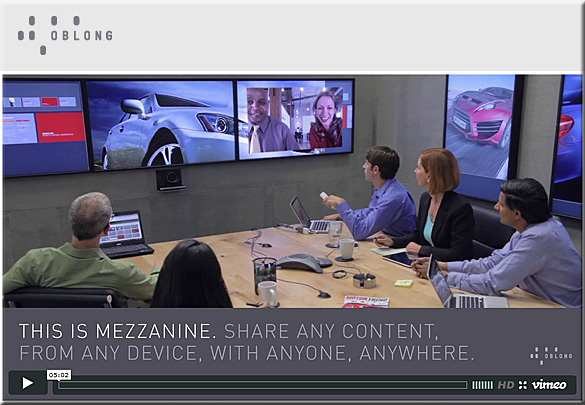
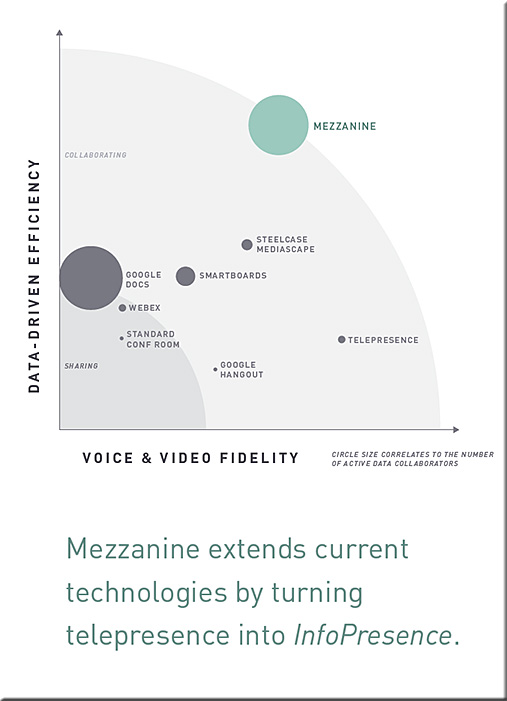
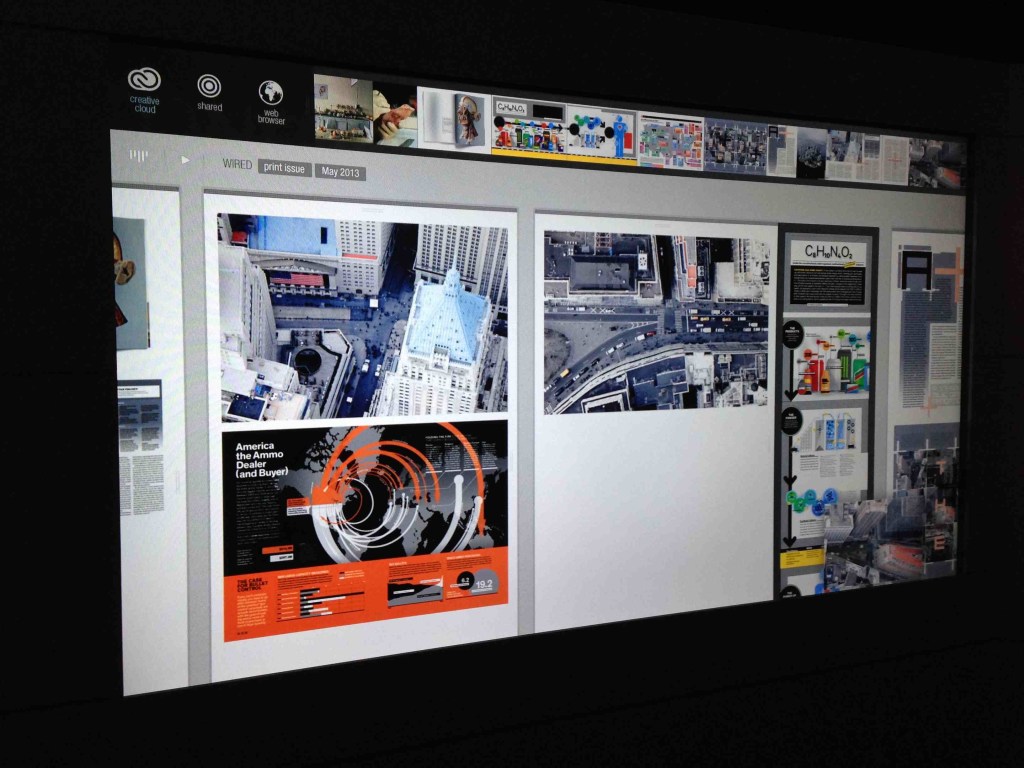
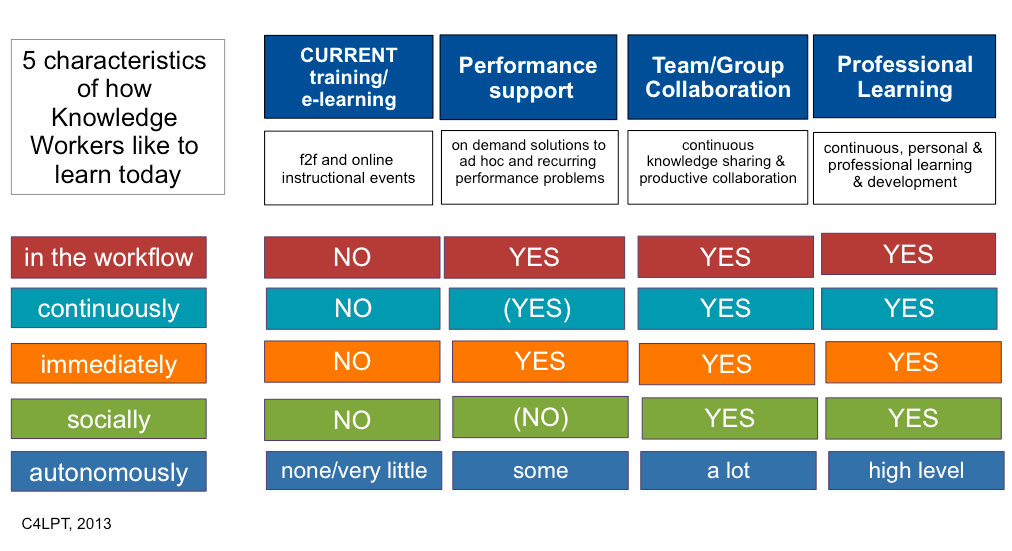
Excerpts:
Learning Space Insights
The following insights result from ongoing testing of new approaches to learning spaces and are not intended to be prescriptive. We hope each insight causes you to consider new approaches to learning space design. As our research continues, we look forward to a continued dialogue on each of the following insights, which will lead to discovery of new ideas for learning space design.
Enhance Collaboration
Idea: Traditional classroom design often limits engagement (due to rows, etc.). Space should enable and encourage student and faculty engagement, as well as student-tostudent interaction.
Foster Engagement
Idea: Spaces that encourage engagement remove barriers, get faculty out from behind the traditional lectern, and allow them to move freely around the space.
Let Learning Happen Everywhere
Idea: Consider adding “lingering” spaces that connect faculty and students outside scheduled learning spaces.
Flex to Meet More Needs
Idea: Furnishings selected with flexibility in mind allow spaces to be used in different ways. Consider a simple kit of furniture parts that will allow you multiple layouts and space options.
Make Technology Work for You
Idea: Technology should serve your teaching and learning needs and not dictate how, where, or when teaching or learning happens.
Provide Supportive Choices
Idea: Whether you spend 50 minutes or several hours in a learning environment, the need for comfort and variety is clear. Learning space design needs to offer options that support variety and comfort—for both faculty and students.
Blur the Lines Between Learning and Work
Idea: Consider spaces that mirror corporate spaces and support the collaboration and engagement skills vital to post-graduation success.