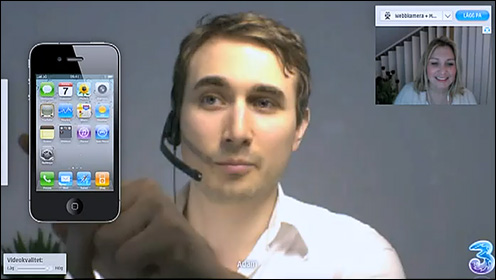
Video Conferencing Guidelines for Faculty and Students in Graduate Online Courses — from jolt.merlot.org and California State University, Fullerton; by Gautreau, Glaeser, Renold, Ahmed, Lee, Carter-Wells, Worden, Boynton, & Schools
Excerpts:
Abstract
A review of the literature revealed that established guidelines were not available to assist faculty who use video conferencing in their online graduate courses. In an effort to address this need, a self-evaluation study was completed with faculty who teach such courses. Drawing on the results of this study together with published Netiquette guidelines and a survey of other extant literature, a set of Video Conferencing Guidelines was created.
Video Conferencing Guidelines for Online Graduate Students
- Guideline #1: Remember you are on camera and live. The advantage of video conferencing is that you can take advantage of facial expressions, inflection, and tone of voice. Remember to think before you respond to make your thoughts and ideas clear and coherent to the video conferencing participants.
- Guideline #2: Adhere to the same standards of behavior during the video conferencing session that you would follow in real life.
- Guideline #3: Be mindful of all video conferencing participants. Allow other participants time and opportunities to contribute to the discussion and share their ideas with the group.
- Guideline #4: Video conferencing provides synchronous opportunities to share knowledge. It is important to consider opinions from other participants who are engaged in the video conferencing session. Strive for a fairly equal balance among the participants.
- Guideline #5: Be mindful of your tone and expressions during the video conferencing session. This is not an anonymous session. Your voice and video are viewed by all who are participating in the chat session.
- Guideline #6: Share your expertise and knowledge. Be an active contributor during the video conferencing session.
- Guideline #7: Remain professional in your communication with participants.
- Guideline #8: Respect the context of the video conferencing session. Keep video conferencing sessions within the context of the conversation. If the session is recorded do not post isolated comments that may be taken out of context. Synchronous discussions take on a life of their own; therefore, it is important to keep conversations in context.
- Guideline #9: Be forgiving of mistakes during the video conferencing session. Video conferencing is a new communication platform. There are bound to be technical glitches; be patient with the participants during the session.