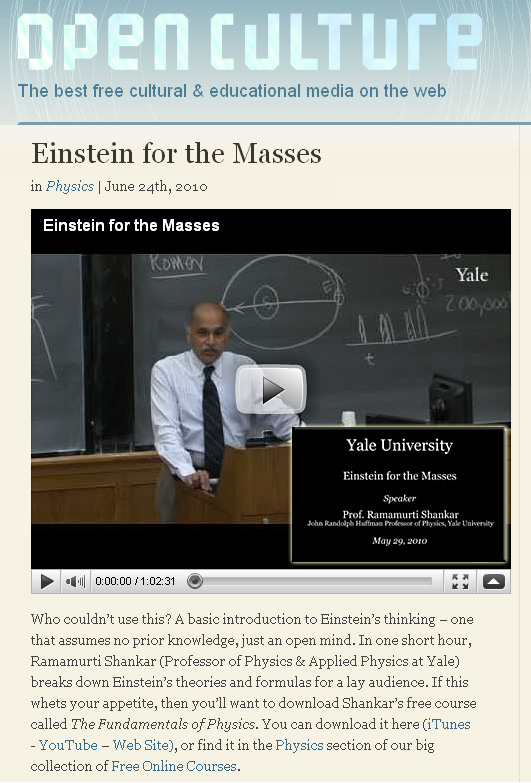
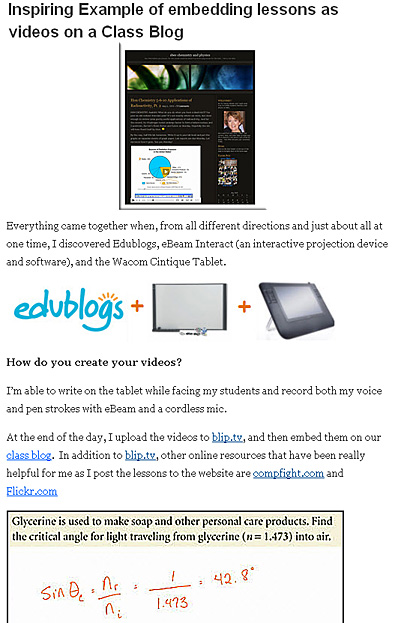
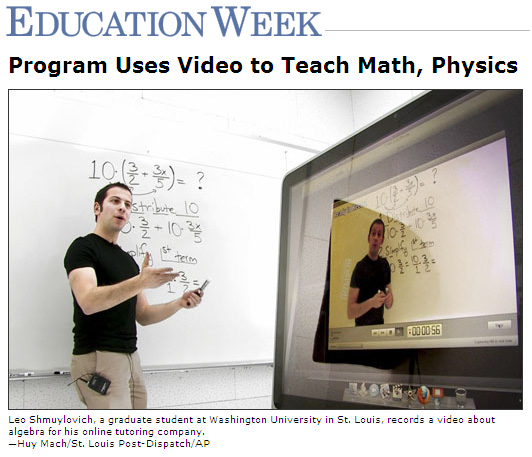
Solving the problem of online problem solving – – from FacultyFocus.com by Ellen Smyth
When first visualizing an online mathematics course, I saw a barren, text-only environment where students learned primarily from the textbook and where instructors provided text-based direction, clarification, and assistance. But typing is not teaching and reading is not learning. Students deserve more from online courses than regurgitated textbooks and opportunities to teach themselves. With today’s technology, we can create a rich learning environment.
So if we don’t teach with pure text, what do we teach with? Traditionally, we write, draw, and talk students through the problem-solving process while we encourage students to actively work along with us. Online, we should aspire to sparking the same level of comprehension, achievable using exactly the same techniques – writing, drawing, and talking students through problems.
But how do we write, draw, and talk to students online? Fortunately, we have a wide variety of tools available to help us available to help us do it digitally.
From DSC:
One of the types of tools mentioned were the tablets from Wacom.