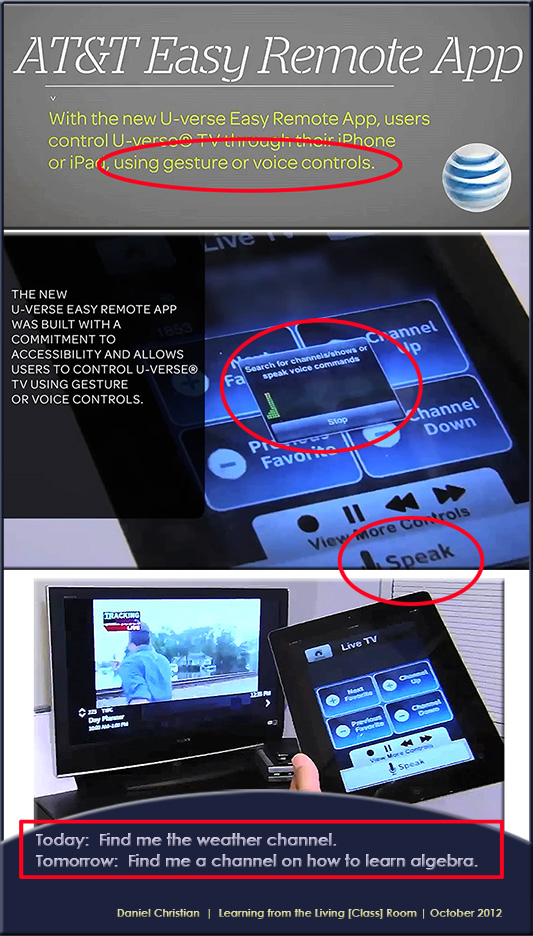
.
“A thousand year old industry on the cusp of profound change”




Excerpt:
The voice control functions of the Easy Remote app are powered by the AT&T Watson? speech recognition technology using AT&T’s Speech API, which uses advanced natural language processing to recognize and understand spoken words. Also developed in AT&T Labs, AT&T Watson? speech recognition technology has been powering advanced speech services in the marketplace for many years and is now available for third-party developers to use in their own apps.
Also see:
IBM’s Watson expands commercial applications, aims to go mobile — from singularityhub.com by Jason Dorrier
.
From DSC:
This relates to what I was trying to get at with the posting on mobile learning. I would add the word “Education” to the list of industries that the technologies encapsulated in Watson will impact in the future. Combine this with the convergence that’s enabling/building the Learning from the Living [Class] Room environment, and you have one heck of an individualized, data-driven, learning ecosystem that’s available 24 x 7 x 365 — throughout your lifetime!!!
.
Also relevant here are some visions/graphics I created from 2012 and from 2008:
.
![The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian---July-2012 The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)
.
.
.
First university system joins edX — from by Tanya Roscorla
Excerpt:
Huge online courses will be coming to the University of Texas System next year, the system announced Monday, Oct. 15.
Who’s investing in ed-tech?: Tech investors and their education portfolios — from hackeducation.com by Audrey Watters
Excerpt:
Below is by no means a complete list of technology investors who have education companies in their portfolio. Nor is it a list of the “top” or the “best” or the “most profitable” or “most active” ones, although for what it’s worth the list does match closely the answer on Quora to “Who are the top (active) VCs in the education technology space?”
.
Student loan default rates jump — from money.cnn.com by Blake Ellis
The Department of Education said 218 schools had three-year default rates of 30% or more, putting the schools at risk of losing their federal student aid.
Excerpt:
NEW YORK (CNNMoney) — Borrowers are having a harder time repaying their student loans.
The percentage of borrowers who defaulted on their federal student loans within two years of their first payment jumped to 9.1% in fiscal year 2011, up from 8.8% the previous year, according to U.S. Department of Education data released Friday.
Too high a price? — from InsideHigherEd.com by Kevin Kiley
Excerpt:
Grinnell College, which this year reported the fifth-largest endowment of any liberal arts college, announced Thursday that it would spend the next few months engaged in a conversation with campus stakeholders about changing its financial aid policies – including potentially, but probably not, going as far as making changes to need-blind admission. That makes it the second high-profile liberal arts college, following Wesleyan University this summer, to broach the topic in recent months.
Grinnell’s announcement stands out for two major reasons. Grinnell is one of the wealthiest liberal arts colleges in the country, so the idea that it would view its current financial aid model as unsustainable could be a bellwether that the sector as a whole is reconsidering the model. Second, the college’s administrators are taking an unusually public approach to a discussion that arouses strong emotions, trying to educate all campus constituents on why they think change might be necessary and hoping that, in doing so, they can mollify potential critics.
Addendums/also see:
The need for more experimentation, innovation within higher education.
By Daniel Christian for the CHFE12 MOOC
Last week, I attended the 18th Annual Sloan Consortium on Online Learning in Orlando, FL (USA). After hearing Sebastian Thrun’s excellent keynote address, I was very troubled by a couple of questions that kept arising in my mind (which I’ll get to in a minute). It turns out that Sebastian had heard Sal Kahn at a TED talk a while back, where he learned of the impact that Sal was having and the pedagogy Sal was using.
Now bear in mind that Sal was not in education. He was working in the financial services industry, putting together training-related items for his nephews/family members.
Then bear in mind that Sal Kahn has arguably had one of the most significant impacts on K-12 of any individual in recent decades – and even on institutions of higher education (in terms of professors investigating or starting to use the flipped/inverted classroom model).
Then bear in mind that Sebastian Thrun didn’t run his idea by anyone in Stanford’s administration! His email out to some folks started going viral, and within days the enrollment numbers were already in the thousands. (And at that point he got asked to drop by his Admin’s offices! 🙂 I wonder what would have happened if Sebastian would have first asked Stanford’s leadership for permission…? It may never have occurred.)
Sebastian’s and Peter Norvig’s AI course went onto graduate 23,000 people (with an initial enrollment around 160,000). Then, there’s the related Coursera organization/endeavor — again, a business that needed to be created outside of the traditional institutions of higher education.
So, recapping things:
So, the following two questions arose in my mind last week:
Any answer to these questions is troubling to me. But one plausible explanation involves leadership. Many of our leaders in higher education did not grow up with the Internet and with LANs, WANs, HTTP protocols, etc. They didn’t grow up using the tools that today’s youth are using.
As such, they don’t always appreciate the power and potential of technology. I don’t mean to point fingers and play a blame game here. That’s not the point. The point is, leaders are people with finite gifts and abilities. Like all of us, they have been shaped by their experiences and they, too, have their histories. They were moved into their positions of responsibility due to the needs of of the institutions at certain points in time. But the needs of those institutions have since changed.
The problem is, those in key leadership positions will either need to:
Blockbuster comes to mind as an organization that was once dominant, but disregarded the disruptive impact of technology and eventually had to declare bankruptcy. One can think of other examples from other industries as well (can’t we Kodak? Borders?).
Such reflections were reinforced when I read Selingo’s (2012) article from earlier today where he wrote, “It’s clear to me that the needed reforms for student financial-aid are unfortunately not going to come from higher education. Many financial-aid officials remain opposed to the model letter, as well as many other regulations.”
Like Selingo, I don’t see change coming from within the current system. I hope that I’m sorely mistaken here, but from the pulse checking I’ve been doing, the conversation seems to be continuing to move away from traditional institutions of higher education (example here and another example here). I hope that we can pick up the pace of experimentation within our organizations to find ways to lower the costs while still providing effective means of educating people.
—
Selingo, J. (2012, October 15). In a Broken Student Aid System, Colleges Are Part of the Problem. In The Quick and the Ed. Retrieved from http://www.quickanded.com/2012/10/in-a-broken-student-aid-system-colleges-are-part-of-the-problem.html
—
Addendum/also see:
Apple TV and the transformation of web apps into tablet and TV dual screen apps — from brightcove.com by Jeremy Allaire
.
Excerpts:
Importantly, designers and developers need to shed the concept that “TVs” are for rendering video, and instead think about “TVs” as large monitors on which they can render applications, content and interactivity that is supported by a touch-based tablet application.
…
The key concept here is that this pervasive adoption of TV monitors is the tip of the spear in creating a social computing surface in the real world.
…
Specifically, Apple has provided the backbone for dual screen apps, enabling:
- Any iOS device (and OSX Mountain Lion-enabled PCs) to broadcast its screen onto a TV. Think of this as essentially a wireless HDMI output to a TV. If you haven’t played with AirPlay mirroring features in iOS and Apple TV, give it a spin, it’s a really exciting development.
- A set of APIs and an event model for enabling applications to become “dual screen aware” (e.g. to know when a device has a TV screen it can connect to, and to handle rendering information, data and content onto both the touch screen and the TV screen).
…
[Jeremy listed several applications for these concepts: Buying a house, buying a car, doctor’s office, kids edutainment, the classroom, retail electronics store, consuming news, consuming video, sales reporting, board games.]
.
Also see:
From DSC:
Graphically speaking — and approaching this from an educational/learning ecosystems standpoint — I call this, “Learning from the Living [Class] Room.
.
![The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian---July-2012 The Living [Class] Room -- by Daniel Christian -- July 2012 -- a second device used in conjunction with a Smart/Connected TV](http://danielschristian.com/learning-ecosystems/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/The-Living-Class-Room-Daniel-S-Christian-July-2012.jpg)

Related item:
From DSC:
Sending a special thanks out to Dr. Kate Byerwalter,
Professor at Grand Rapids Community College for this resource!
Also see:
Debt collectors cashing in on student loans — from the New York Times by Andrew Martin
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
…many borrowers are struggling to pay off their student loans, and the debt collection industry is cashing in.
As the number of people taking out government-backed student loans has exploded, so has the number who have fallen at least 12 months behind in making payments — about 5.9 million people nationwide, up about a third in the last five years.
In all, nearly one in every six borrowers with a loan balance is in default. The amount of defaulted loans — $76 billion — is greater than the yearly tuition bill for all students at public two- and four-year colleges and universities, according to a survey of state education officials.
In an attempt to recover money on the defaulted loans, the Education Department paid more than $1.4 billion last fiscal year to collection agencies and other groups to hunt down defaulters.
From DSC:
Administrators throughout the country need to ask, how can we cut the price of our degrees by 50% or more? No kidding! I realize that sounds crazy, but if we don’t do this, cheaper — and increasingly attractive/convenient — alternatives will continue to develop. The conversation is not moving in a positive direction folks. There is a limit to people’s incomes and patience here.
Excerpt:
The ongoing carnage in the newspaper industry provides an object lesson of what can happen when a long-established, information-focused industry’s business model is challenged by low-price competitors online. The disruptive power of information technology may be our best hope for curing the chronic college cost disease that is driving a growing number of students into ruinous debt or out of higher education altogether. It may also be an existential threat to institutions that have long played a crucial role in American life.
.
From DSC:
If higher ed doesn’t respond more forcefully/significantly to the perfect storm it finds itself in, people will find other ways of getting employed and staying employed. The conversation continues to move away from institutions of traditional higher education (here’s but one example). Control is an illusion.
iTunes U Course Manager hands on — from UCL – London’s Global University by Matt Jenner
Excerpt:
iTunes U is known as a wonderful platform for finding recorded lectures and podcasts from academics and institutions across the world. But recently it’s also become a location for entire courses, with students, multiple resources and some interaction all happening on devices such as the iPad. It’s all very Apple-based, which means anyone without this hardware can’t access it and thus it remains a little elitist. BUT there’s still some good reasons to look into it – and I hope this begins to explain why.
From DSC:
Thanks Matt for the helpful screenshots and overview of what iTunes U is offering these days!
If Apple were to devote more resources to create a fully-stocked CMS/LMS, they could add a significant piece to the overall ecosystem they continue to build. But this time, it would have significant benefits to those who want to learn and to reinvent themselves over time.
For example, what if:
Could be a potent learning setup as such cloud-based materials are available to everyone throughout the globe — at very attractive prices.
From DSC:
Along with a host of other trends, this is a piece of the perfect storm in higher ed. People will find a way to make a living — whether this involves “traditional” higher education or not. From a career development side of things, robotics may make these graphics even more pronounced as jobs move from being done by humans to jobs being done by robots.
Also see:

.
Addendums:
From DSC:
My cousin helps Fortune 500 companies innovate and deal with change management-related issues. Something he once said is rather haunting to me now…
“Often when organizations start feeling the pain, it’s too late at that point.” (Think Blockbuster, Kodak, Borders, and many others.)
So that has been the question I’ve been pondering these last couple of years — are we already too late to the game?
Public universities see familiar fight at Virginia — from the NYT by Tamar Lewin on 6/25/12
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
The tumult at the University of Virginia …reflects a low-grade panic now spreading through much of public higher education.
…
But the 10-point outline she offered — listing state and federal financing challenges, the changing role of technology, a rapidly changing health care environment, prioritization of scarce resources, faculty workload and the quality of the student experience, faculty compensation, research financing and the like — was almost generic, and would have applied to nearly every public university in the nation.
Rebuilding Mr. Jefferson’s University — from insidehighered.com by Kevin Kiley
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
In a statement before the vote, Dragas said the events of the past two weeks have actually unified the campus around a series of questions it needs to address. “Prior to these events, there seemed to be a roadblock between the board’s sense of urgency around our future in a number of critical areas, and the administration’s response to that urgency,” she said. “Also, many of our concerns about the direction of the university remained unknown to all but a few. This situation has now keenly focused the attention of the entire university community on the reality and urgency of the specific challenges facing the university – most of which, once again, are not unique to U.Va. – but whose structural and long-term nature do require a deliberate and strategic approach.”
University of Virginia: Only the Beginning — from The American Interest by Walter Russell Mead
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
What we see at UVA this month is just a foretaste of the storm that is coming — a few early raindrops and gusts of wind before the real storm hits. The country needs more education than the current system can affordably supply, and the pressure on the educational system will not abate until this problem is resolved.
Excerpt:
Other information industries, from journalism to music to book publishing, enjoyed similar periods of success right before epic change enveloped them, seemingly overnight.We now know how those industries have been transformed by technology, resulting in the decline of the middleman — newspapers, record stores, bookstores and publishers.
Colleges and universities could be next, unless they act to mitigate the poor choices and inaction from the lost decade by looking for ways to lower costs, embrace technology and improve education.
Ousted Head of University Is Reinstated in Virginia — from the NYT by Richard Perz-Pena
Excerpt (emphasis DSC):
CHARLOTTESVILLE, Va. — Facing a torrent of criticism, the University of Virginia trustees made a stunning turnabout on Tuesday, voting unanimously to reinstate the president they had forced to resign over concerns that the university was not adapting fast enough to financial and technological pressures.
The future of higher education and other imponderables — from elearnspace.org by George Siemens
Excerpt:
Educators are not driving the change bus. Leadership in traditional universities has been grossly negligent in preparing the academy for the economic and technological reality it now faces. This failure is apparent in interactions I’ve had with several universities over the past several months. Universities have not been paying attention. As a result, they have not developed systemic capacity to function in a digital networked age. In order to try and ramp up capacity today, they have to acquire the skills that they failed to develop over the last decade by purchasing services from vendors. Digital content, testing, teaching resources, teaching/learning software, etc. are now being purchased to try and address the capacity shortage. Enormous amounts of organizational resources are now flowing outside of education in order to fill gaps due to poor leadership. Good for the startups that were smart enough to anticipate the skill and capacity shortage in higher education. Bad for the university, faculty, and support staff.
I have delivered two presentations recently on the scope of change in higher education, one in Peru at Universidad de San Martin Porres and the other at the CANHEIT conference. Slides from CANHEIT are below…
.
Addendum on 6/20/12:
Addendum on 6/21/12:
Book Description
Publication Date: June 26, 2012
America is facing a higher education bubble. Like the housing bubble, it is the product of cheap credit coupled with popular expectations of ever-increasing returns on investment, and as with housing prices, the cheap credit has caused college tuitions to vastly outpace inflation and family incomes. Now this bubble is bursting.
In this Broadside, Glenn Harlan Reynolds explains the causes and effects of this bubble and the steps colleges and universities must take to ensure their survival. Many graduates are unable to secure employment sufficient to pay off their loans, which are usually not dischargeable in bankruptcy. As students become less willing to incur debt for education, colleges and universities will have to adapt to a new world of cost pressures and declining public support.
About the Author
Glenn Harlan Reynolds is the Beauchamp Brogan Distinguished Professor of Law at the University of Tennessee. He writes for such publications as The Atlantic Monthly, Forbes, Popular Mechanics, The Wall Street Journal, and the Washington Examiner. He blogs at InstaPundit.com.
Also see:
.
From DSC:
Note many of the relevant categories and tags I put this under — items I’ve been covering for years:
How would you like a graduate degree for $100 — from forbes.com by George Anders
Sebastian Thrun wants to fix what’s broken with higher ed. How about a master’s degree for $100?