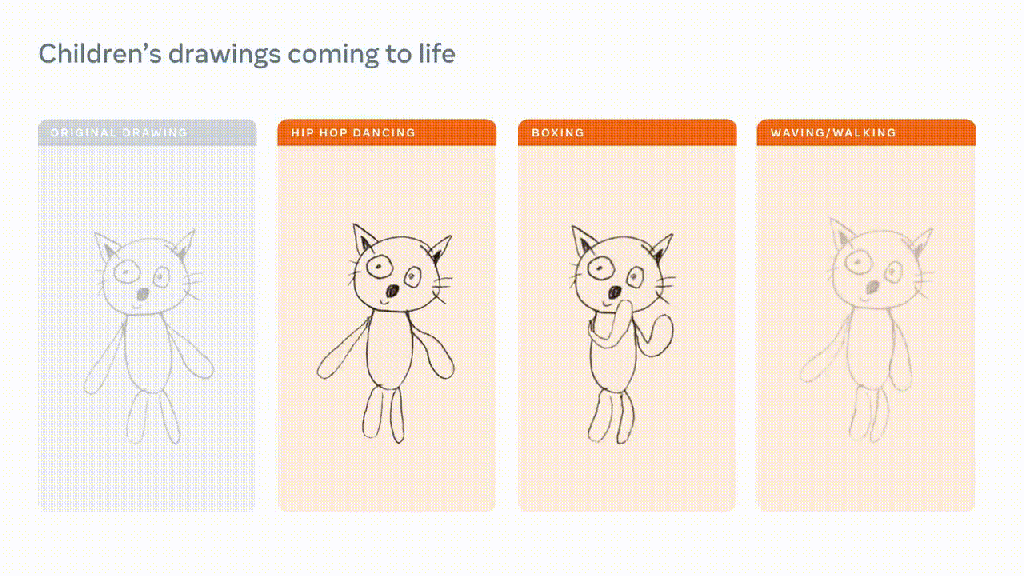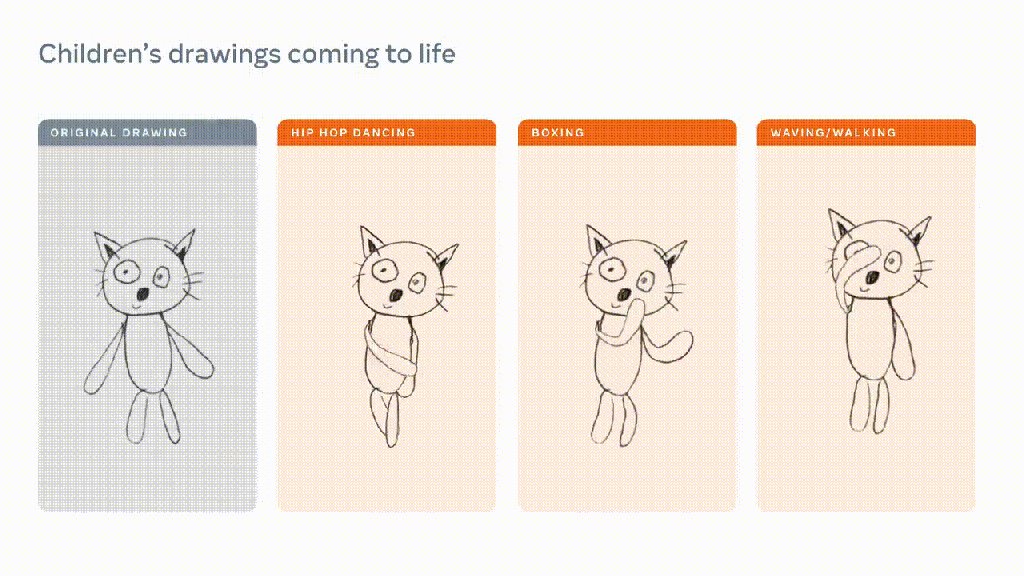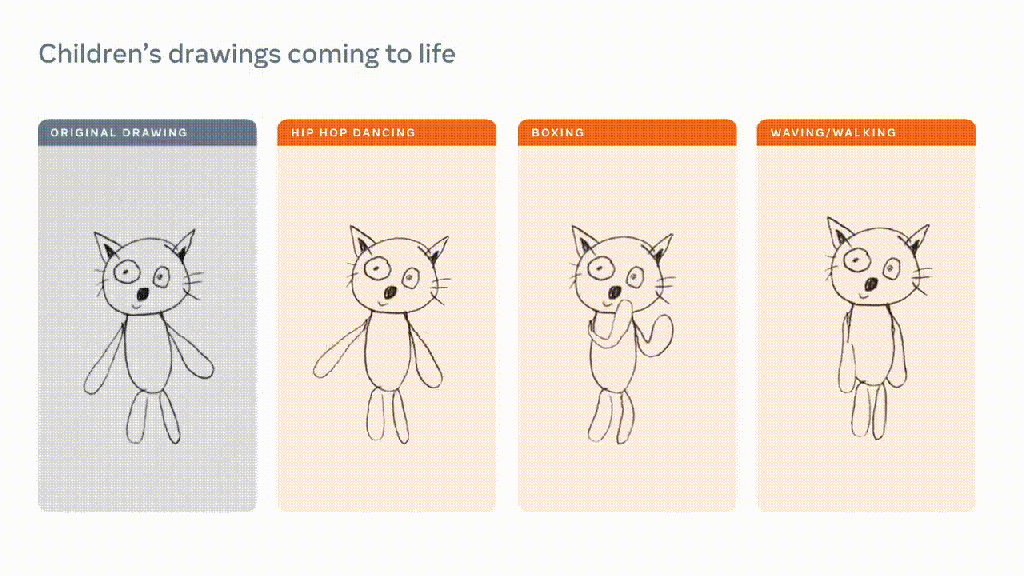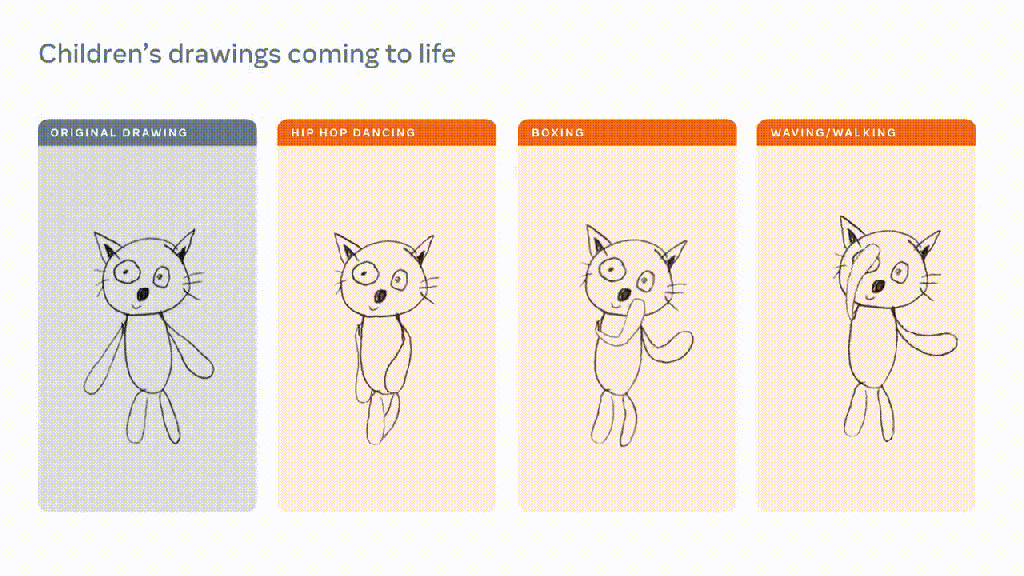
we think there is room to make search much better than it is today.
we are launching a new prototype called SearchGPT: https://t.co/A28Y03X1So
we will learn from the prototype, make it better, and then integrate the tech into ChatGPT to make it real-time and maximally helpful.
— Sam Altman (@sama) July 25, 2024
“Who to follow in AI” in 2024? [Part I] — from ai-supremacy.com by Michael Spencer [some of posting is behind a paywall]
#1-20 [of 150] – I combed the internet, I found the best sources of AI insights, education and articles. LinkedIn | Newsletters | X | YouTube | Substack | Threads | Podcasts
Also see:
- “Who to follow in AI” in 2024? [Part II] — from ai-supremacy.com by Michael Spencer [some of posting is behind a paywall]
Part II – #19-34 - “Who to follow in AI” in 2024? [Part III] — from ai-supremacy.com by Michael Spencer [some of posting is behind a paywall]
Part III – #35-55
Along these lines, also see:
Lots of folks talk about AI influencer content, but these AI influencers are also just damn good humans ?@rowancheung@nonmayorpete@decisionleader@rachel_l_woods@emollick@conorgrennan@sineadbovell@DonAllenIII@ManuVision@karenxcheng
*non-exhaustive, too many to include
— Allie K. Miller (@alliekmiller) July 13, 2024
AI In Medicine: 3 Future Scenarios From Utopia To Dystopia — from medicalfuturist.com by Andrea Koncz
There’s a vast difference between baseless fantasizing and realistic forward planning. Structured methodologies help us learn how to “dream well”.
Key Takeaways
- We’re often told that daydreaming and envisioning the future is a waste of time. But this notion is misguided.
- We all instinctively plan for the future in small ways, like organizing a trip or preparing for a dinner party. This same principle can be applied to larger-scale issues, and smart planning does bring better results.
- We show you a method that allows us to think “well” about the future on a larger scale so that it better meets our needs.
Adobe Unveils Powerful New Innovations in Illustrator and Photoshop Unlocking New Design Possibilities for Creative Pros — from news.adobe.com
- Latest Illustrator and Photoshop releases accelerate creative workflows, save pros time and empower designers to realize their visions faster
- New Firefly-enabled features like Generative Shape Fill in Illustrator along with the Dimension Tool, Mockup, Text to Pattern, the Contextual Taskbar and performance enhancement tools accelerate productivity and free up time so creative pros can dive deeper into the parts of their work they love
- Photoshop introduces all-new Selection Brush Tool and the general availability of Generate Image, Adjustment Brush Tool and other workflow enhancements empowering creators to make complex edits and unique designs
.
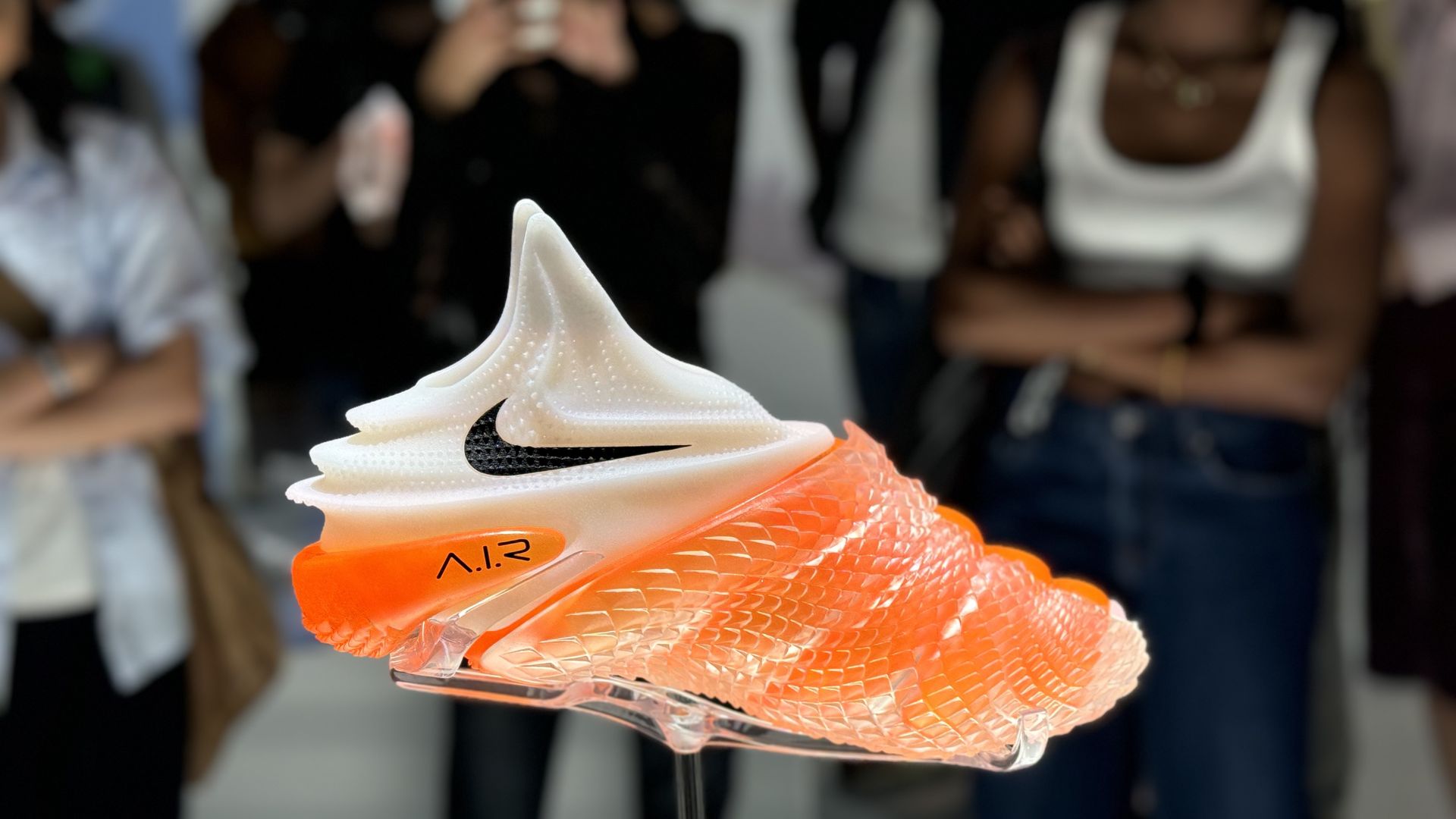
Nike is using AI to turn athletes’ dreams into shoes — from axios.com by Ina Fried
Zoom in: Nike used genAI for ideation, including using a variety of prompts to produce images with different textures, materials and color to kick off the design process.
What they’re saying: “It’s a new way for us to work,” Nike lead footwear designer Juliana Sagat told Axios during a media tour of the showcase on Tuesday.
.
AI meets ‘Do no harm’: Healthcare grapples with tech promises — from finance.yahoo.com by Maya Benjamin
Major companies are moving at high speed to capture the promises of artificial intelligence in healthcare while doctors and experts attempt to integrate the technology safely into patient care.
“Healthcare is probably the most impactful utility of generative AI that there will be,” Kimberly Powell, vice president of healthcare at AI hardware giant Nvidia (NVDA), which has partnered with Roche’s Genentech (RHHBY) to enhance drug discovery in the pharmaceutical industry, among other investments in healthcare companies, declared at the company’s AI Summit in June.
Mistral reignites this week’s LLM rivalry with Large 2 (source) — from superhuman.ai
Today, we are announcing Mistral Large 2, the new generation of our flagship model. Compared to its predecessor, Mistral Large 2 is significantly more capable in code generation, mathematics, and reasoning. It also provides a much stronger multilingual support, and advanced function calling capabilities.
Meta releases the biggest and best open-source AI model yet — from theverge.com by Alex Heath
Llama 3.1 outperforms OpenAI and other rivals on certain benchmarks. Now, Mark Zuckerberg expects Meta’s AI assistant to surpass ChatGPT’s usage in the coming months.
Back in April, Meta teased that it was working on a first for the AI industry: an open-source model with performance that matched the best private models from companies like OpenAI.
Today, that model has arrived. Meta is releasing Llama 3.1, the largest-ever open-source AI model, which the company claims outperforms GPT-4o and Anthropic’s Claude 3.5 Sonnet on several benchmarks. It’s also making the Llama-based Meta AI assistant available in more countries and languages while adding a feature that can generate images based on someone’s specific likeness. CEO Mark Zuckerberg now predicts that Meta AI will be the most widely used assistant by the end of this year, surpassing ChatGPT.
4 ways to boost ChatGPT — from wondertools.substack.com by Jeremy Caplan & The PyCoach
Simple tactics for getting useful responses
To help you make the most of ChatGPT, I’ve invited & edited today’s guest post from the author of a smart AI newsletter called The Artificial Corner. I appreciate how Frank Andrade pushes ChatGPT to produce better results with four simple, clever tactics. He offers practical examples to help us all use AI more effectively.
…
Frank Andrade: Most of us fail to make the most of ChatGPT.
- We omit examples in our prompts.
- We fail to assign roles to ChatGPT to guide its behavior.
- We let ChatGPT guess instead of providing it with clear guidance.
If you rely on vague prompts, learning how to create high-quality instructions will get you better results. It’s a skill often referred to as prompt engineering. Here are several techniques to get you to the next level.