AI for Education Webinars — from youtube.com by Tom Barrett and others
Post-AI Assessment Design — from drphilippahardman.substack.com by Dr. Philippa Hardman
A simple, three-step guide on how to design assessments in a post-AI world
Excerpt:
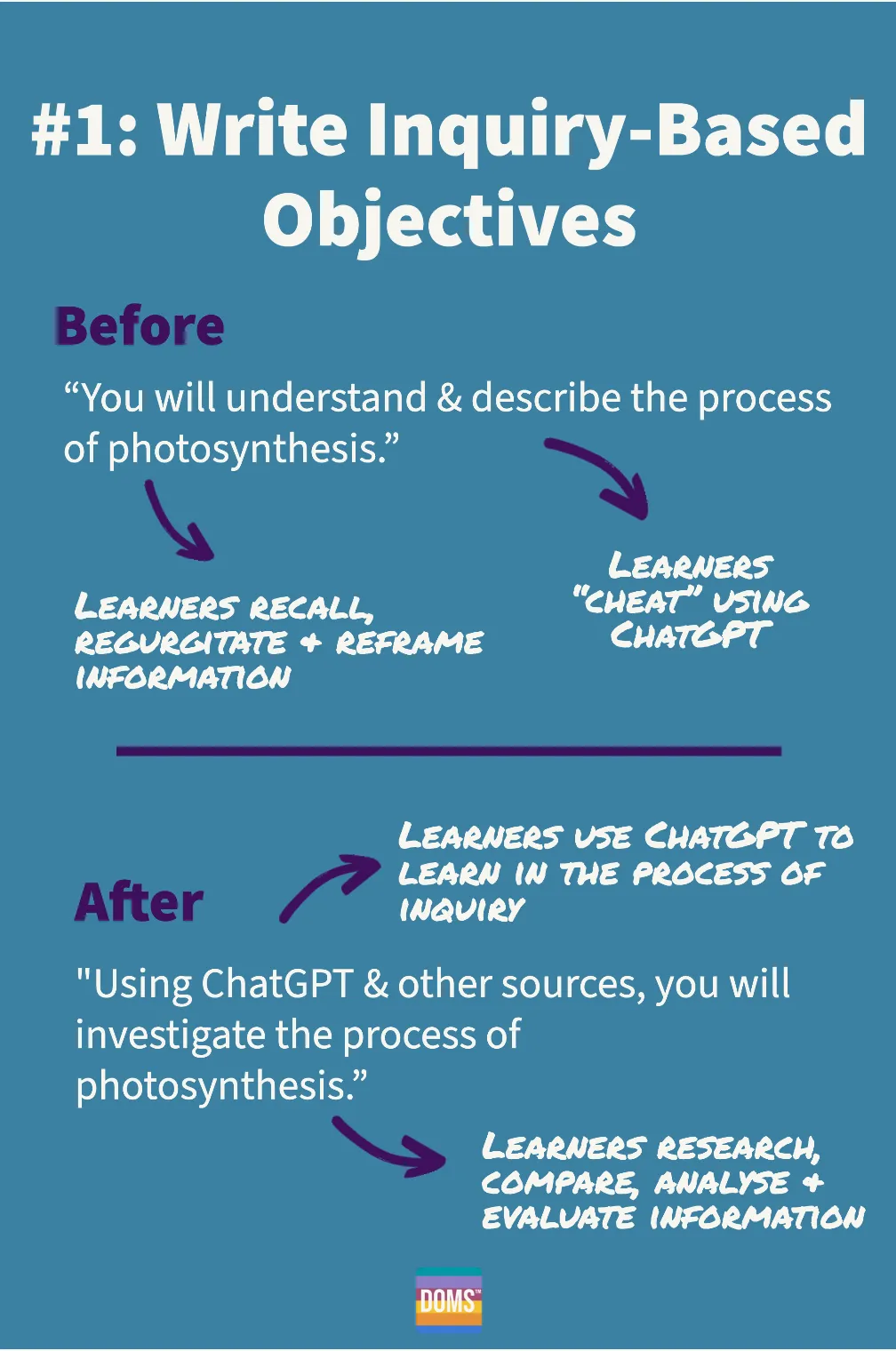
Step 1: Write Inquiry-Based Objectives
Inquiry-based objectives focus not just on the acquisition of knowledge but also on the development of skills and behaviours, like critical thinking, problem-solving, collaboration and research skills.
They do this by requiring learners not just to recall or “describe back” concepts that are delivered via text, lecture or video. Instead, inquiry-based objectives require learners to construct their own understanding through the process of investigation, analysis and questioning.
.
Massive Disruption Now: What AI Means for Students, Educators, Administrators and Accreditation Boards
— from stefanbauschard.substack.com by Stefan Bauschard; via Will Richardson on LinkedIn
The choices many colleges and universities make regarding AI over the next 9 months will determine if they survive. The same may be true for schools.
Excerpts:
Just for a minute, consider how education would change if the following were true –
- AIs “hallucinated” less than humans
- AIs could write in our own voices
- AIs could accurately do math
- AIs understood the unique academic (and eventually developmental) needs of each student and adapt instruction to that student
- AIs could teach anything any student wanted or need to know any time of day or night
- AIs could do this at a fraction of the cost of a human teacher or professor
Fall 2026 is three years away. Do you have a three year plan? Perhaps you should scrap it and write a new one (or at least realize that your current one cannot survive). If you run an academic institution in 2026 the same way you ran it in 2022, you might as well run it like you would have in 1920. If you run an academic institution in 2030 (or any year when AI surpasses human intelligence) the same way you ran it in 2022, you might as well run it like you would have in 1820. AIs will become more intelligent than us, perhaps in 10-20 years (LeCun), though there could be unanticipated breakthroughs that lower the time frame to a few years or less (Benjio); it’s just a question of when, not “if.”
On one creative use of AI — from aiandacademia.substack.com by Bryan Alexander
A new practice with pedagogical possibilities
Excerpt:
Look at those material items again. The voiceover? Written by an AI and turned into audio by software. The images? Created by human prompts in Midjourney. The music is, I think, human created. And the idea came from a discussion between a human and an AI?
…
How might this play out in a college or university class?
Imagine assignments which require students to craft such a video. Start from film, media studies, or computer science classes. Students work through a process:
Generative Textbooks — from opencontent.org by David Wiley
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
I continue to try to imagine ways generative AI can impact teaching and learning, including learning materials like textbooks. Earlier this week I started wondering – what if, in the future, educators didn’t write textbooks at all? What if, instead, we only wrote structured collections of highly crafted prompts? Instead of reading a static textbook in a linear fashion, the learner would use the prompts to interact with a large language model. These prompts could help learners ask for things like:
- overviews and in-depth explanations of specific topics in a specific sequence,
- examples that the learner finds personally relevant and interesting,
- interactive practice – including open-ended exercises – with immediate, corrective feedback,
- the structure of the relationships between ideas and concepts,
- etc.
Also relevant/see:
.
Generating The Future of Education with AI — from aixeducation.com
Designed for K12 and Higher-Ed Educators & Administrators, this conference aims to provide a platform for educators, administrators, AI experts, students, parents, and EdTech leaders to discuss the impact of AI on education, address current challenges and potentials, share their perspectives and experiences, and explore innovative solutions. A special emphasis will be placed on including students’ voices in the conversation, highlighting their unique experiences and insights as the primary beneficiaries of these educational transformations.
How Teachers Are Using ChatGPT in Class — from edweek.org by Larry Ferlazzo
Excerpt:
The use of generative AI in K-12 settings is complex and still in its infancy. We need to consider how these tools can enhance student creativity, improve writing skills, and be transparent with students about how generative AI works so they can better understand its limitations. As with any new tech, our students will be exposed to it, and it is our task as educators to help them navigate this new territory as well-informed, curious explorers.
Japan emphasizes students’ comprehension of AI in new school guidelines — from japantimes.co.jp by Karin Kaneko; via The Rundown
Excerpt:
The education ministry has emphasized the need for students to understand artificial intelligence in new guidelines released Tuesday, setting out how generative AI can be integrated into schools and the precautions needed to address associated risks.
Students should comprehend the characteristics of AI, including its advantages and disadvantages, with the latter including personal information leakages and copyright infringement, before they use it, according to the guidelines. They explicitly state that passing off reports, essays or any other works produced by AI as one’s own is inappropriate.
AI’s Teachable Moment: How ChatGPT Is Transforming the Classroom — from cnet.com by Mark Serrels
Teachers and students are already harnessing the power of AI, with an eye toward the future.
Excerpt:
Thanks to the rapid development of artificial intelligence tools like Dall-E and ChatGPT, my brother-in-law has been wrestling with low-level anxiety: Is it a good idea to steer his son down this path when AI threatens to devalue the work of creatives? Will there be a job for someone with that skill set in 10 years? He’s unsure. But instead of burying his head in the sand, he’s doing what any tech-savvy parent would do: He’s teaching his son how to use AI.
In recent months the family has picked up subscriptions to AI services. Now, in addition to drawing and sculpting and making movies and video games, my nephew is creating the monsters of his dreams with Midjourney, a generative AI tool that uses language prompts to produce images.
The AI Dictionary for Educators — from blog.profjim.com
To bridge this knowledge gap, I decided to make a quick little dictionary of AI terms specifically tailored for educators worldwide. Initially created for my own benefit, I’ve reworked my own AI Dictionary for Educators and expanded it to help my fellow teachers embrace the advancements AI brings to education.
7 Strategies to Prepare Educators to Teach With AI — from edweek.org by Lauraine Langreo; NOTE: Behind paywall