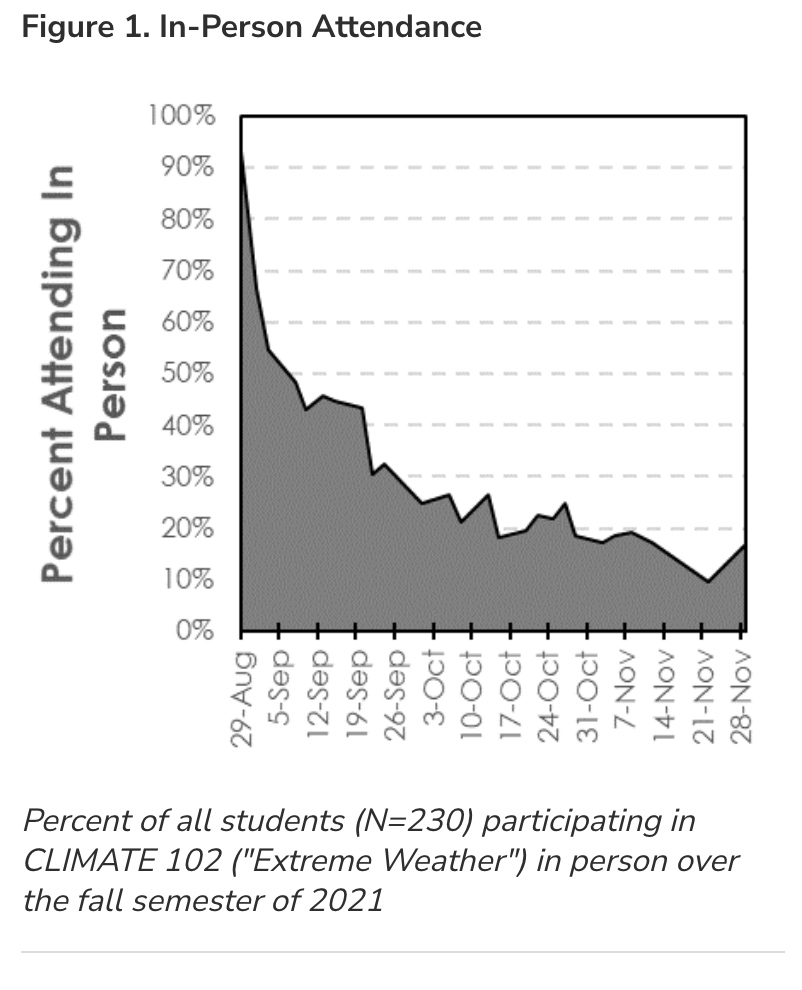
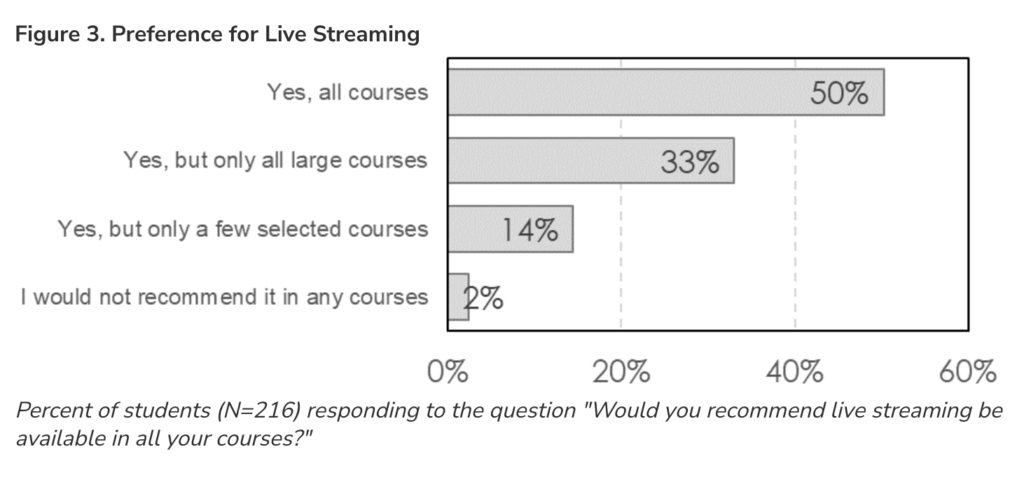
From DSC:
The resource below (from The Chronicle of Higher Education) is one of the best, most useful articles I’ve read in a long time. It’s full of innovative and/or powerful ideas. I like the part about seeking to give students “more voice, more choice, more control.”

5 No-Cost or Low-Cost Ways to Improve Your Campus — from chronicle.com by Richard J. Light and Allison Jegla
Change doesn’t have to be expensive. It’s often sparked by a simple suggestion and a leader willing to give it a try.
Excerpts (emphasis DSC):
No. 1: Reward innovative teaching. Lynne Schofield, a professor of statistics at Swarthmore College, has fundamentally changed the way her students learn basic and intermediate statistics. She lectures and assigns problem sets but she also teams up with local Philadelphia organizations such as food banks and blood-donation centers to give students an opportunity to solve real-world problems using their classroom knowledge. The organizations benefit from data and analysis that they may not have had time or bandwidth to collect themselves, and the students see the practical application of what they might ordinarily have perceived as a dry subject.
No. 2: Solicit ideas from students. …
They met with a dean and proposed a public event called, “10 Big Ideas, 10 Professors, 10 Minutes Each.”
When the dean agreed, the students took the lead on selecting and inviting professors to each present the “most exciting new idea” in their academic field, in less than 10 minutes.