Addendum on 4/5/11:
A free, weeklong online experience consisting of online activities, resources, web seminars, and discussions on mobile computing.
Join us April 25–29 for a focused learning opportunity on one of the top IT issues in higher education today—mobile computing.
Perhaps no area of higher education IT is evolving more rapidly. Colleges and universities are making important decisions about mobile computing and how it can be incorporated into effective technology programs—today and tomorrow.
In an effort to bring the community together on this topic, EDUCAUSE will convene a Mobile Computing 5-Day Sprint. This experience will allow you to engage in activities and discussions on the many ways mobile technologies are undeniably altering higher education.
How to Participate
Mark your calendar to visit this website throughout the week. The 5-Day Sprint will include synchronous and asynchronous activities.
The sprint is a build-your-own experience—you choose which activities to participate in, based on your interests and needs. No registration is required, except for the free daily EDUCAUSE Live! web seminars, where virtual seating is limited; sign up today.
What to Expect During the Week
Join us each day to explore solutions to common challenges and share experiences and ideas through articles, podcasts, web seminars, and online discussions. Each day will be dedicated to a specific theme related to mobile computing.
Monday, April 25: The Future of Mobile Computing
Hear how the community is framing and contextualizing the depth and breadth of what mobile computing means on campus, setting the stage for a week of rich and dynamic discussion on this issue.
Tuesday, April 26: Teaching and Learning
Join us as we discuss the learning that is—or could be—enabled by mobile technology.
Wednesday, April 27: Mobile Enterprise Integration
Engage in the conversation about how to plan for a fully integrated mobile experience for faculty, staff, and students.
Thursday, April 28: Security, Privacy, and Policy
Bring your experiences and ideas as we examine the current state of mobile security, anticipate what’s coming, and explore effective practices.
Friday, April 29: Mobile Infrastructure
Explore the wide range of hardware, software, and network infrastructure components necessary to make mobile computing an effective addition to campus services.










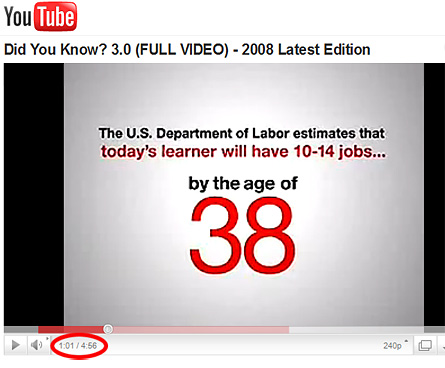

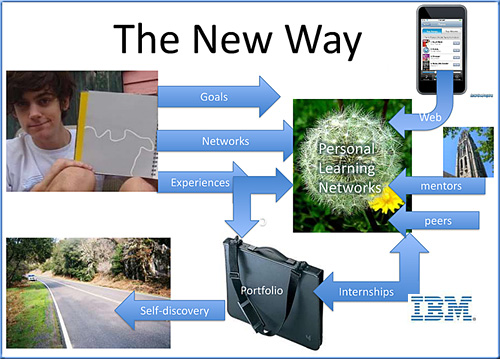




 Workplace Learning is changing!
Workplace Learning is changing! differently about the way work and learning is happening. For an increasing number of individuals and groups are using these new technologies in the workplace to connect with colleagues both inside and outside the organisation in order to share ideas, resources and experiences – often under the radar of IT and L&D. This use of social media has become a revolution in the sense that these tools are now in the hands of the employees. So the question is what role does L&D play in all this?
differently about the way work and learning is happening. For an increasing number of individuals and groups are using these new technologies in the workplace to connect with colleagues both inside and outside the organisation in order to share ideas, resources and experiences – often under the radar of IT and L&D. This use of social media has become a revolution in the sense that these tools are now in the hands of the employees. So the question is what role does L&D play in all this?