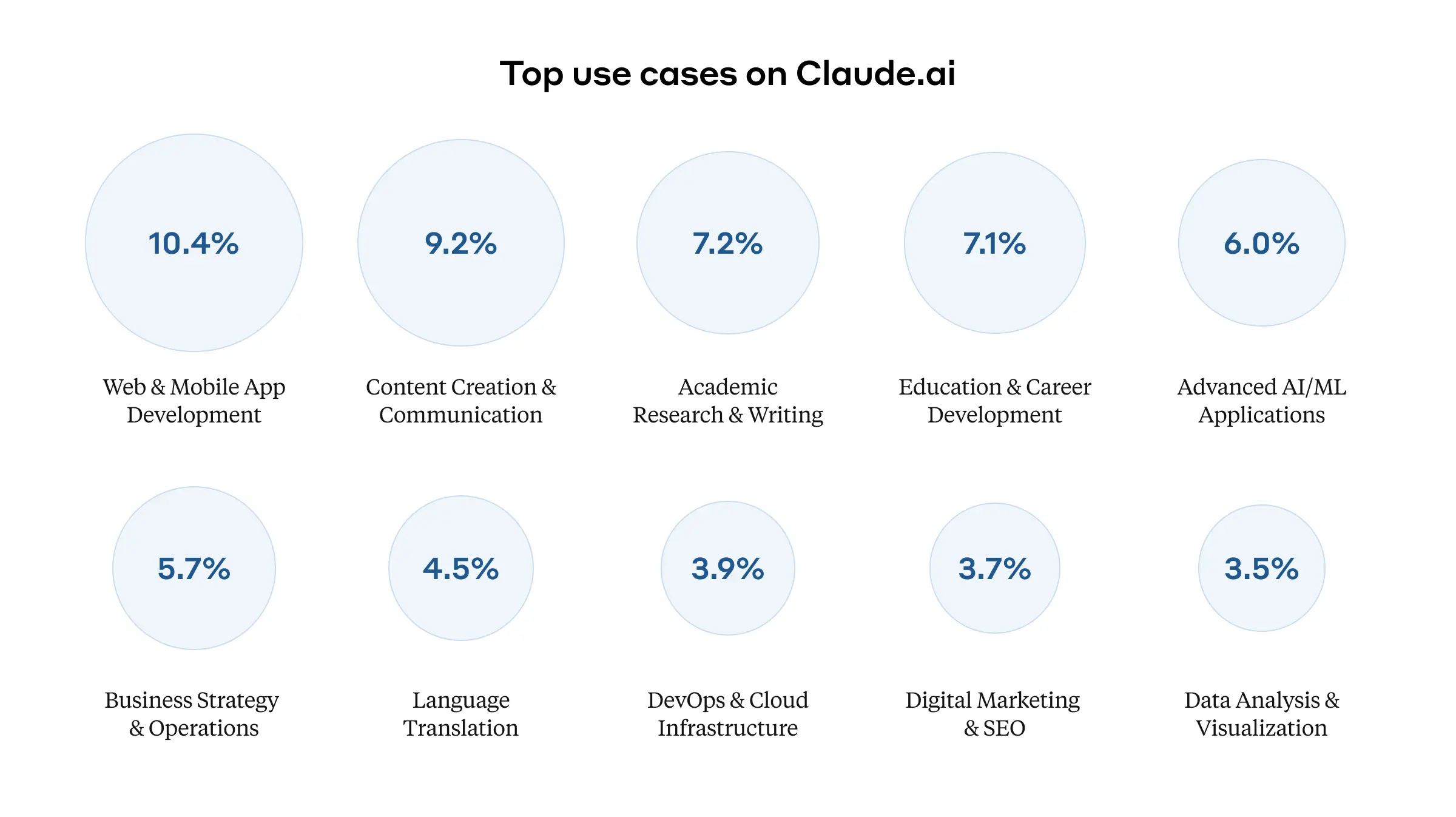
The AI-enhanced learning ecosystem: A case study in collaborative innovation — from chieflearningofficer.com by Kevin Jennings
How artificial intelligence can serve as a tool and collaborative partner in reimagining content development and management.
Learning and development professionals face unprecedented challenges in today’s rapidly evolving business landscape. According to LinkedIn’s 2025 Workplace Learning Report, 67 percent of L&D professionals report being “maxed out” on capacity, while 66 percent have experienced budget reductions in the past year.
Despite these constraints, 87 percent agree their organizations need to develop employees faster to keep pace with business demands. These statistics paint a clear picture of the pressure L&D teams face: do more, with less, faster.
This article explores how one L&D leader’s strategic partnership with artificial intelligence transformed these persistent challenges into opportunities, creating a responsive learning ecosystem that addresses the modern demands of rapid product evolution and diverse audience needs. With 71 percent of L&D professionals now identifying AI as a high or very high priority for their learning strategy, this case study demonstrates how AI can serve not merely as a tool but as a collaborative partner in reimagining content development and management.
.
How we use GenAI and AR to improve students’ design skills — from timeshighereducation.com by Antonio Juarez, Lesly Pliego and Jordi Rábago who are professors of architecture at Monterrey Institute of Technology in Mexico; Tomas Pachajoa is a professor of architecture at the El Bosque University in Colombia; & Carlos Hinrichsen and Marietta Castro are educators at San Sebastián University in Chile.
Guidance on using generative AI and augmented reality to enhance student creativity, spatial awareness and interdisciplinary collaboration
Blend traditional skills development with AI use
For subjects that require students to develop drawing and modelling skills, have students create initial design sketches or models manually to ensure they practise these skills. Then, introduce GenAI tools such as Midjourney, Leonardo AI and ChatGPT to help students explore new ideas based on their original concepts. Using AI at this stage broadens their creative horizons and introduces innovative perspectives, which are crucial in a rapidly evolving creative industry.
Provide step-by-step tutorials, including both written guides and video demonstrations, to illustrate how initial sketches can be effectively translated into AI-generated concepts. Offer example prompts to demonstrate diverse design possibilities and help students build confidence using GenAI.
Integrating generative AI and AR consistently enhanced student engagement, creativity and spatial understanding on our course.
How Texas is Preparing Higher Education for AI — from the74million.org by Kate McGee
TX colleges are thinking about how to prepare students for a changing workforce and an already overburdened faculty for new challenges in classrooms.
“It doesn’t matter if you enter the health industry, banking, oil and gas, or national security enterprises like we have here in San Antonio,” Eighmy told The Texas Tribune. “Everybody’s asking for competency around AI.”
It’s one of the reasons the public university, which serves 34,000 students, announced earlier this year that it is creating a new college dedicated to AI, cyber security, computing and data science. The new college, which is still in the planning phase, would be one of the first of its kind in the country. UTSA wants to launch the new college by fall 2025.
But many state higher education leaders are thinking beyond that. As AI becomes a part of everyday life in new, unpredictable ways, universities across Texas and the country are also starting to consider how to ensure faculty are keeping up with the new technology and students are ready to use it when they enter the workforce.
In the Room Where It Happens: Generative AI Policy Creation in Higher Education — from er.educause.edu by Esther Brandon, Lance Eaton, Dana Gavin, and Allison Papini
To develop a robust policy for generative artificial intelligence use in higher education, institutional leaders must first create “a room” where diverse perspectives are welcome and included in the process.
Q&A: Artificial Intelligence in Education and What Lies Ahead — from usnews.com by Sarah Wood
Research indicates that AI is becoming an essential skill to learn for students to succeed in the workplace.
Q: How do you expect to see AI embraced more in the future in college and the workplace?
I do believe it’s going to become a permanent fixture for multiple reasons. I think the national security imperative associated with AI as a result of competing against other nations is going to drive a lot of energy and support for AI education. We also see shifts across every field and discipline regarding the usage of AI beyond college. We see this in a broad array of fields, including health care and the field of law. I think it’s here to stay and I think that means we’re going to see AI literacy being taught at most colleges and universities, and more faculty leveraging AI to help improve the quality of their instruction. I feel like we’re just at the beginning of a transition. In fact, I often describe our current moment as the ‘Ask Jeeves’ phase of the growth of AI. There’s a lot of change still ahead of us. AI, for better or worse, it’s here to stay.
AI-Generated Podcasts Outperform Textbooks in Landmark Education Study — form linkedin.com by David Borish
A new study from Drexel University and Google has demonstrated that AI-generated educational podcasts can significantly enhance both student engagement and learning outcomes compared to traditional textbooks. The research, involving 180 college students across the United States, represents one of the first systematic investigations into how artificial intelligence can transform educational content delivery in real-time.
What can we do about generative AI in our teaching? — from linkedin.com by Kristina Peterson
So what can we do?
- Interrogate the Process: We can ask ourselves if we I built in enough checkpoints. Steps that can’t be faked. Things like quick writes, question floods, in-person feedback, revision logs.
- Reframe AI: We can let students use AI as a partner. We can show them how to prompt better, revise harder, and build from it rather than submit it. Show them the difference between using a tool and being used by one.
- Design Assignments for Curiosity, Not Compliance: Even the best of our assignments need to adapt. Mine needs more checkpoints, more reflective questions along the way, more explanation of why my students made the choices they did.
Teachers Are Not OK — from 404media.co by Jason Koebler
The response from teachers and university professors was overwhelming. In my entire career, I’ve rarely gotten so many email responses to a single article, and I have never gotten so many thoughtful and comprehensive responses.
One thing is clear: teachers are not OK.
…
In addition, universities are contracting with companies like Microsoft, Adobe, and Google for digital services, and those companies are constantly pushing their AI tools. So a student might hear “don’t use generative AI” from a prof but then log on to the university’s Microsoft suite, which then suggests using Copilot to sum up readings or help draft writing. It’s inconsistent and confusing.
I am sick to my stomach as I write this because I’ve spent 20 years developing a pedagogy that’s about wrestling with big ideas through writing and discussion, and that whole project has been evaporated by for-profit corporations who built their systems on stolen work. It’s demoralizing.