‘Press Play’ Isn’t a Teaching Strategy: Why Educators Need New Methods for Video — from edsurge.com by Reed Dickson
Excerpt:
As I prepared to teach my first educational videography course earlier this year, I found that we lacked a common vocabulary for talking about how we design learning with video in mind. Since then, I’ve been advancing the term “video paratext” to reflect the myriad ways that we design educational guidance, prompts, activities or interactive elements to surround or be included within a video.
I pulled the word “paratext” from the field of poetry translation because, personally, I love the “paratext” that precedes or follows a poem—or even interrupts it. At poetry readings in particular, I lean into the words that a poet shares before or after reading each poem. Paratext helps me connect with and make sense of the poem.
Likewise, I ask educators to consider how to help students connect with videos through various prompts and activities that surround, or are included within, the video.” Might such “paratext” inspire students to take a closer look at a video they’ve watched, the way I might want to reread a poem to see how it works or what it means?
Resources for Teachers of Psychology — from teachpsych.org; with thanks to Christine Renner for this resource
Excerpt:
The Society for the Teaching of Psychology (STP) curates and distributes teaching and advising materials to all teachers of psychology (e.g., 4-year instructors, 2-year instructors, and high-school teachers). The resources available below are documents that can pertain to any aspect of teaching. (NOTE: Syllabi have their own listings under Project Syllabus.)
Instructors have generously shared classroom activities, annotated bibliographies, film guides, lab manuals, advising aids, textbook compendiums, and much more. Notations indicate those that developed from Instructional Resource Awards.
Strategies for Teaching Quantitative Concepts Online — from facultyecommons.com
Excerpt:
Collaborative learning is particularly helpful in statistics education. Technology can facilitate and promote collaborative exploration and inquiry allowing students to generate their own knowledge of a concept or new method in a constructivist learning environment. Group interactions have an important role in questioning and critiquing individual perspectives in a mutually supportive fashion so that a clear understanding of statistical concepts energy and knowledge of statistical ideas develops. Research has shown that it is important to discuss the output and results with the students and require them to provide explanations and justifications for the conclusions they draw from the output and to be able to communicate their conclusions effectively.
Worksheet to WOW: 10 ways to upgrade your worksheet — from ditchthattextbook.com by Matt Miller
Excerpt:
Can we turn a worksheet into a “WOW” experience?
We’re about to find out! Here are 10 ways your classroom technology can help transform your worksheet to “WOW” …
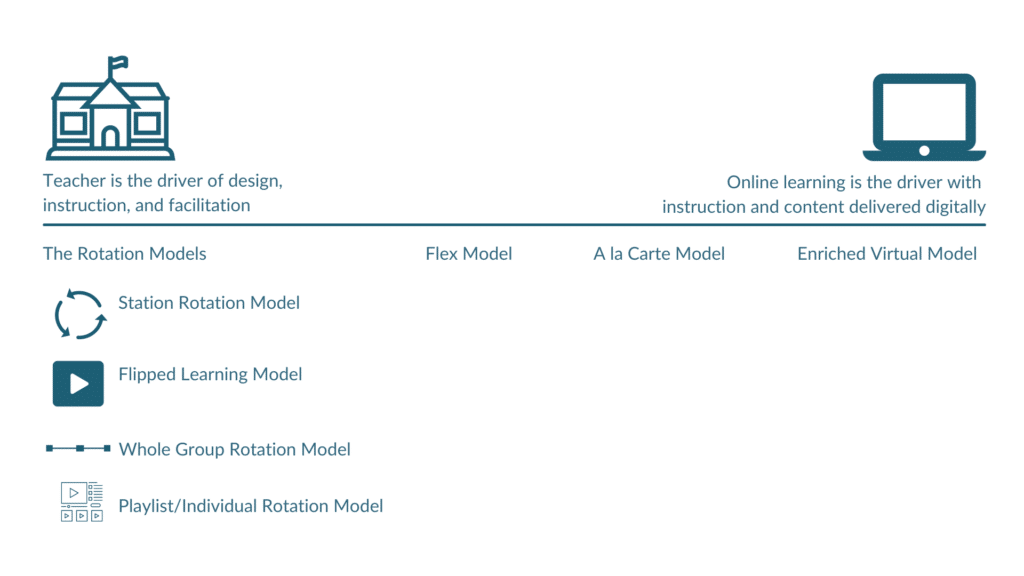
Which Blended Learning Model Should I Use? — from catlintucker.com by Dr. Catlin Tucker
Excerpts:
I get this question all the time in coaching and training sessions! First, let’s be clear about the definition of blended learning.
Blended learning is the combination of active, engaged learning online with active, engaged learning offline to provide students with more control over the time, place, pace, and path of their learning.
Creating Classroom Camaraderie to Promote Learning: 3 Strategies — from scholarlyteacher.com by Donna Downs
Key Statement: Intentionally developing a welcoming classroom environment increases student engagement and cultivates meaningful classroom relationships.
Keywords: engagement, motivation, relationship
Although researchers suggest flipped classrooms, engaging humor, and online polling, I have found taking a more personal approach to engagement to be successful, specifically the following three guidelines: show your human side, share your professional experiences and wisdom, and admit your mistakes.
Somewhat related:
How to Receive Feedback With a Growth Mindset — from neuroleadership.com by the NeuroLeadership Institute
Excerpt:
A growth mindset can help us view feedback as a good thing, which ultimately makes performance reviews more effective. After all, we want to learn, grow, and improve our skills. People with a fixed mindset view criticism as an attack on their self-worth. Growth mindset, by contrast, leaves room for the possibility that we all have blind spots — and that your manager may have valuable insights on how you can hone your skills. Feedback, in other words, isn’t personal. A manager may critique our performance, but a growth mindset helps keep us from tying our performance to our identity.









[…] Read the full story by Learning Ecosystems […]