More for Less: New Research Points to Blended Learning — from EdReformer.com by Bennet Ratcliff
…which links to “The rise of K-12 blended learning” from the Innosight Institute by Michael Horn and Heather Staker




More for Less: New Research Points to Blended Learning — from EdReformer.com by Bennet Ratcliff
…which links to “The rise of K-12 blended learning” from the Innosight Institute by Michael Horn and Heather Staker
From DSC:
It shouldn’t surprise anyone who knows my work when I say that I think Sajan George is right on the mark! 🙂
For example, below are the main points of what I heard him say (with some graphics of my own that back up what I have been saying):
Sajan George: The Future of Education
January Series at Calvin College (January 24, 2011)
We are living in a new age, the Conceptual Age — primary skill sets that we now need are for creators and empathizers. Why? Because those two skillsets aren’t easily automated or outsourced (Sajan referenced Dan Pink’s work).
We built our education system in between the agricultural and industrial ages; mass production model was built during a much different time with different needs.
Speed and acceleration of change has greatly increased. At a phenomenal pace!
From DSC:
You may have seen me post this graphic a few times:

Sajan gave an example that focused on an older model of a coffee maker vs. a newer model: Coffee Maker 1.0 vs. Coffee Maker 2.0. Point was that we still need skills, but design, esthetic, and emotion have become more important.
Also, we live in a society that demands Coffee Maker 2.0 — but our educational systems are still offering Education 1.0. We are still batching kids by age, using a 1-to-many model, etc.
We still are offering “Education 1.0” where
…but we are living in a “Society 2.0” world
Also, our current methods of educating students is not scalable, not sustainable!
Previous attempts at changing our educational systems have failed because they’ve been trying to fix the status quo of education! It’s a design problem.
From DSC:
You may have seen me post this graphic a few times:
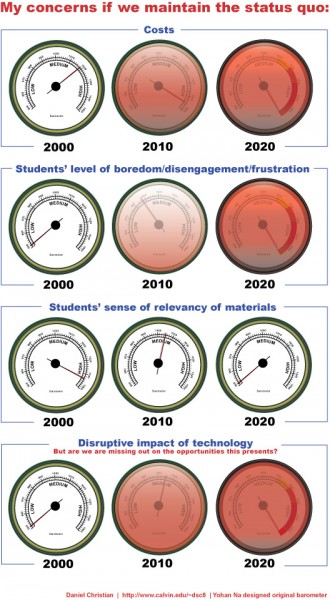
Current educational system needs to be completely blown up and redesigned! We live in a digital world, yet kids sitting in analog world.
Technology that customizes learning – recommendation engines, adaptive learning; personalized/customized learning.
Online learning is scalable, sustainable – while offering instantaneous feedback. Per Sajan, “But it’s happening on the fringes; home school kids; supplemental, etc.”
Hybrid environment – hoping to nationally launch this year
Use data to differentiate instruction.
Design problem in education.
Hybrid learning <– Sajan’s current work promoting this model; brings power of human interaction with the customization that technology can bring.
From DSC:
You may have seen this graphic I’ve posted a few times — that aims to capture the best of both worlds:

When trying to change things, you need a compelling vision of what you are trying to build/achieve.
From DSC:
You may have seen the vision I was trying to relay here.
From Q&A session…with a hybrid mode:
Algebra, meet the iPad: A year-long study explores learning with the tablet — fromMind/Shift by Tina Barseghian
Excerpt:
Q. How will the iPad-taught class different from a traditional algebra class?
What we’ve seen in practice is the fact that it’s bringing everything to one place that’s making it exciting. The convenience factor, the simplicity factor — that’s revolutionary. For example, if you’re working through a lesson, there are three or four algorithms presented. With a textbook, if you want to learn more about one of the examples, you have to stop looking in your book and go online to our website and navigate that particular section and view our video there.
Instead, on the iPad, you simply click on “view video” and up comes our professor, Dr. Edward Burger, the Bill Nye of education. Students have written to him saying he’s changed their opinion of what math is. So to have him right there, you can see how it’s natural for students to tap “view video,” as opposed to setting their book down and going to the computer.
Another example is, when students are working on a problem, they can simply click on “check answer,” and up comes, “that’s correct, and here’s why,” or “that’s incorrect, and here’s why.” As opposed to when they’re working on paper or even online, those pieces are a little more drawn out.
Press Release:
EDUCAUSE and NGLC announce second wave of funding
SEATTLE – Next Generation Learning Challenges today announced a new round of challenge grants that will provide up to $10 million to expand promising technology tools and applications that help more students master seventh- through ninth-grade math and literacy competencies, which are critical to college and career readiness. The initiative, which is already supported by a grant from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, also announced today a $1.4 million investment from the William and Flora Hewlett Foundation to broaden funding for the program’s grants to innovators.
“This initiative has the potential to help change how the next generation of students learns,” said Paul Brest, president of the Hewlett Foundation. “Technology has a great role to play in advancing ‘deeper learning,’ an approach to improving education that helps students achieve a critical combination of the fundamental knowledge and practical skills they will need to succeed in a fiercely competitive global economy.”
Next Generation Learning Challenges provides investment capital to technologists, institutions, educators, and entrepreneurs to bring promising technology solutions to more students across the K-12 to postsecondary spectrum. The initiative released its first request for proposals (RFP)—focused on improving postsecondary education—in October 2010. Finalists eligible for funding from this round will be announced within the next several weeks.
Excerpt from “Challenging the Gifted” — from EducationNext.org by June Kronholz
I asked Davidson teachers and staffers what lessons public schools could take away from the academy. Their answers struck me a lot like the idea of getting rid of seat-time laws: logical, good for kids, and political showstoppers.
- Allow youngsters to accelerate by subject. Colleen Harsin, the academy’s longtime director, proposed that a school group its core classes—hold all math classes during 2nd period, say; all English during 3rd—so students can move up or down according to their ability.
- Promote dual enrollment so youngsters can take classes in both elementary and middle school, middle and high school, high school and college. That may strain transportation budgets, but students will graduate sooner, offsetting the costs.
- Individualize learning. Davidson students each have a learning plan that’s refined during weekly meetings with their advisors, semester meetings with Garcia, and yearly what’s-next meetings with Harsin. That might strain a school of 2,000, but so do discipline problems caused by bored or out-of-their depth youngsters.
- Group students by ability, not age. “You can’t teach to the middle,” Ripley said. “To say we’re all at an Algebra 2 level just isn’t accurate.”
That’s Bob Davidson’s mantra: Ability grouping “may fly in the face of closing the achievement gap,” but neglecting the country’s brightest kids flies in the face of logic. “Don’t stop them,” he says.
Also see:
An episode of ABC’s Nightline from 2007 takes a look at the Davidson Academy, a public school for profoundly gifted students in Reno, Nev. June Kronholz writes about the Davidson Academy in “Challenging the Gifted,” which appears in the Spring 2011 issue of Ed Next. A promotional video produced by the school appears here.
Game by 14-year-old outsoars Angry Birds — from CNET
While Angry Birds is still the top paid iPhone game, a game written by an eighth-grader has spent the last few days atop Apple’s free charts. Bubble Ball, a physics simulator, was coded by Robert Nay, a 14-year-old from Spanish Fork, Utah. The game challenges players to use objects and gravity to guide a ball to its destination.
Connecting classrooms globally — from prometheanplanet.com
A Big Idea: Blended CBO — from EdReformer.com by Tom Vander Ark

The nation received a friendly ‘C’ in the annual state of the nation last week. We need quality at scale and there is finally a way achieve it.
More than two million students learn online. The scaled providers (Apex, K12, Connections, Florida Virtual, NC Virtual, and Lincoln Interactive to name a few) could triple in size given 60 days notice and do it with consistent quality. We’ve never had an opportunity like that; it’s only local and state policy that stands in the way of better learning opportunities for several million kids and fast.
Community–based organizations (CBO) build powerful sustained relationships with youth, engage them in developmental activities, and connect them to youth and family services. Many of them are frustrated by working around struggling schools.
If we combine the two assets—online instruction and powerful community connections—we get one big scalable idea: blended CBOs. A blended school model incorporates online learning and onsite support in ways that are often more flexible and cost effective than traditional schools.
Michael Robbins, Department of Education’s Office of Faith-Based Partnerships, is interested in expanding the educational impact of CBOs. He thinks blended CBOs is a big idea. Over breakfast at DC’s Tabard Inn, Michael and I sketched out a couple ways this idea could scale:
Half of Detroit’s schools may close — from good.is

Financial mismanagement and declining enrollment are ringing a death knell for Detroit’s schools. According to Detroit Public School Emergency Manager Robert Bobb, to close a $327 million budget deficit, he’ll need to shut half of the city’s campuses over the next two years.
Under the plan, the 142 current schools in the district would be reduced to 72 by the 2012-13 school year. What will happen to the students attending those schools? Bobb plans to shift them over to the remaining campuses, raising class sizes to 62 students per teacher.
From DSC:
Seriously…this is crazy and completely unfair! Those of us who have more resources need to step in and help out. But how can we best do this? How can folks outside of the Detroit area make a solid, helpful impact? Coming from the tech side of the house, I’d like to see us offer FREE materials…online.
That assistance could come from private corporations, individuals, colleges, universities or for-profit organizations such as K12 Inc. Another idea along the lines of individuals, is to allocate $1-$5 billion from the amounts being donated by some of the nation’s wealthiest people. Use those funds to make outstanding educational materials that engage our youth. Then we could offer those incredibly-well done, multimedia-based, interactive, engaging, highly-sophisticated materials FREELY to anyone who wants access to them — whether inside or outside the United States. This would be a massive undertaking from a curricular, instructional design, programming, production, etc. standpoint. But WOW! What a difference it could make to level the playing field!
Perhaps working with vendors, some of the funding could be used for loaning out the devices needed to “play” and interact with the materials, and perhaps some other funding could be allocated to the city of Detroit to provide wireless access throughout the city and surrounding suburbs.
Also see:
The $600 billion challenge– from Fortune
Bill Gates, Melinda Gates, and Warren Buffett are asking the nation’s billionaires to pledge to give at least half their net worth to charity, in their lifetimes or at death. If their campaign succeeds, it could change the face of philanthropy.
Six predictions for education in 2011 — from Forbes.com by Michael Horn
Excerpts:
As 2011 dawns, expect to see the rate of innovation in education increase. The weak economy that has bogged down the United States for the past two years will continue to lift the online learning innovations to new heights in both K-12 and postsecondary education.
Here are six trends and predictions to watch for in the New Year.
1. Just under 40 percent of all U.S. postsecondary students will enroll in at least one fully online course in the fall of 2011.
2. Public school budgets will continue to shrink, so more districts will do more business with online learning providers to fill in the gaps.
3. An increasing number of suburban schools will begin using online learning, too.
4. Not to be outdone, education entrepreneurs will create high quality chartered schools that jump in the online learning game as well.
5. User-generated online content will begin to explode in education.
6. Mobile learning, the subject of increasing hype in the United States, will make its impact in the developing world first.
The 19,100-student Grand Rapids school district in Michigan launched blended-learning classes this past fall. The district has started with high school social studies and math classes.
“There was some initial resistance from the public—concerned parents with the perception that kids are just going to be stuck in computer labs—but that’s absolutely contrary to what [this] is,” said John Helmholdt, the director of communications for the district. “When you say blended, people don’t understand what that means. It took months of really trying to educate and raise awareness of really what it was we were trying to do.”
Moving to a blended model actually made teacher-student ratios better, according to Mr. Helmholdt, by layering on support-staff members to circulate when the students were completing work online.
In Grand Rapids, the blended classes go through a three-day rotation of face-to-face and online instruction. During the first day, students receive a traditional lecture-based class in a regular classroom where a new concept is introduced. On the second day, the class starts by going over the concept again and then beginning to use some of the online software and support tools that reinforce the concept. On the third day, the students work solely with digital resources. [Rest of article here.]
From DSC:
I am very glad that the Grand Rapids school system is moving in this direction! It is a huge step in the right direction and I congratulate the district’s leadership for their vision and patience while this plane gets off the runway. This endeavor will help the students begin to build digital/information literacy. It will open their minds up to numerous creative possibilities — as well as career opportunities and goals. They are beginning to have “the world as their school“.
Recession’s toll on K-12 budgets both wide and deep — from EdWeek.org by Alyson Klein
.
From DSC:
I post this here — with higher ed included in the tags/categories — because if the trend within K-12 continues (i.e. that of using such technologies as the iPad, digital textbooks, mobile learning devices, etc.), students’ expectations WILL be impacted. When they hit our doorsteps, they will come with their heightened sets of expectations. The question is, will we in higher ed be ready for them?