year. The good news raised the possibility that a range of proposals and programs could begin to arrest the steep loss of local news over the past two decades and, perhaps, revive journalism in some places that have lost their news. The headlines on the bad news resoundingly conveyed the message that urgent action is needed in many venues — from boardrooms to the halls of Congress — and by many, including civic-minded organizations and entrepreneurs.
At the same time, however, the number of local news outlets continued to contract at an even steeper rate in 2023. On the current trajectory, by the end of next year, the country will have lost a third of its newspapers since 2005. Discouragingly, the growth in alternative local news sources — digital and ethnic news outlets, as well as public broadcasting — has not kept pace with what’s being lost.
Newspapers are continuing to vanish at an average rate of more than two a week.
…
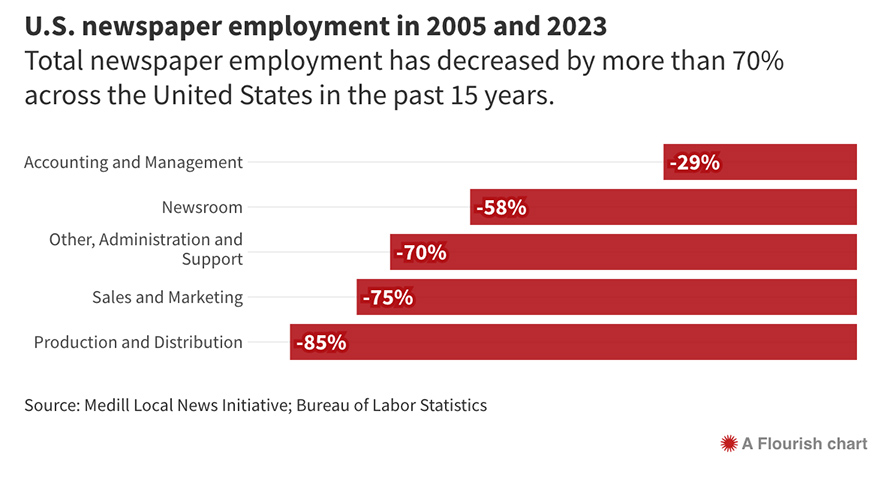
In addition to losing almost a third of its newspapers, the country has lost almost two-thirds of its newspaper journalists — 43,000 — since 2005.
Opinion: Local news can seize the moment — from crainsdetroit.com by Sue Ellen Christian
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
Our society isn’t short on news, we’re short on attention. How do we get honest reporting on local events and issues noticed by readers, viewers and listeners in our digital age of content saturation, misinformation and online chaos? Plus, not only are adults overall consuming less news, but many also now intentionally avoid any news and its attendant hyperbole, negativity and fear-mongering.
Local news is an oasis from the national muck. The Gallup/Knight study from last year showed that adults in the U.S. trust local news organizations two times more than national news outlets (44% to 21%), and perceive local journalists as caring more about the impact of their reporting.
For the collaborative and the nation’s many struggling local news outlets, there was this hope-giving finding: “When Americans perceive that local news organizations do not have the resources to report the news accurately and fairly, they are more likely to say they would consider paying for news in the future,” stated the report.
The future is now, people.
A healthy democracy depends on an informed citizenry. Local news is essential, and today’s financially struggling outlets need local paying subscribers.
From DSC: Also as a relevant aside:
Wonder Media
This website is dedicated to helping you learn more about how to use
the media for your purposes, and not to be used by media. Explore
the site to learn about media literacy and news media literacy
through games, videos, quizzes, and more.
Opinion: Stronger democracy is worth the investment — from crainsdetroit.com by Hugh Dellios
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
By itself, philanthropy isn’t the ultimate solution. But it can be a bridge to a moment when this generation’s media entrepreneurs have had a chance to solve the puzzle of a more sustainable business model, one that serves audience needs, counts on a variety of solid revenue streams, and restores value in producing news.
A strong, free press is essential to the functioning of our society – and that’s why it’s the only private industry specifically protected by the U.S. Constitution. But unless we invest in real newsrooms, we’ll continue to see the disappearance of real reporters who ask the tough, informed questions that help forge good policy and hold our leaders accountable.
The return on that investment? A better-functioning, more stable democracy. The alternative? Maybe waking up one day without one.
With local journalism ‘in crisis,’ Michigan newsrooms get creative to fill the gap — from crainsdetroit.com by Julie Mack
Local journalism is “in crisis,” said Tim Franklin, who heads Northwestern’s Local News Initiative and is a former top editor at the Indianapolis Star, Orlando Sentinel and Baltimore Sun.
“I equate the local news crisis to being journalism’s climate change. It’s this grinding attrition,” he said. “We’re at a real inflection point for local news in America. The question is, how are we going to get out of this?”
.
“I really do believe there’s never been a better time to be a corrupt local politician because nobody is watching the henhouse,” said Sue Ellen Christian, a former Chicago Tribune reporter and now a Western Michigan University journalism professor. “There are very few local reporters now, few local news outlets with the bandwidth to pull the documents, go to obscure committee meetings — that’s where you find the story, the string that you pull that becomes a really good, important local news story.”