From DSC:
On a macro scale…this is on my heart these days.
I ran across some troubling but informative items re: religion in America from item #5 at Rex Woodbury’s 10 Charts That Capture How the World Is Changing:
- How Religious Are Americans? — from news.gallup.com
- The long-term decline in church attendance is linked to a drop in religious identification in general — particularly for Protestant religions — but also to decreasing weekly attendance among U.S. Catholics.
- Steep Decline in U.S. Church Membership
Additionally, less than half of Americans, 45%, belong to a formal house of worship. Church membership has been below the majority level each of the past four years. When Gallup first asked the question in 1937, 73% were members of a church, and as recently as 1999, 70% were. The decline in formal church membership has largely been driven by younger generations of Americans. Slightly more than one-third of U.S. young adults have no religious affiliation. Further, many young adults who do identify with a religion do not belong to a church. But even older adults who have a religious preference are less likely to belong to a church today than in the past.
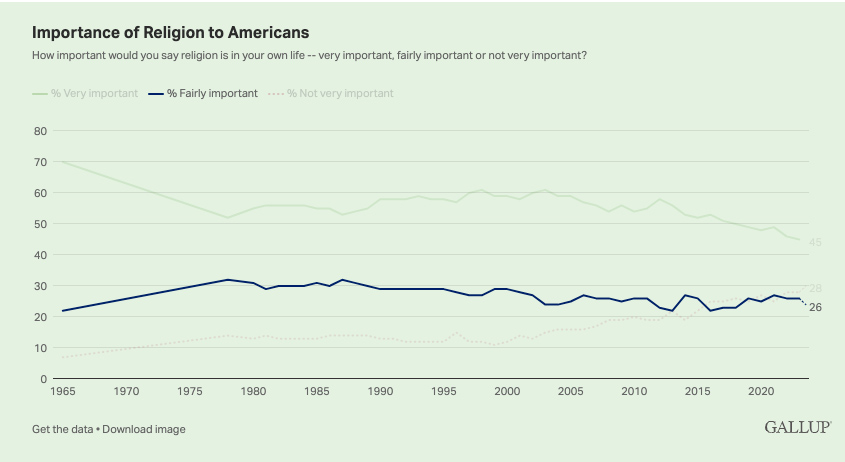
.
I’ve known about this decline for years now, but Rex’ posting and graphs were disheartening nonetheless. And Samuel Abrams’ article contains many reflections that I’ve had as well.
The Christian journey is about transformation — our hearts and minds are changed so that we become more like Jesus Christ (the pioneer and perfecter of [our] faith, per Hebrews 12:2). This transformation involves how we see and experience the world as well as how we are supposed to treat others. We receive new “glasses” if you will — new lenses on the world. In fact, Jesus said in Matthew 22:37-40:
37 Jesus replied: “‘Love the Lord your God with all your heart and with all your soul and with all your mind.’ 38 This is the first and greatest commandment. 39 And the second is like it: ‘Love your neighbor as yourself.’ 40 All the Law and the Prophets hang on these two commandments.”
So Christians are taught to love our neighbors. I/we mess up on this constantly, but many of us are trying to get better at it.
But what happens when we don’t love — or even care for/about — our neighbor? Do you know that if you are living in the United States right now, you are already feeling and experiencing the impact of this in an enormous way?
Here are a few ways that you can see this playing out — even from a secular/business standpoint:
- Numerous businesses don’t care at all if their products harm you, your family, or your future. For example, food companies don’t care if their products aren’t good for you — they just want your repeat business. They are concerned FAR more about Wall Street and their shareholders than about your health. With knowing that I am a chief sinner, I could also point to those businesses pushing marijuana/cannabis (especially right next to universities and colleges), cigarettes, gambling, and others. There are some dubious folks within the healthcare and pharmaceutical industries as well.
- Many businesses lie to you when you call into their 800 #’s and they tell you that they care about you and your business. Again we see that they greatly appreciate your money, but they really don’t care about you or your time. They often put you in a long queue. The worst voice response units are programmed to make it extremely difficult — if not impossible — to let you talk to a live person.
- Many businesses have embarked on the shrinkification of their products: offering smaller amounts but charging the same.
- Many businesses don’t care if our youth are being negatively impacted (social media companies may come to some peoples’ minds. Disclaimer: I use Twitter/X and LinkedIn frequently).
- Many businesses don’t care if their technologies are beneficial to society. They don’t stop to think about whether they should design and produce their products…just whether or not they can. Little to no wisdom is being displayed here.
- …and I — and you — could list many more here.
So you and I are already being impacted when we push God out of our lives and out of our institutions. When we Americans look around these days..how’s that going for us? In my own life, the further I get away from God, the worse things get.
Also, we could talk about mental health*, shootings in our schools and on our streets, and several other things.
Do we care? I do. I think about this kind of thing more and more these days. LORD, forgive us. We need your help.
* I realize that Christians can struggle with mental health too





















