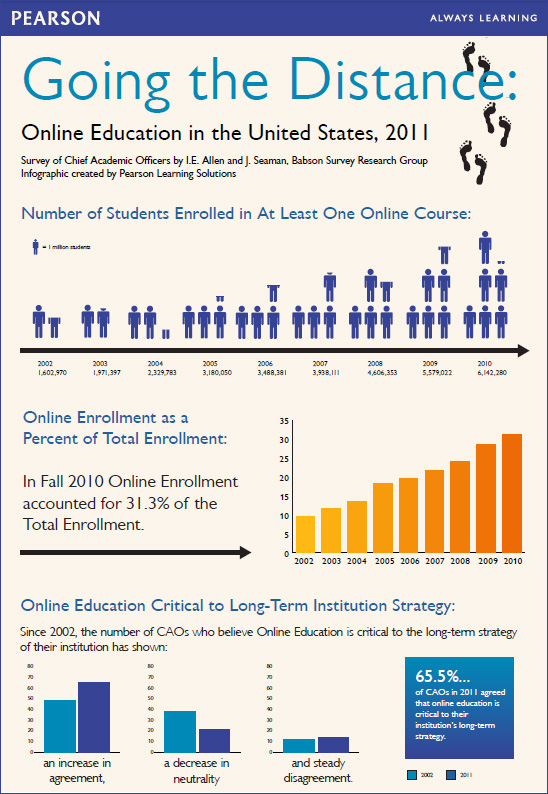
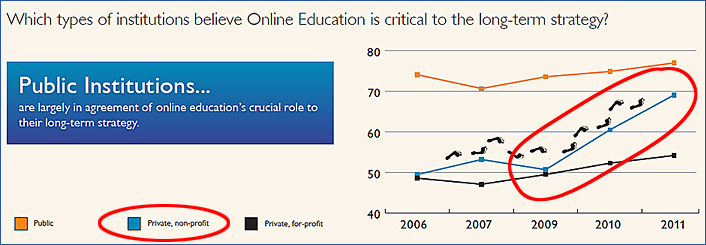
A list of Allen Partridge’s on-demand/online-based seminars (free, requires free ID at Adobe):
1: Making Effective Adobe Captivate eLearning Modules
… a foundation in multimedia design concepts for eLearning, and help you understand the reasons / rationale behind many of the eLearning strategies you see implemented today.
2: Balancing cognitive load in eLearning content with Adobe Captivate 5
…session focuses on the Multimedia eLearning Design Principle known as Personalization, which suggests that people learn more effectively when conversational styles and or learning agents are used to enhance the social aspects of the experience.
3: Applying Personalization to eLearning with Adobe Captivate 5
…session focuses on the Multimedia eLearning Design Principle known as Personalization, which suggests that people learn more effectively when conversational styles and or learning agents are used to enhance the social aspects of the experience.
4: Creating effective eLearning Multimedia with Adobe Captivate 5
…session will center on the Multimedia Principle (the importance of combining images & text) of eLearning Design.
5: Making Effective Adobe Captivate eLearning Modules Part 5: Contiguity
…the Contiguity Principle, which indicates that the spatial relationship (proximity) of symbols (like text) to analogous images (things that look like the subject of the learning) is significant, and plays a key role in how effectively we learn.
6: Making Effective Adobe Captivate eLearning Modules Part 6: Redundancy
…focuses on the Multimedia eLearning Design Principle known as Redundancy, which suggests that presenting symbols via both text and aural channels is less effective than presenting via only one.
7: Making Effective Adobe Captivate eLearning Modules Part 7 : Coherence
…focuses on the Multimedia eLearning Design Principle known as Coherence, which suggests that off topic ancillary material can distract from learning. This theory stands in opposition to arousal theory, providing research based evidence that when stimulating animation or any form of non-relevant information is provided, it can actually decrease the efficacy of the instruction.
8: Making Effective Adobe Captivate eLearning Modules Part 8: Segmenting
...the Multimedia eLearning Design Principle known as the Segmenting Principle, which suggests that authors of eLearning content should break content up into small pieces or chunks in order to help avoid cognitive overload for the learners.
9: Making Effective Adobe Captivate eLearning Modules Part 9: Pre-Training
The session focuses on the Multimedia eLearning Design Principle known as pre-training, which suggests that elearning content authors should first build up basic information about essential elements which are pre-requisites to understanding the larger concepts.
10: Making Effective Adobe Captivate eLearning Modules Part 10: Individual Differences
…the Individual Differences Principle, which suggests that design effects are stronger for low-knowledge learners than for high knowledge learners, and for high-spatial learners rather than for low-spatial learners.
More resources re: Adobe Captivate
Using Twitter? @AdobeElearning OR HASHTAG: #AdobeCaptivate
Using YouTube? http://www.youtube.com/adobeElearning/
On Adobe TV: http://tv.adobe.com/channel/e-learning/
Captivate Blog: http://blogs.adobe.com/captivate/
Also see: