Nearly half of CEOs believe that AI not only could—but should—replace their own jobs — from finance.yahoo.com by Orianna Rosa Royle; via Harsh Makadia
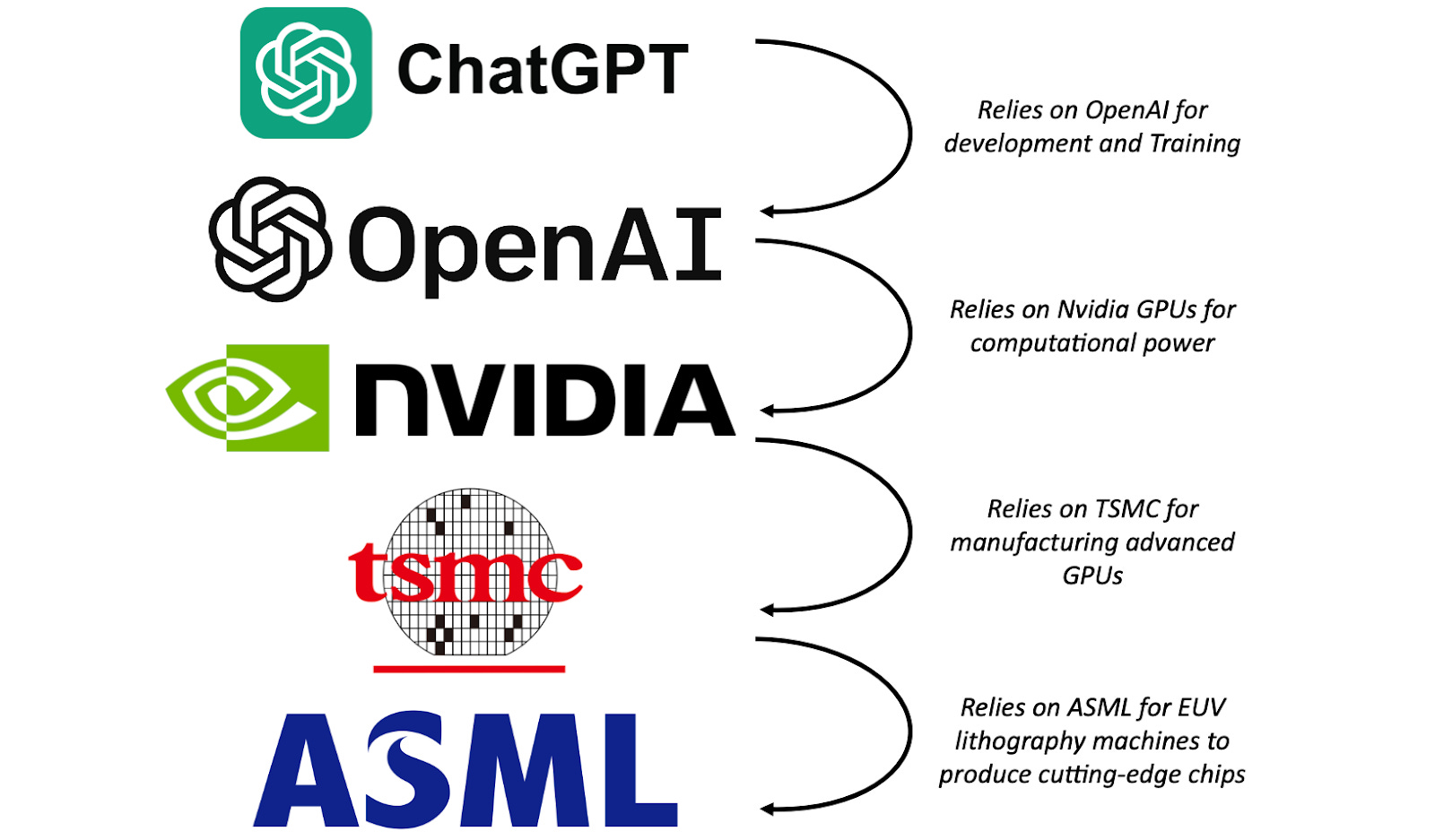
Researchers from edX, an education platform for upskilling workers, conducted a survey involving over 1,500 executives and knowledge workers. The findings revealed that nearly half of CEOs believe AI could potentially replace “most” or even all aspects of their own positions.
What’s even more intriguing is that 47% of the surveyed executives not only see the possibility of AI taking over their roles but also view it as a desirable development.
Why? Because they anticipate that AI could rekindle the need for traditional leadership for those who remain.
“Success in the CEO role hinges on effective leadership, and AI can liberate time for this crucial aspect of their role,” Andy Morgan, Head of edX for Business comments on the findings.
“CEOs understand that time saved on routine tasks can stimulate innovation, nurture creativity, and facilitate essential upskilling for their teams, fostering both individual and organizational success,” he adds.
But CEOs already know this: EdX’s research echoed that 79% of executives fear that if they don’t learn how to use AI, they’ll be unprepared for the future of work.
From DSC:
By the way, my first knee-jerk reaction to this was:
WHAT?!?!?!? And this from people who earn WAAAAY more than the average employee, no doubt.
After a chance to calm down a bit, I see that the article does say that CEOs aren’t going anywhere. Ah…ok…got it.
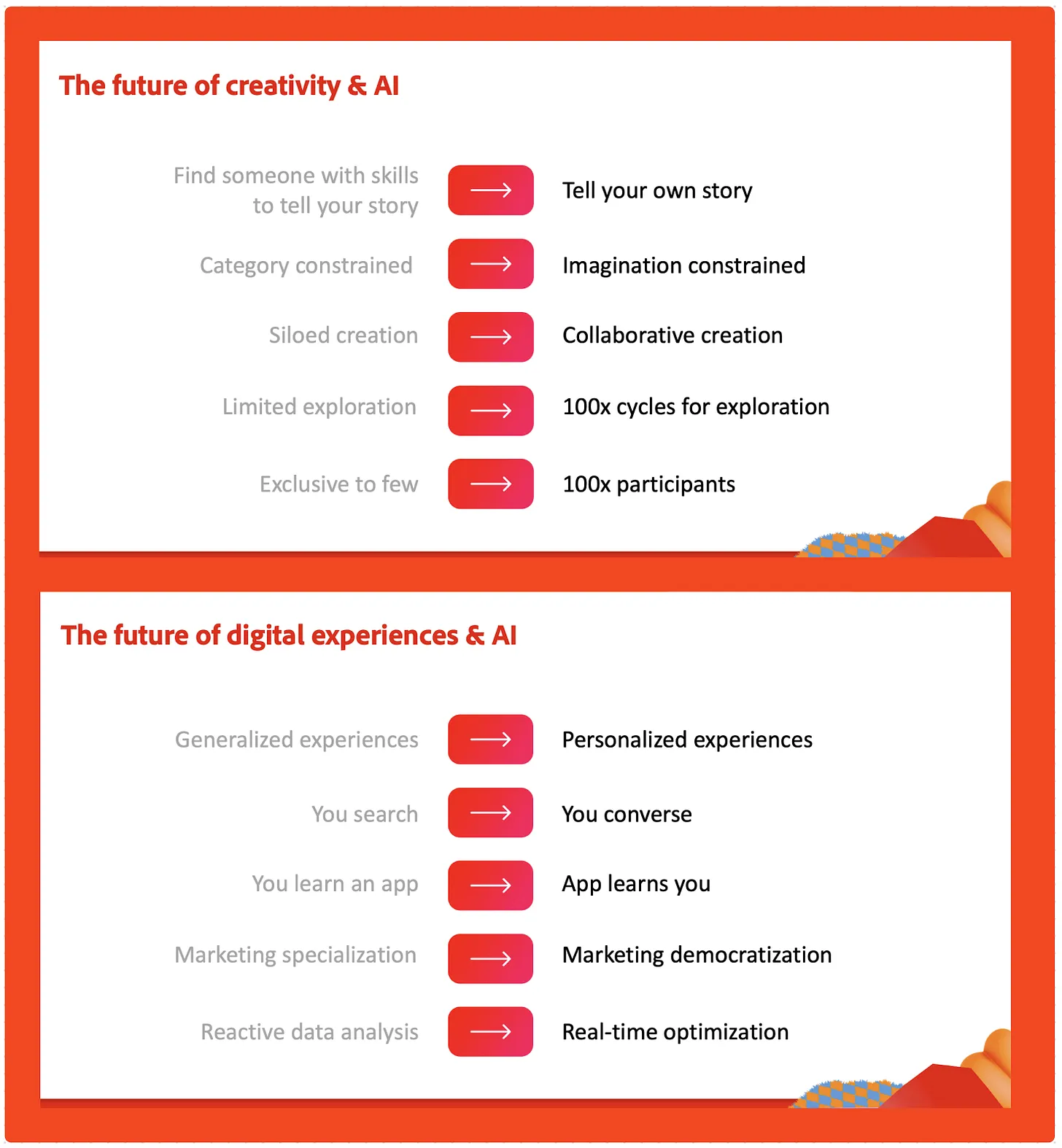
Strange Ways AI Disrupts Business Models, What’s Next For Creativity & Marketing, Some Provocative Data — from .implications.com by Scott Belsky
In this edition, we explore some of the more peculiar ways that AI may change business models as well as recent releases for the world of creativity and marketing.
Time-based business models are liable for disruption via a value-based overhaul of compensation. Today, as most designers, lawyers, and many trades in between continue to charge by the hour, the AL-powered step-function improvements in workflows are liable to shake things up.
…
In such a world, time-based billing simply won’t work anymore unless the value derived from these services is also compressed by a multiple (unlikely). The classic time-based model of billing for lawyers, designers, consultants, freelancers etc is officially antiquated. So, how might the value be captured in a future where we no longer bill by the hour? …
The worlds of creativity and marketing are rapidly changing – and rapidly coming together.
#AI #businessmodels #lawyers #billablehour
It becomes clear that just prompting to get images is a rather elementary use case of AI, compared to the ability to place and move objects, change perspective, adjust lighting, and many other actions using AI.
AlphaFold DB provides open access to over 200 million protein structure predictions to accelerate scientific research. — from
AlphaFold is an AI system developed by DeepMind that predicts a protein’s 3D structure from its amino acid sequence. It regularly achieves accuracy competitive with experiment.

After 25 years of growth for the $68 billion SEO industry, here’s how Google and other tech firms could render it extinct with AI — from fortune.com by Ravi Sen and The Conversation
But one other consequence is that I believe it may destroy the $68 billion search engine optimization industry that companies like Google helped create.
For the past 25 years or so, websites, news outlets, blogs and many others with a URL that wanted to get attention have used search engine optimization, or SEO, to “convince” search engines to share their content as high as possible in the results they provide to readers. This has helped drive traffic to their sites and has also spawned an industry of consultants and marketers who advise on how best to do that.
As an associate professor of information and operations management, I study the economics of e-commerce. I believe the growing use of generative AI will likely make all of that obsolete.
ChatGPT Plus members can upload and analyze files in the latest beta — from theverge.com by Wes Davis
ChatGPT Plus members can also use modes like Browse with Bing without manually switching, letting the chatbot decide when to use them.
OpenAI is rolling out new beta features for ChatGPT Plus members right now. Subscribers have reported that the update includes the ability to upload files and work with them, as well as multimodal support. Basically, users won’t have to select modes like Browse with Bing from the GPT-4 dropdown — it will instead guess what they want based on context.
Google agrees to invest up to $2 billion in OpenAI rival Anthropic — from reuters.com by Krystal Hu
Oct 27 (Reuters) – Alphabet’s (GOOGL.O) Google has agreed to invest up to $2 billion in the artificial intelligence company Anthropic, a spokesperson for the startup said on Friday.
The company has invested $500 million upfront into the OpenAI rival and agreed to add $1.5 billion more over time, the spokesperson said.
Google is already an investor in Anthropic, and the fresh investment would underscore a ramp-up in its efforts to better compete with Microsoft (MSFT.O), a major backer of ChatGPT creator OpenAI, as Big Tech companies race to infuse AI into their applications.











.webp)