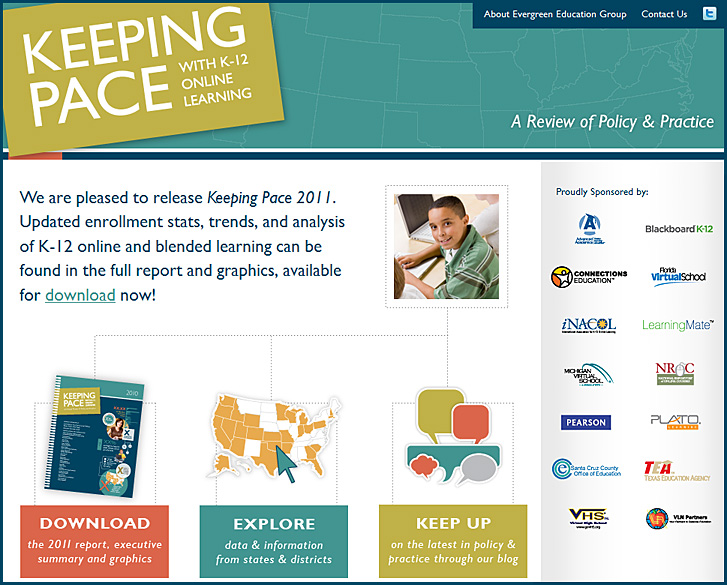
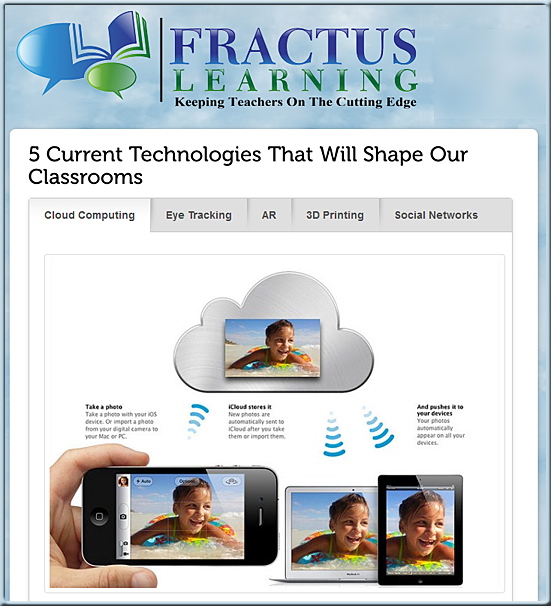
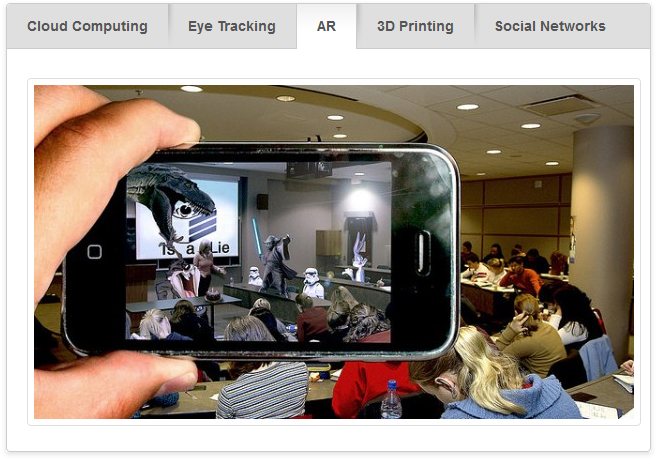
Knewton, Pearson pair up to deliver customized learning experience — from The Journal by Kanoe Namahoe
Excerpt:
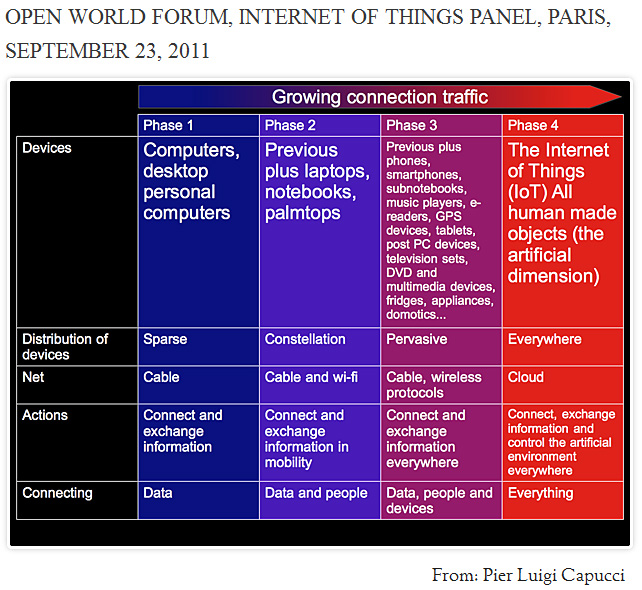
We were asked to consider the Internet of Things (IoT) from the user’s viewpoint. Well, my viewpoint is exactly this, since I’m neither a company director nor a software coder or a hardware creator. From an user’s viewpoint I think we are undergoing a big transformation. The Internet of Things comes out from an evolution process which involves calculation power, connections, networking, personal technologies, and that can be resumed in four phases.
Also see:
Above items originally/ultimately from:
- Pervasive Entertainment – Games, film, real world, TV merged with social networks — from personalizemedia.com by Gary Hayes
Apollo to buy adaptive-learning company for $75-Million — from The Chronicle by Josh Keller
Excerpt:
The Apollo Group, which runs the University of Phoenix, announced on Tuesday that it plans to pay $75-million to purchase Carnegie Learning, which develops interactive math instruction that adapts to the needs of individual students.
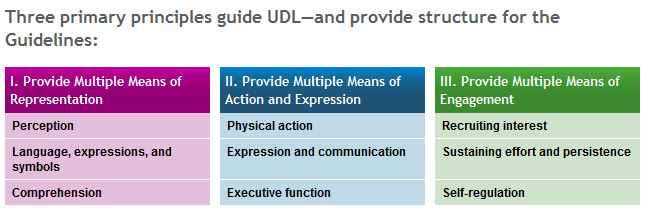
Universal Design for Learning: It’s Not Just for Disability Experts Anymore (The Confessions of a First-Time Teacher) — from National Collaborative on Workforce & Disability for Youth (NCWD/Youth) by Amy Katzel
Excerpt:
All students, with or without disabilities, have different strengths and weaknesses. Early on, it was clear to me that I had a wide range of abilities in the room. Some students started out unable to consistently construct full sentences, while others were already writing complex prose. Some students raised their hand frequently to answer questions, while others preferred to stay quiet. When we did reading assignments during class, everyone read at different speeds. Some youth demonstrated they understood the material on quizzes, but then struggled with applying those concepts to their essays.
When I get up in front of the class, to which student am I teaching?
Also see:
- Leading Project-Based Learning / Universal Design for Learning
- Universal Design for Learning (UDL): What it is and Why You Should Care — from ISTE.org